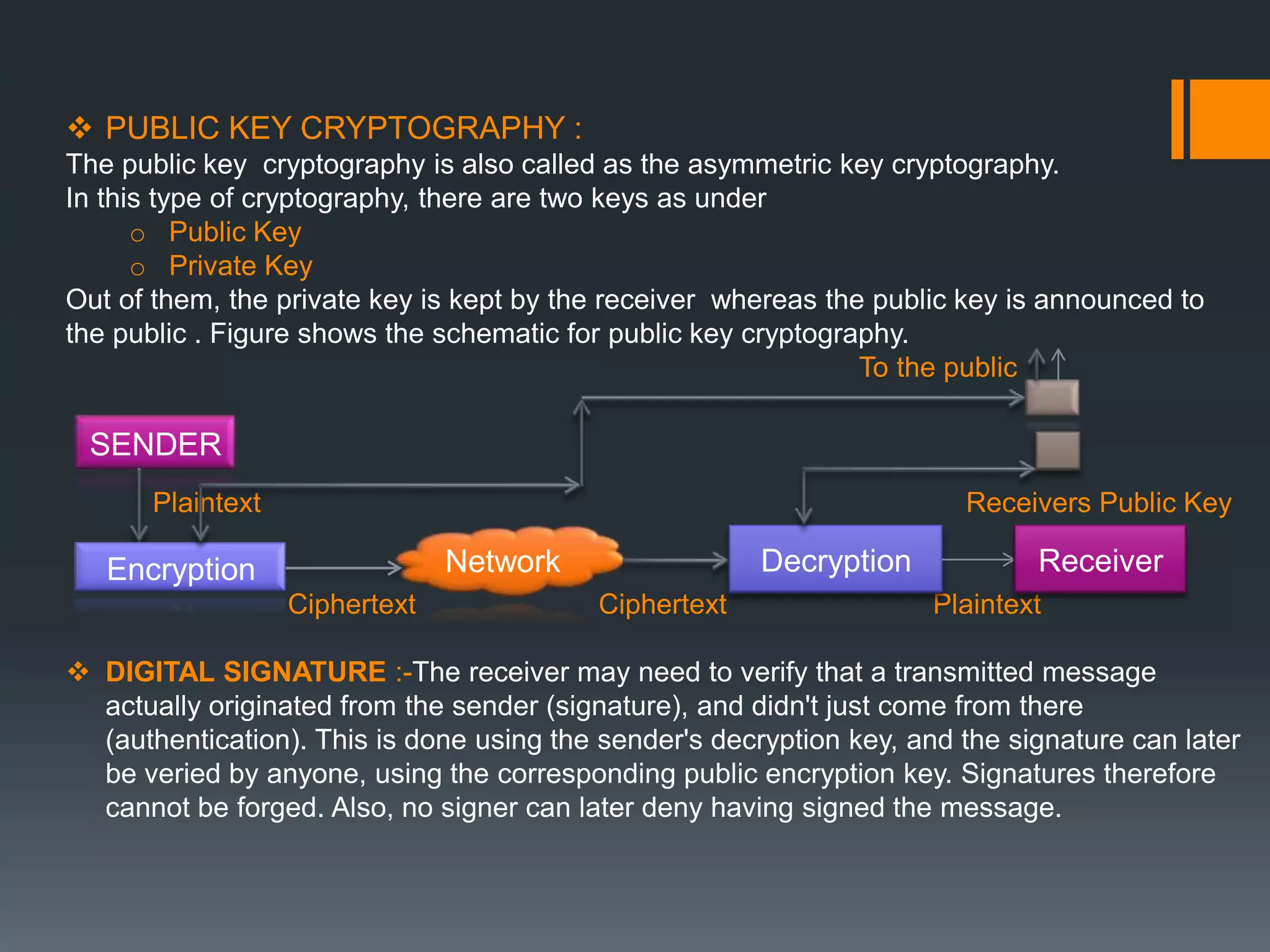
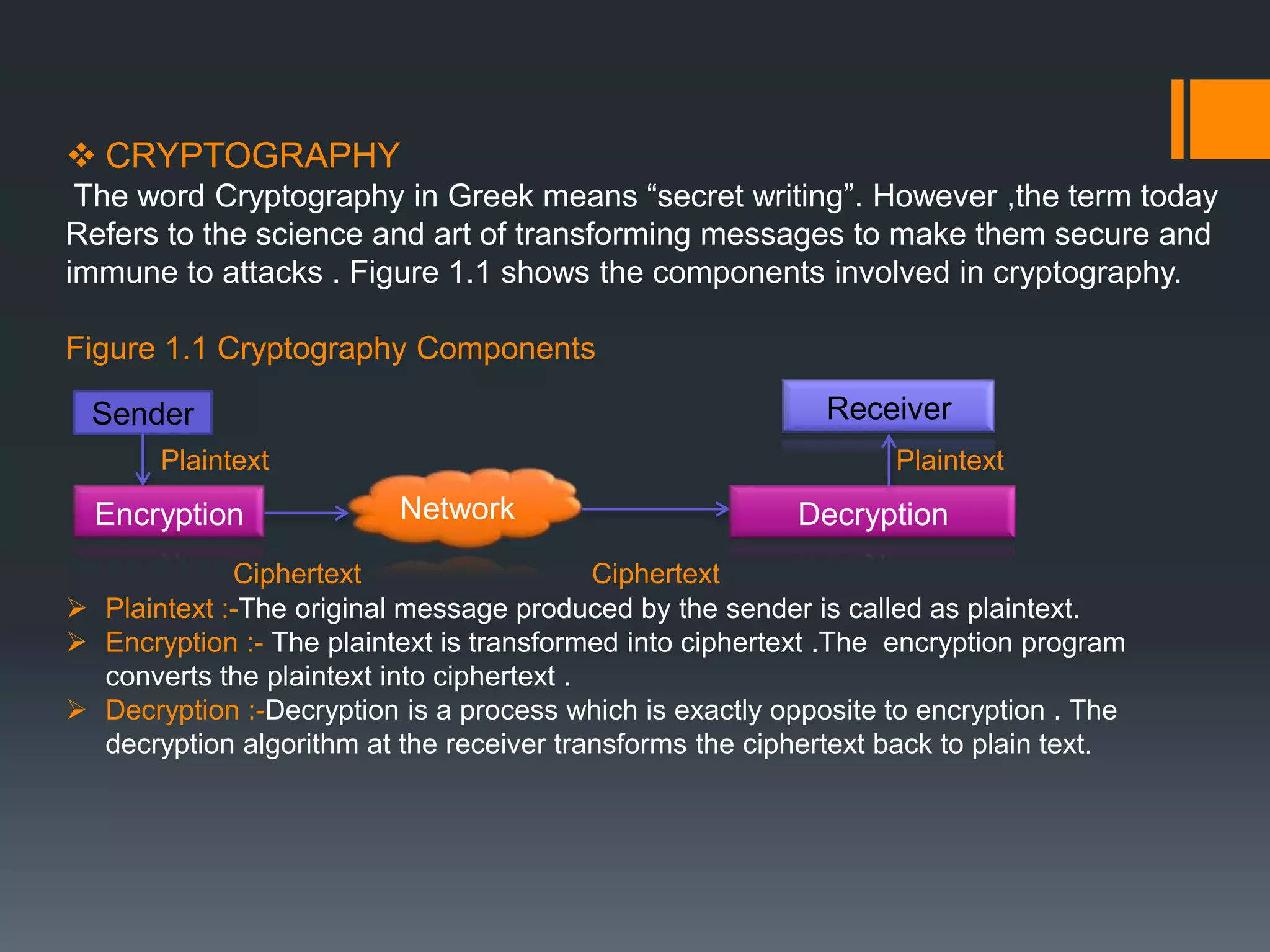
Cryptography involves encrypting messages to make them secure and immune to attacks. There are traditional ciphers like substitution and transposition ciphers that encrypt text by shifting letters or rearranging them. Modern algorithms like DES use symmetric keys and RSA uses public/private key pairs to encrypt and decrypt messages. Public key cryptography uses different public and private keys, allowing secure communication without pre-sharing keys. Digital signatures authenticate messages using the sender's private key and can be verified by anyone using their public key.


![ CRYPTOGRAPHIC ALGORITHM
DES :-Data Encryption Standard
US encryption standard [NIST 1993]
56-bit symmetric key, 64-bit plaintext input
Block cipher with cipher block chaining
How secure is DES?
o DES Challenge: 56-bit-key-encrypted phrase decrypted (brute force) in less than a day
o No known good analytic attack
Making DES more secure:
o 3DES: encrypt 3 times with 3 different keys (actually encrypt, decrypt, encrypt)
RSA :-Rivest,Shamir and Alderman One of the most commonly used public key
algorithms.The public key in RSA is a pair of numbers (N,e) and the private key also is a
pair of numbers (N,d).The number N is common between the private and public
keys.The algorithm used by the sender to encrypt the message is as follows:
C = Pe mod N
P = Plaintext represented as a number
C = Ciphertext represented as a number
e and N are components of public key
The algorithm used by the receiver to decrypt the message is as under :
P = Cd mod N
P = Plaintext
C = Ciphertext
d and N are components of private key](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cryptography1-130501141513-phpapp02/75/Cryptography-4-2048.jpg)