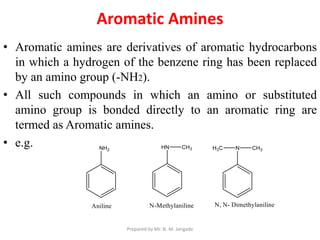
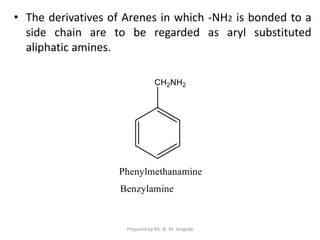
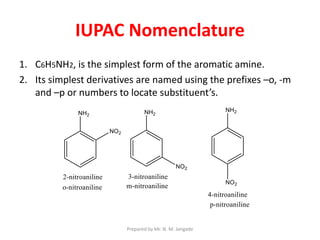
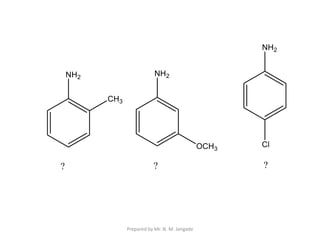
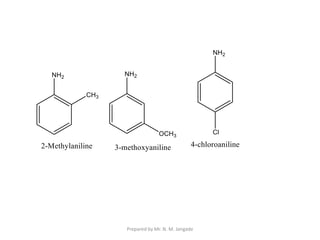
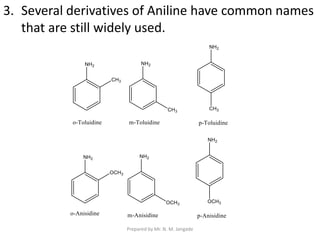
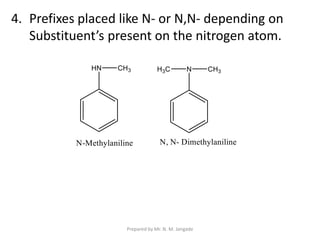
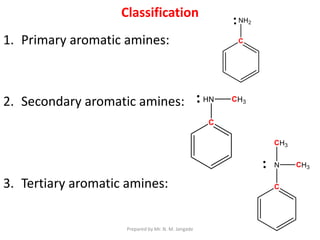
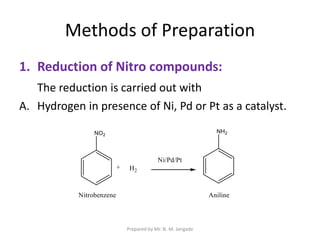
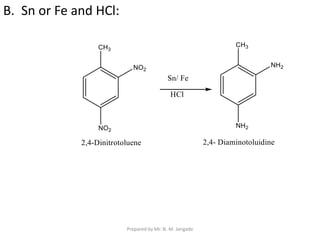
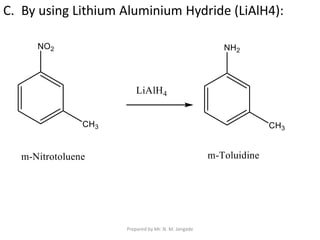
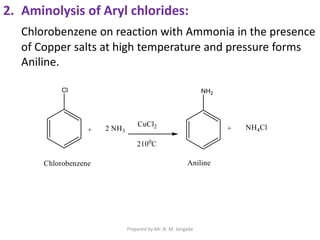
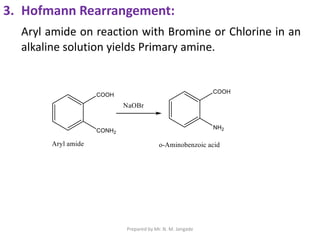
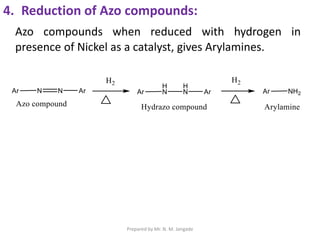
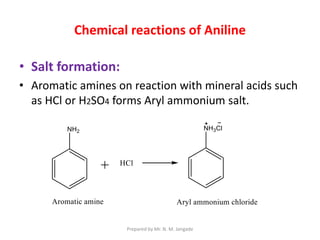
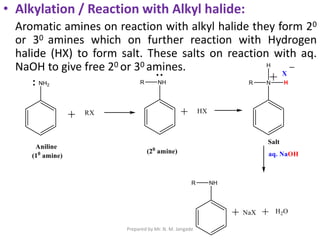
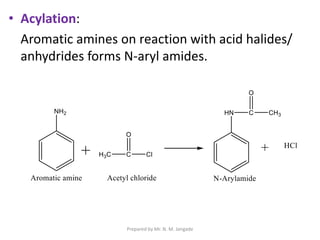
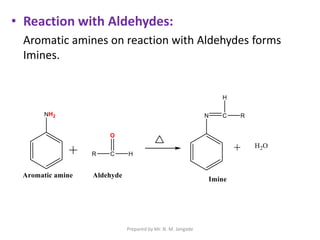
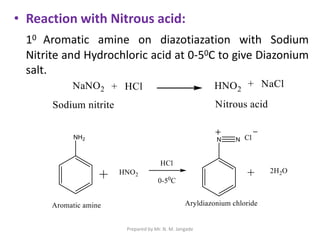
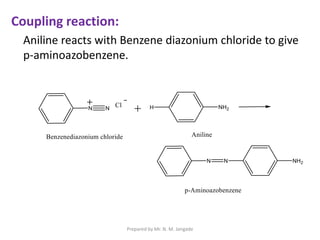
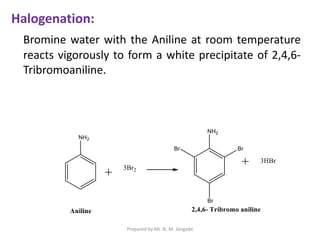
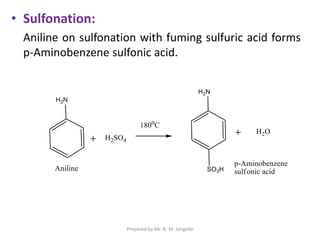
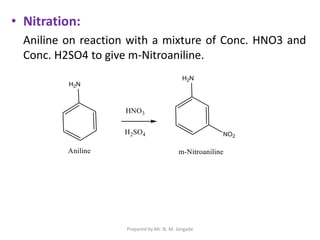
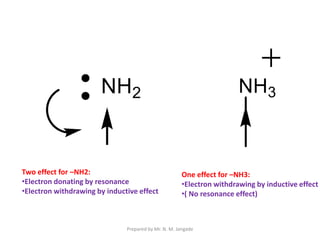
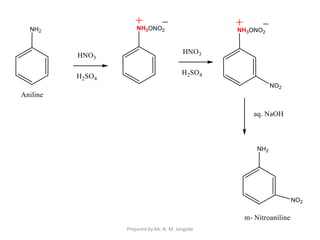
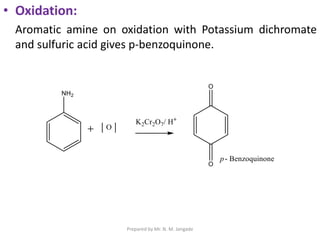
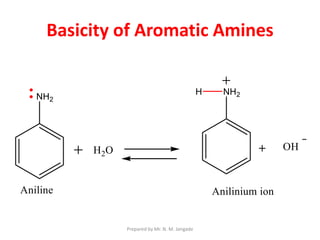
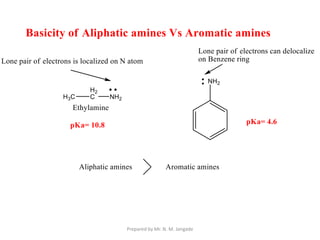
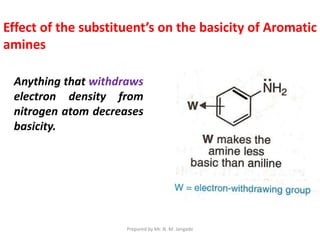
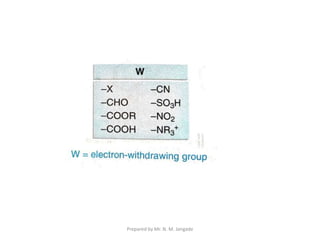
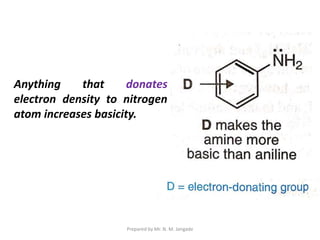
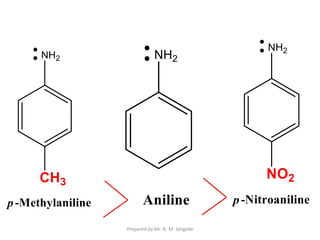
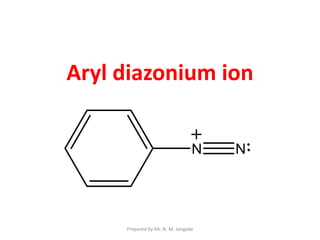
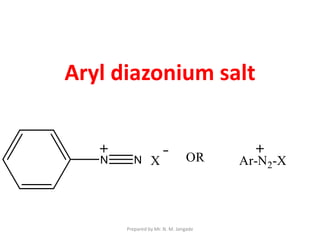
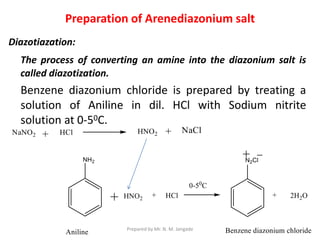
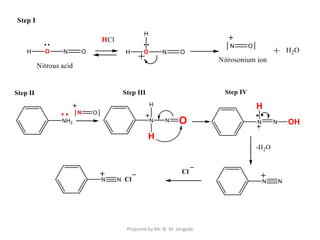
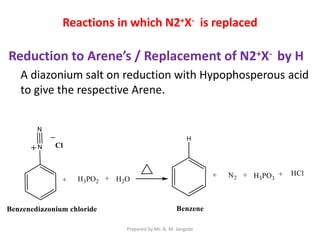
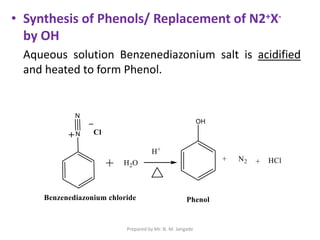
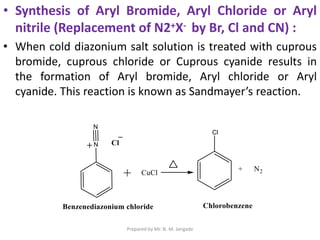
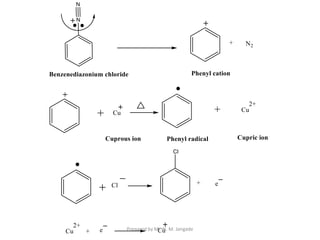
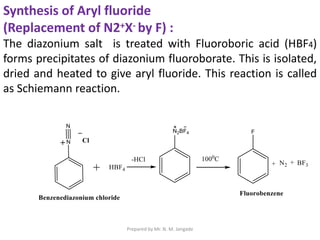
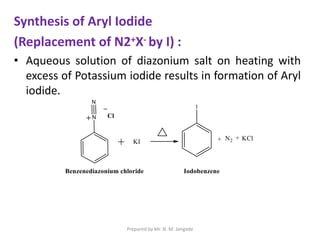
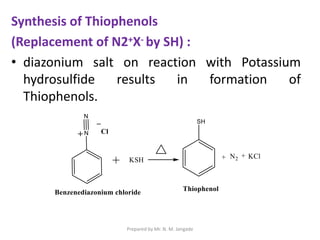
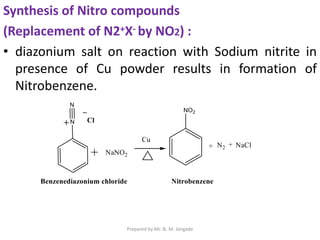
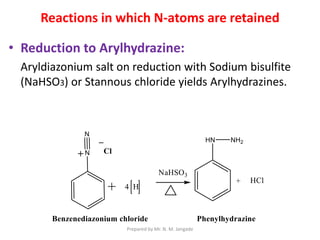
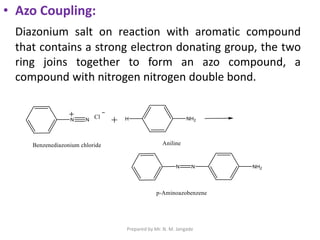
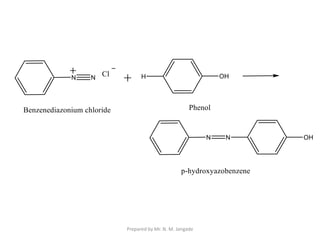
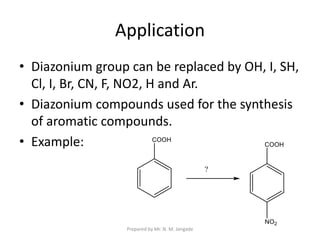
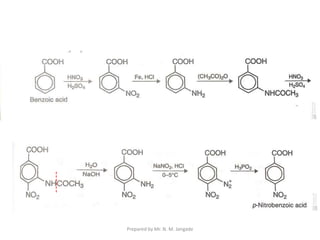
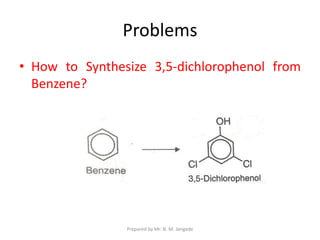
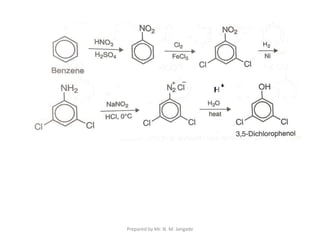
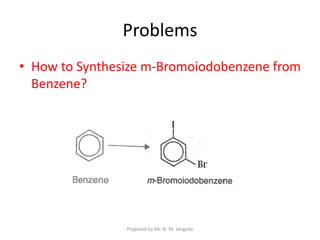
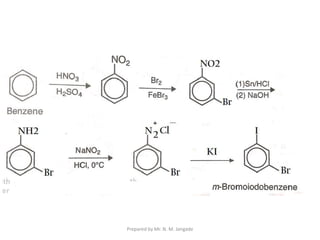
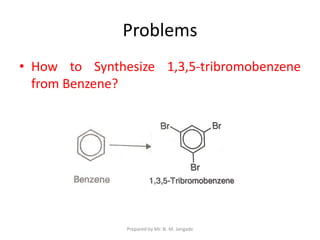
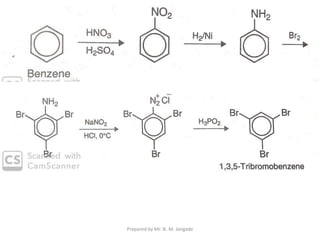
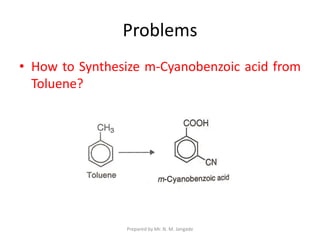
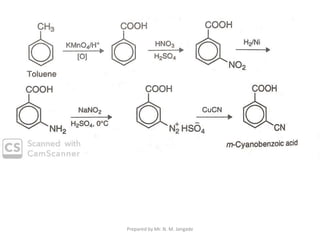
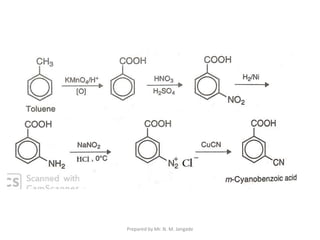
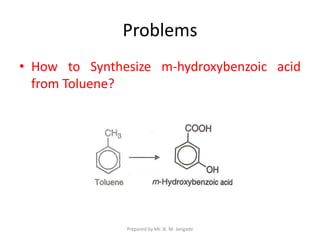
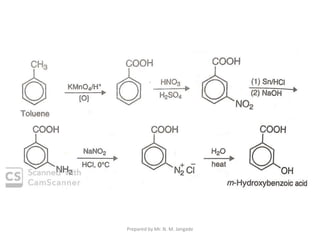
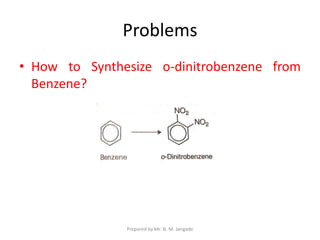
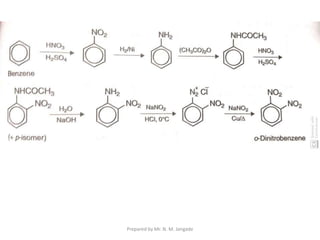
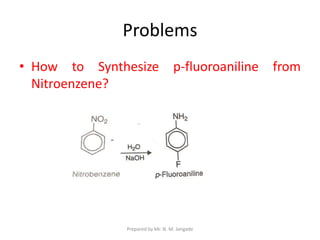
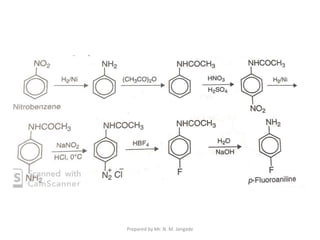
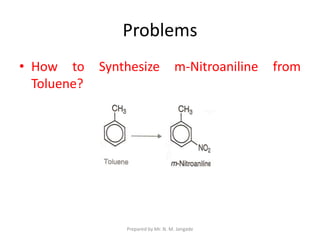
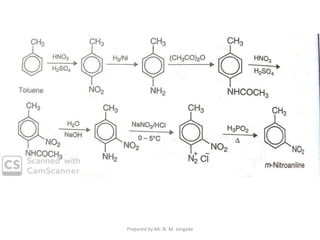
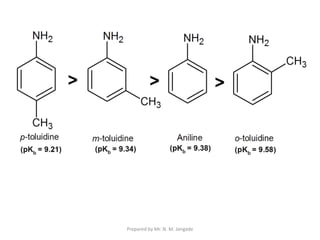
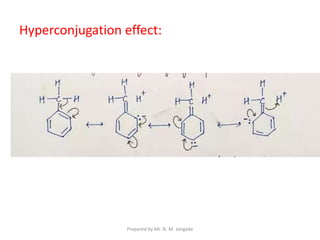
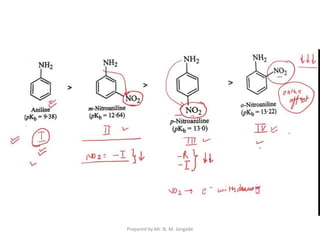
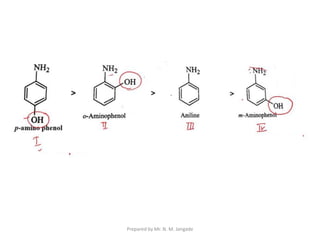
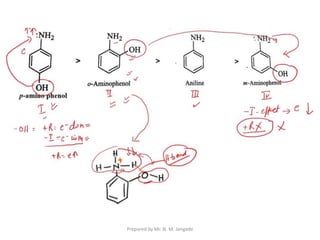
The document provides an in-depth overview of aromatic amines, including their definition, classification into primary, secondary, and tertiary types, and methods of preparation. It discusses their physical properties, various chemical reactions, and basicity, emphasizing the influence of substituents on their chemical behavior. Additionally, it details the synthesis and properties of aryl diazonium salts and their applications in organic synthesis.