The document provides an overview of cryptography, detailing its definitions, main goals, types, and techniques, including RSA and DES. It explains key terms and concepts such as plain text, cipher text, and both asymmetric and symmetric key cryptography. The document also discusses the historical development of cryptography and its applications in areas like ATM, smart cards, and electronic money.


![CryptographyCryptography
●
The word ‘Cryptology’ has a Greek etymology; it means ‘secret word’.
●
The art was transformed into a science by a 1948 paper [205] written by
Shannon. This was arguably the beginning of modern cryptology, in which
checking the integrity of the messages and authenticating the identities of
the communicating parties have become as essential as ensuring
message confidentiality.
●
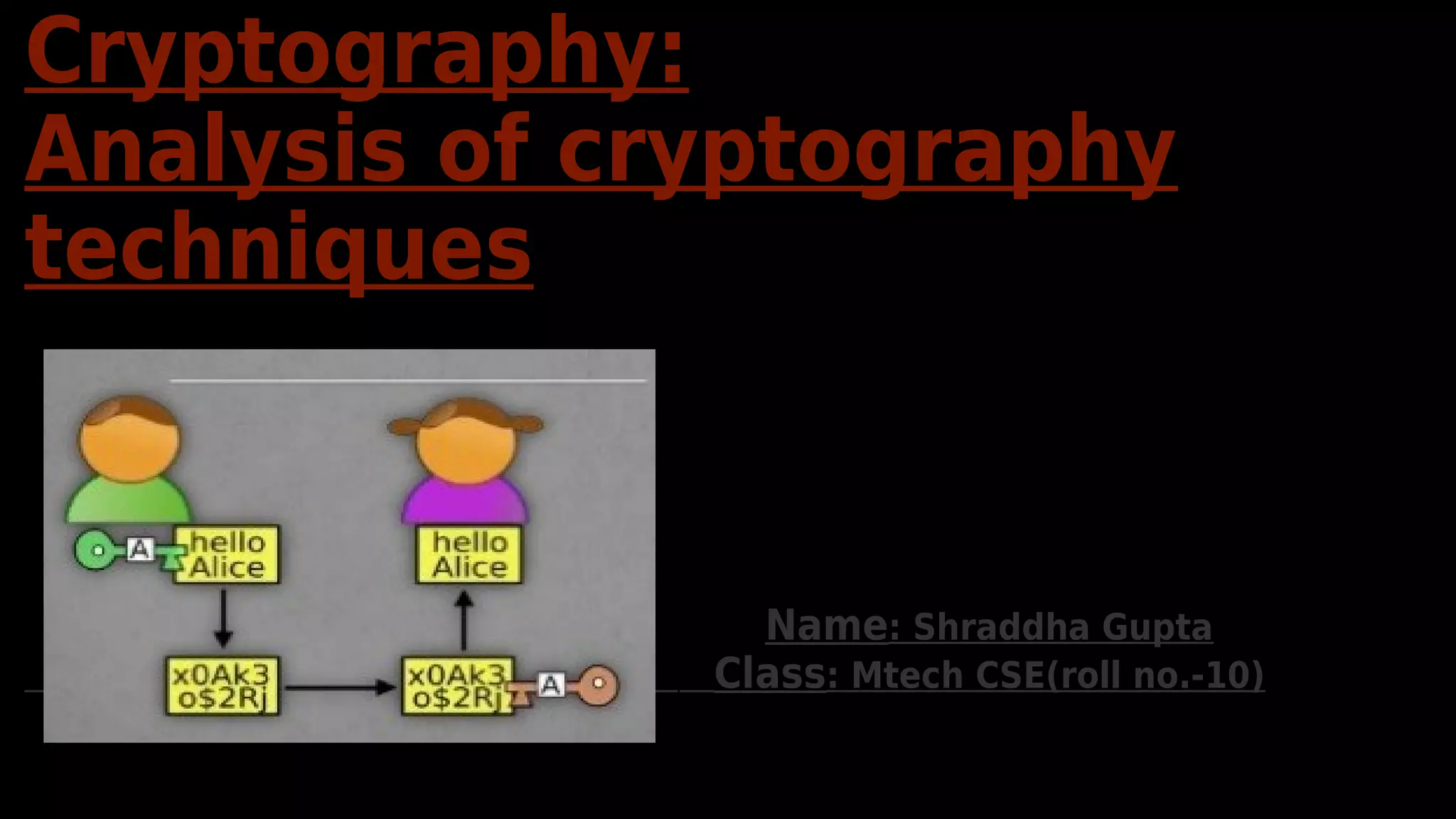
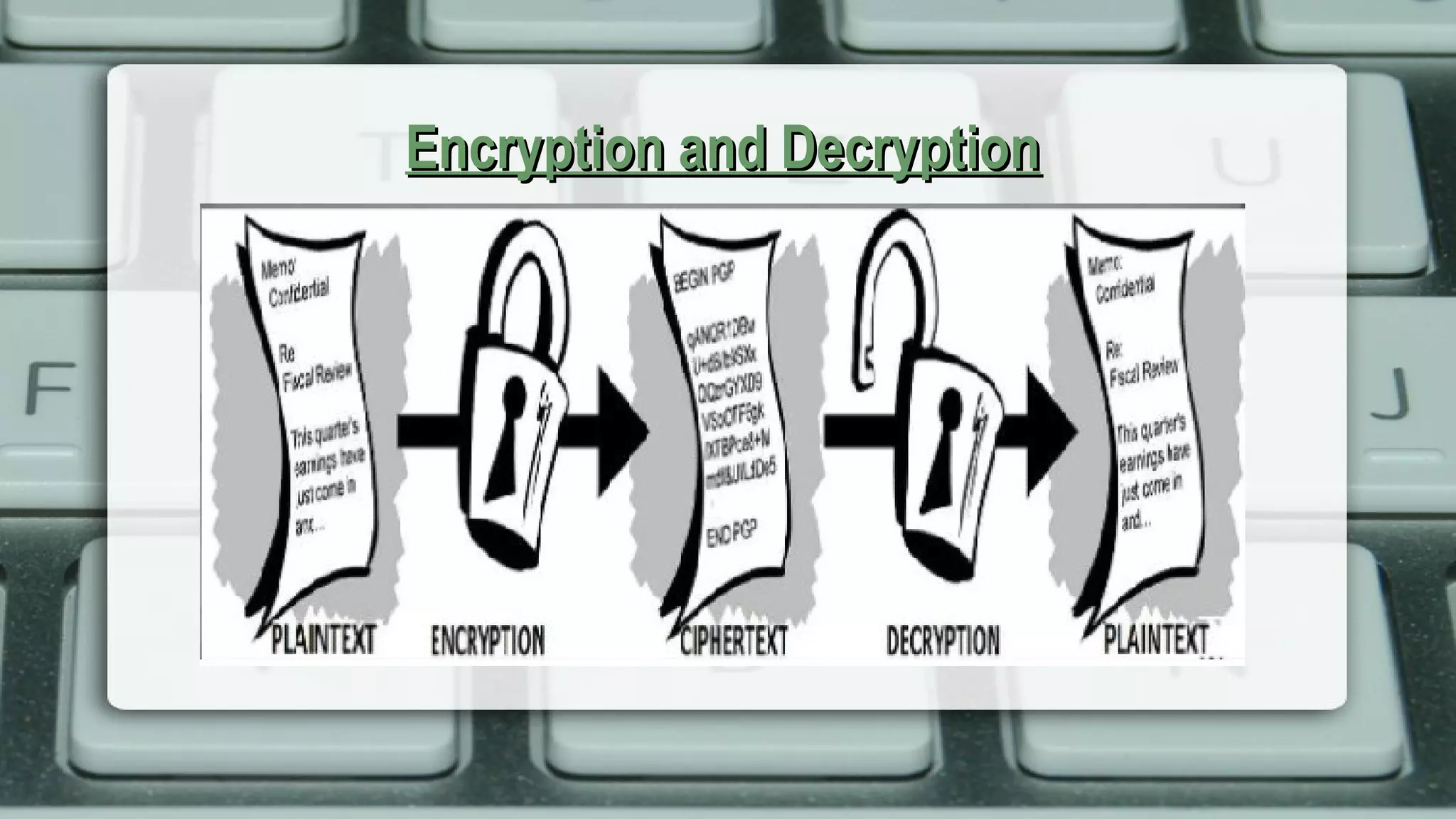
Cryptography is the science and art of transforming messages to make
them secure and immune to attack.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cryptographyshraddha-171128153046/75/Basic-techniques-in-cryptography-4-2048.jpg)




![RSA AlgorithmRSA Algorithm
● 1)Choose two distinct prime numbers p and q.
For security purposes, the integers p and q should
be chosen at random, and should be similar in
magnitude but 'differ in length by a few digits to
make factoring harder. Prime integers can be
efficiently found using a primality test.
2)Compute n = pq.[n is used as the modulus for
both the public and private keys. Its length, usually
expressed in bits, is the key length.]
3)Compute z=(p-1)(q-1)
4)Choose an integer e such that 1 < e < z and
gcd(e, z) = 1; i.e., e and z are coprime.
5)Determine d as d ≡ e−1 (mod z); i.e., d is the
modular multiplicative inverse of e (modulo z).
This is more clearly stated as: solve for d given d e⋅
≡ 1 (mod z).
6)e is released as the public key exponent.
7)d is kept as the private key exponent.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cryptographyshraddha-171128153046/75/Basic-techniques-in-cryptography-11-2048.jpg)
![Example:Example:
● Step1- Take two prime numbers p and q ->p=3 q=11
● Step2- find n=pxq → 3x11=33
● Step3- choose a variable z such that z=(p-1)(q-1) [z will be coprime to e] -----> 2x10=20
● Step4-choose a variable e such that coprime such that 0<e<z------->1<e<20,where e is a prime number
and is coprime to z, so we take e=7
● Step5-choose a variable d such that d=(dxe)modn -->(dxe)mod20=1
Let d=3,since where multiplied with 7 it will give 21mod20 that is =1
● Therefore Public key=(e,n) -----> (7,33)
● Therefore Private key=(d,n) -----> (3,33)
● For eg: If message is 2 suppose then
– Encrypt : C= m^emod n 2^7 mod 33=29
– Decrypt : M= c^dmod n 29^3mod 33=2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cryptographyshraddha-171128153046/75/Basic-techniques-in-cryptography-12-2048.jpg)