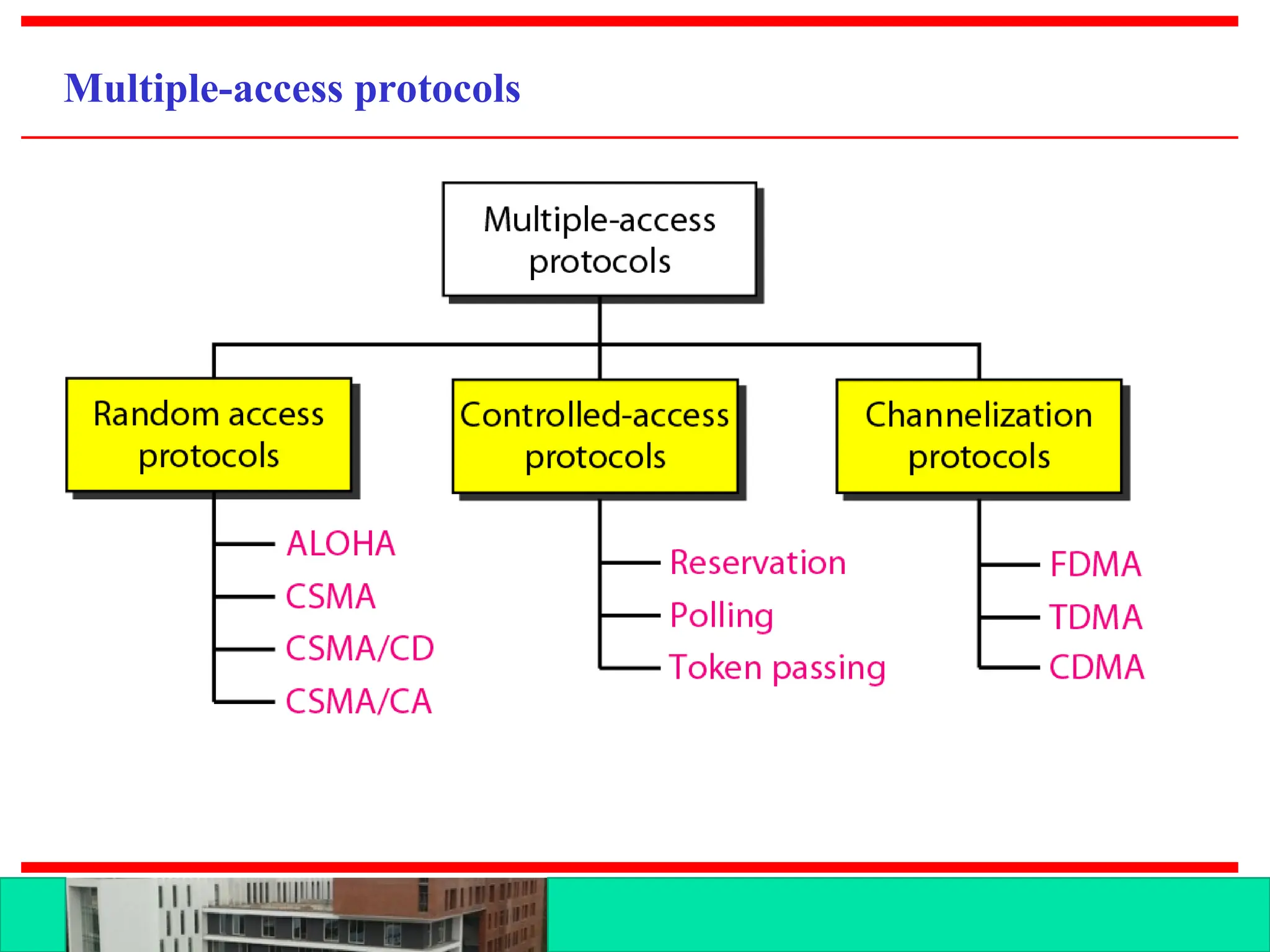
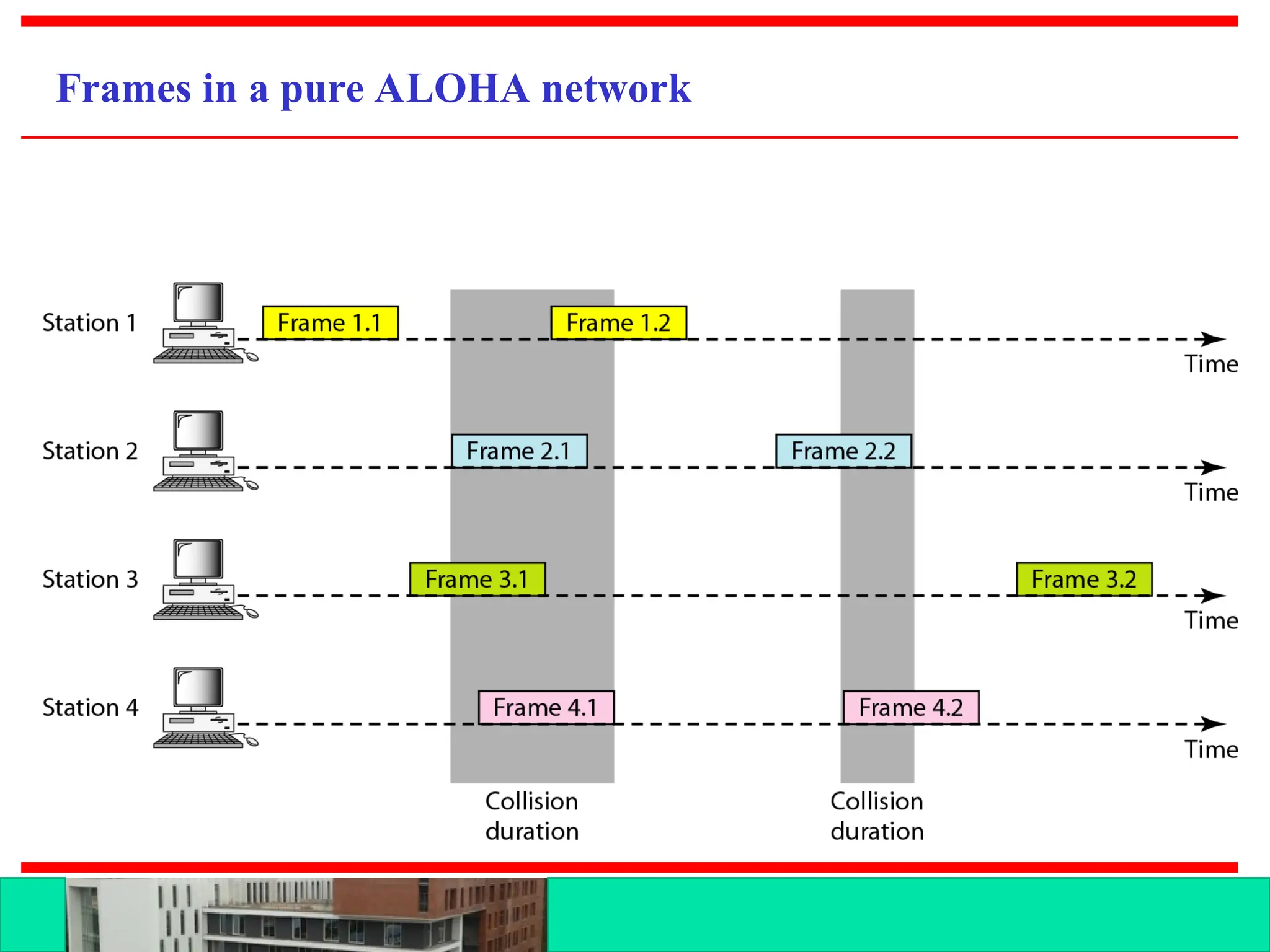
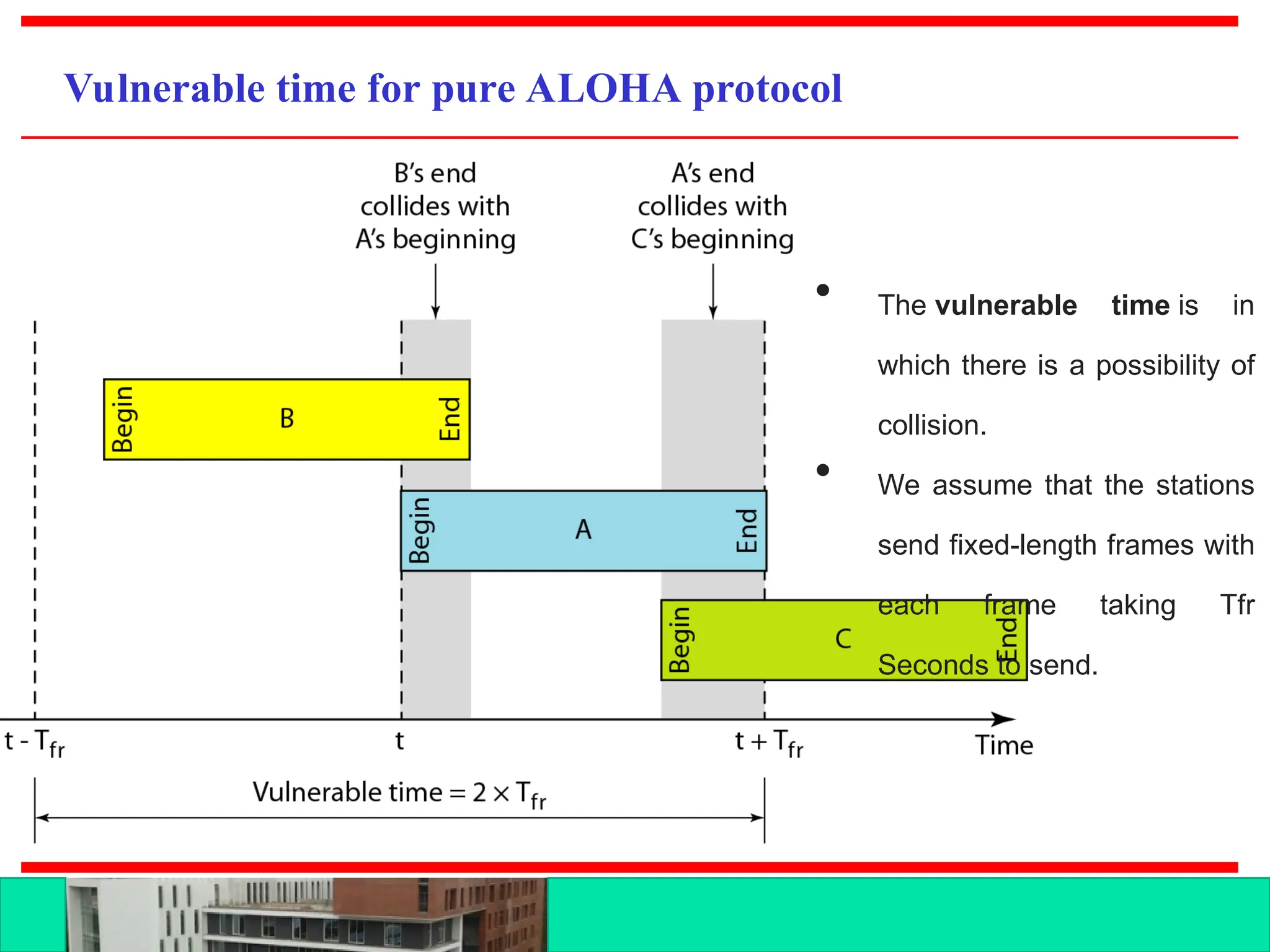
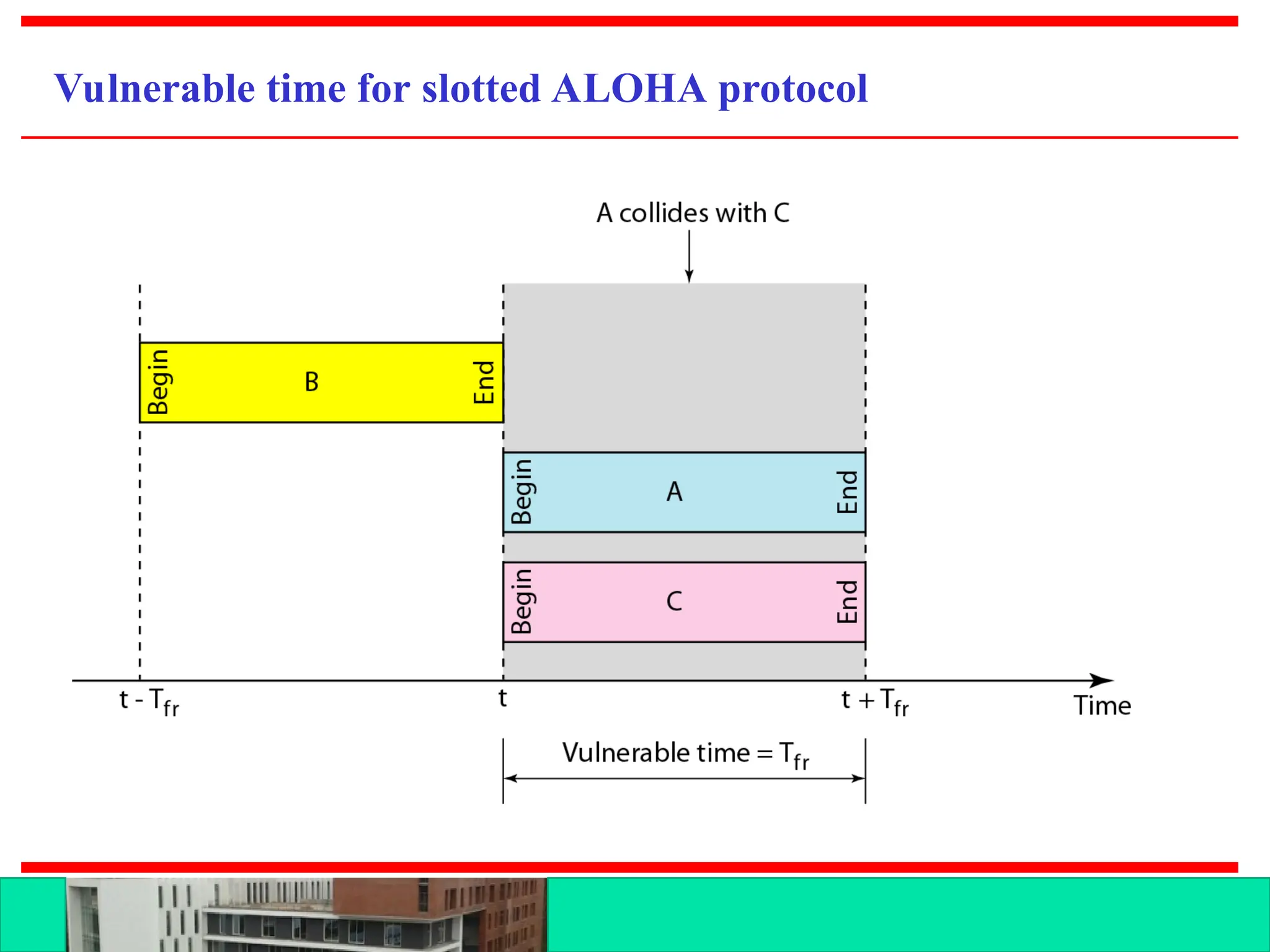
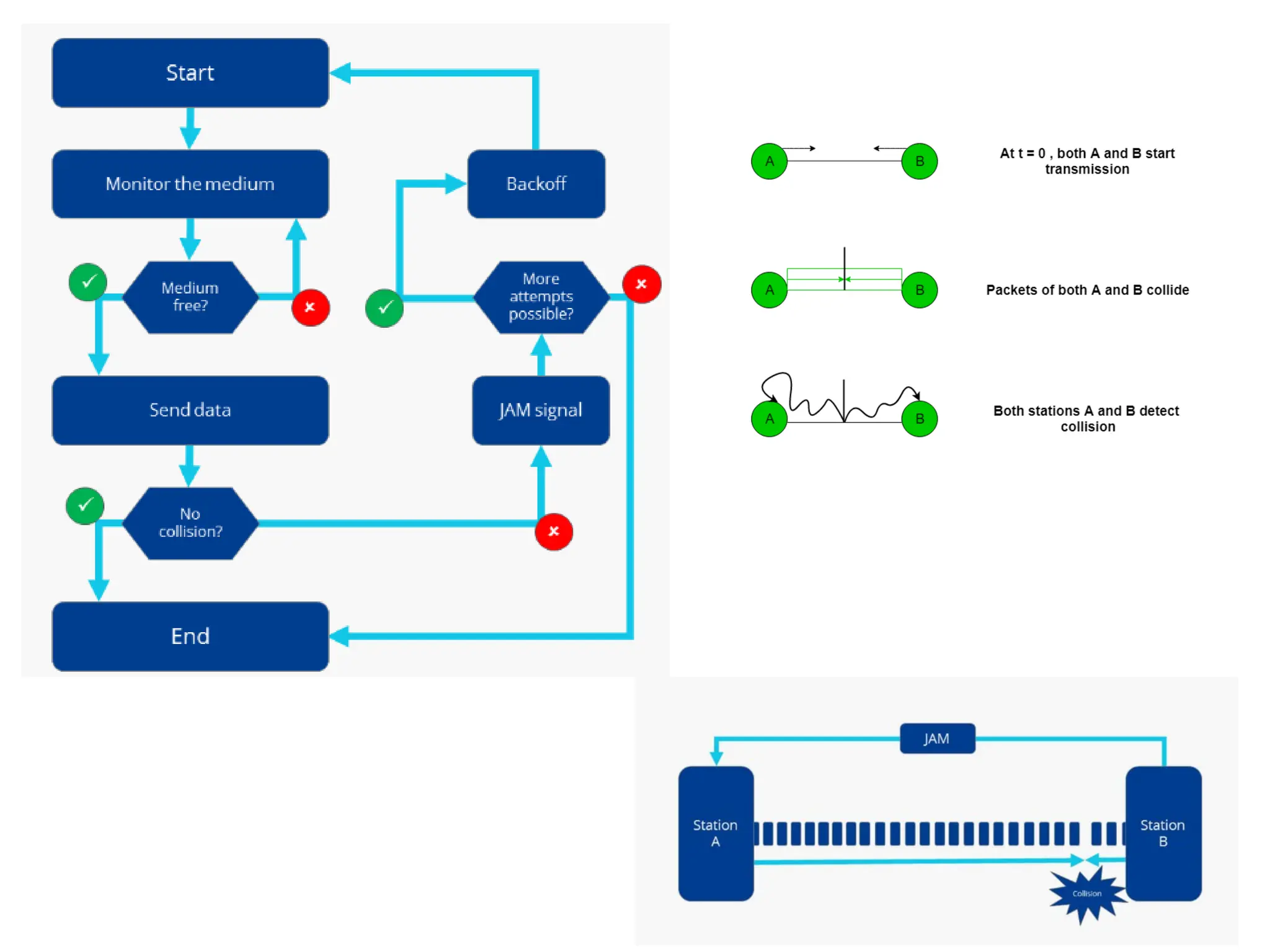
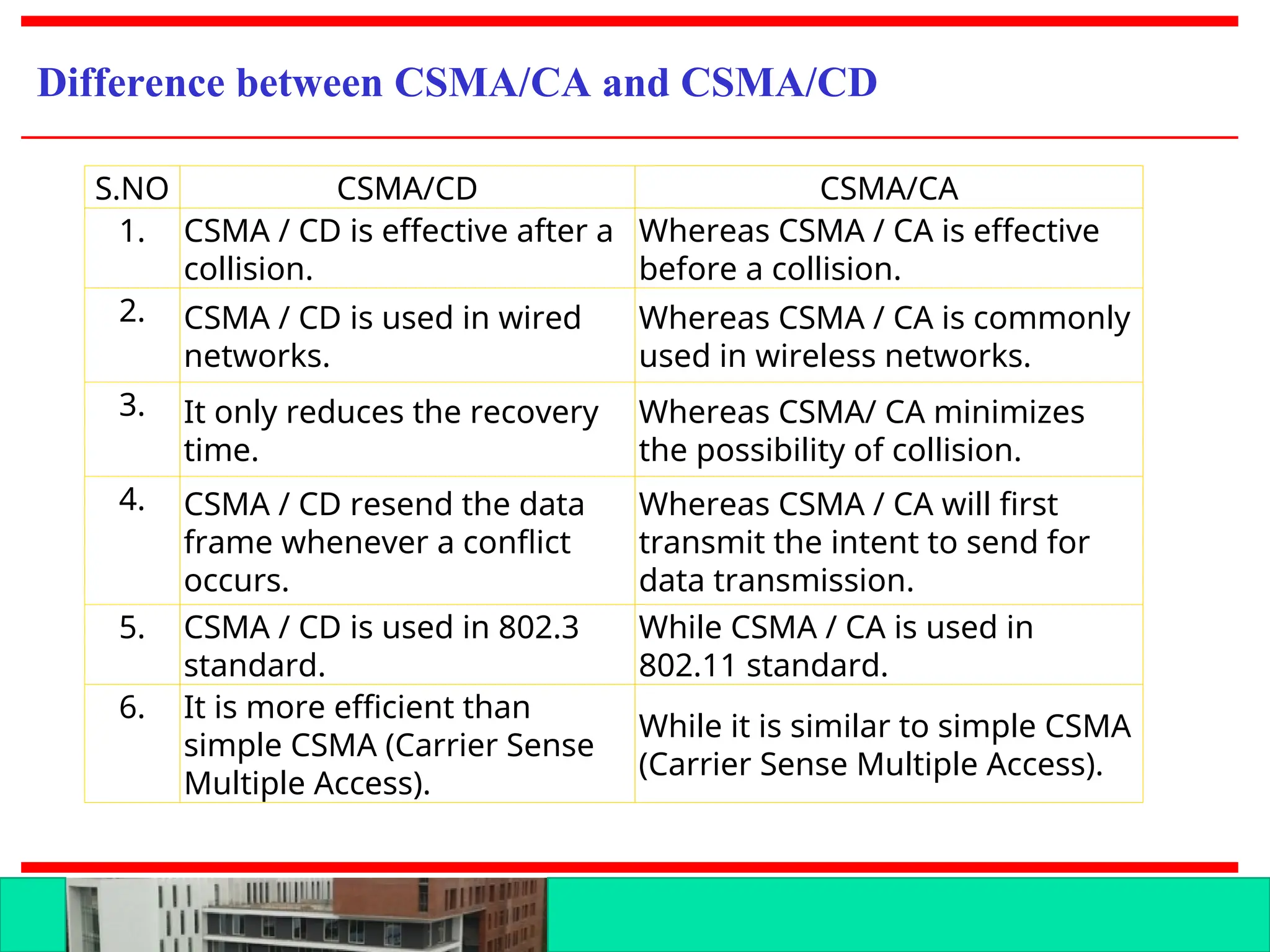
The document discusses multiple access protocols for network communication, focusing on Aloha, CSMA, CSMA/CD, and CSMA/CA. It explains the mechanics of these protocols, including their vulnerabilities and throughput rates, particularly emphasizing the differences between CSMA/CD and CSMA/CA regarding collision detection and prevention. The document highlights the conditions under which these protocols operate in wired and wireless networks.