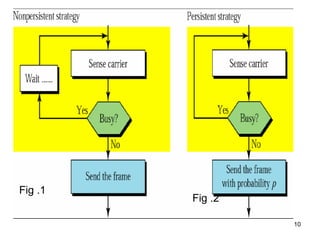
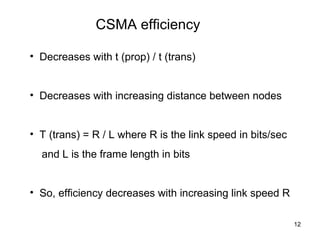
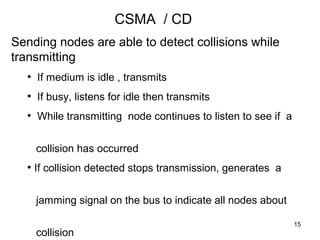
CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access) is a protocol where nodes listen to detect if other nodes are transmitting before transmitting themselves to avoid collisions. There are different types of CSMA including persistent CSMA, non-persistent CSMA, and CSMA/CD. CSMA/CD adds collision detection, allowing nodes to detect collisions while transmitting and stop transmitting to avoid wasting bandwidth.