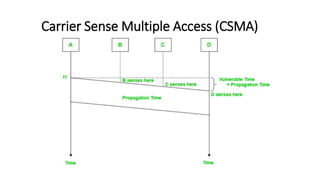
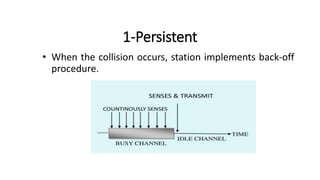
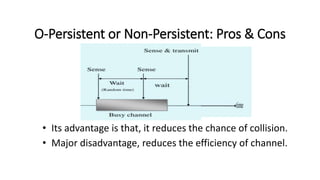
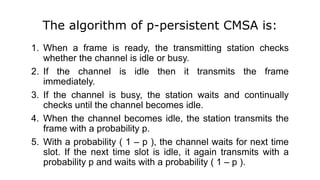
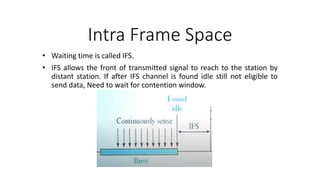
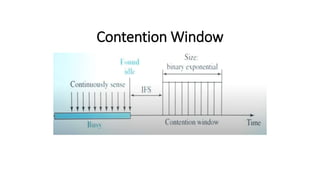
Carrier Sense Multiple Access (CSMA) is designed to reduce collisions in data transmission by sensing the channel before transmission, although it does not eliminate collisions completely. There are three main types of CSMA protocols: 1-persistent, non-persistent (o-persistent), and p-persistent, each with distinct methods for channel access and collision handling. CSMA/CD and CSMA/CA are variations that manage collisions differently, with CSMA/CD focusing on detection and resolution after a collision occurs, while CSMA/CA aims to prevent collisions, particularly in wireless environments.