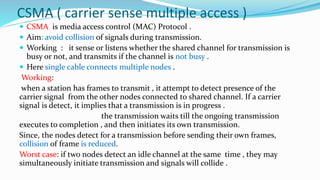
Carrier Sense Multiple Access (CSMA) is a media access control protocol designed to avoid signal collisions during transmission by allowing nodes to sense the channel before transmitting. The document outlines various CSMA modes, such as 1-persistent, non-persistent, and p-persistent, each with different methods for addressing channel usage and collision risks. CSMA improves channel utilization while reducing the chances of collision, especially in shared channel environments like Wi-Fi.
![CARRIER SENSE MULTIPLE ACCESS [CSMA]
PREPARED BY : MUSKAN DHAWAN
YOUTUBE CHANNEL : IT Hub by Muskan Dhawan
E-MAIL ID : muskan.dhawan99@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csma-210123063926/85/CSMA-IN-COMPUTER-NETWORK-1-320.jpg)





![P-persistent CSMA
Hybrid Approach
This approach is between 1-persistent and non-persistent CSMA access modes.
When the transmitting node is ready to transmit data ,it sense the transmission
medium for idle or busy . If idle then it transmits immediately. If busy then it
sense the transmission medium continuously until it becomes idle., then
transmits with probability ( p). If the node doesn’t transmit (the probability of
the event is 1-p) it wait until the next available time slot.
If the transmission medium is not busy it transmits again with the same
probability [p]. This probabilistic hold-off repeats until the frame is finally
transmitted or when the medium is Found to become busy again ( some other
node has already started transmitting) then whole logic cycle repeated.
P – persistent CSMA used in wi-fi.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csma-210123063926/85/CSMA-IN-COMPUTER-NETWORK-8-320.jpg)
