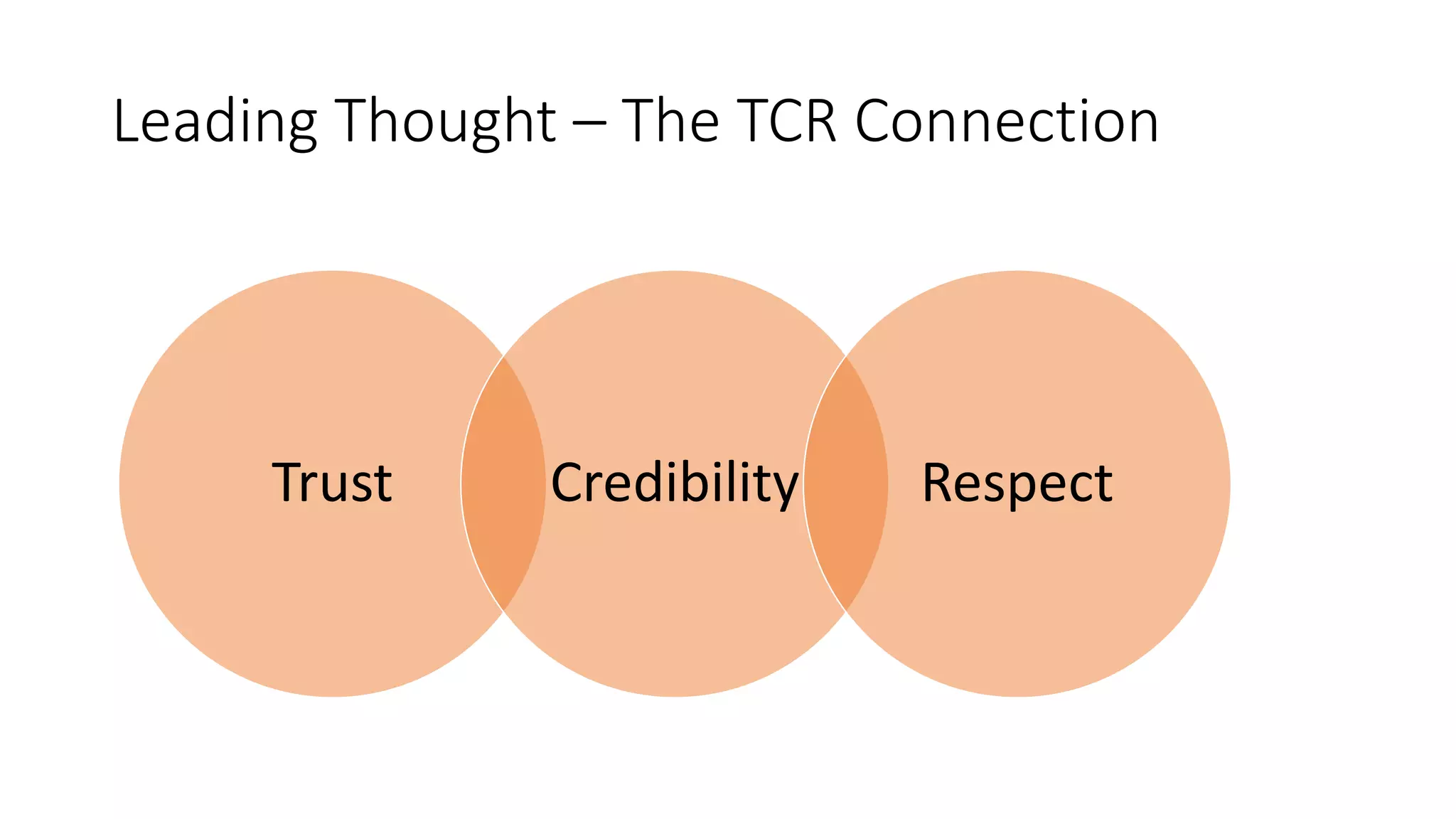
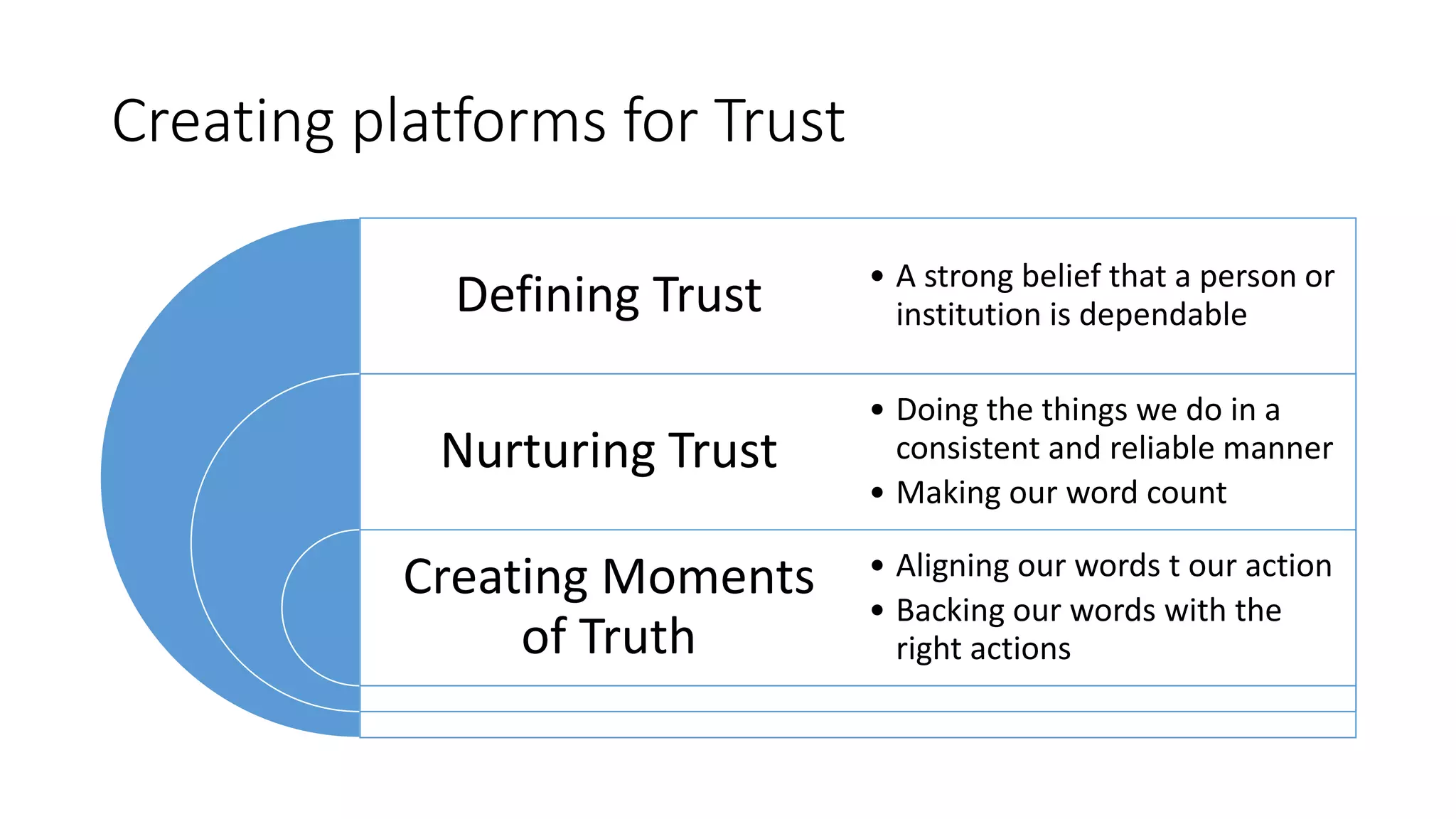
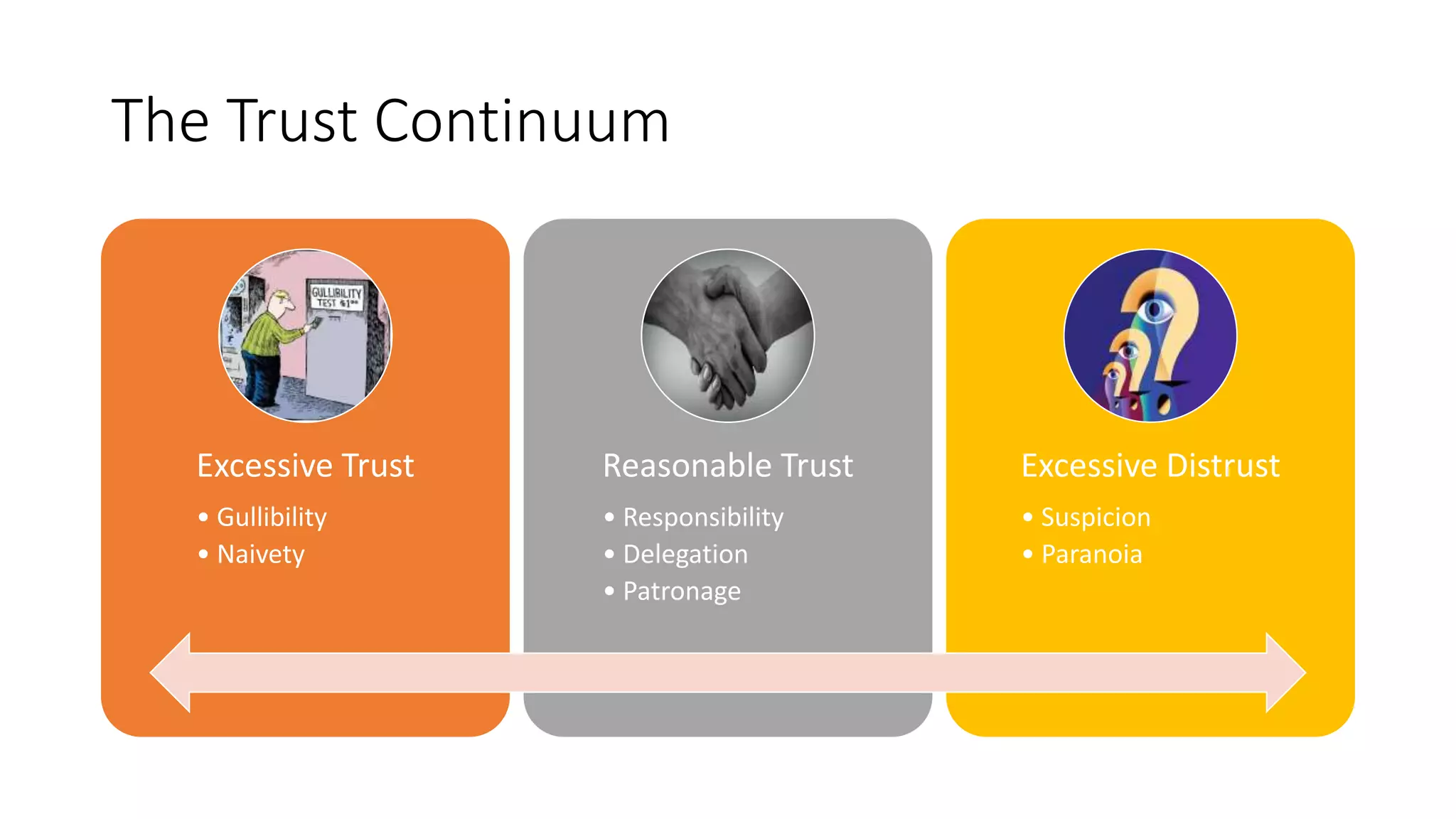
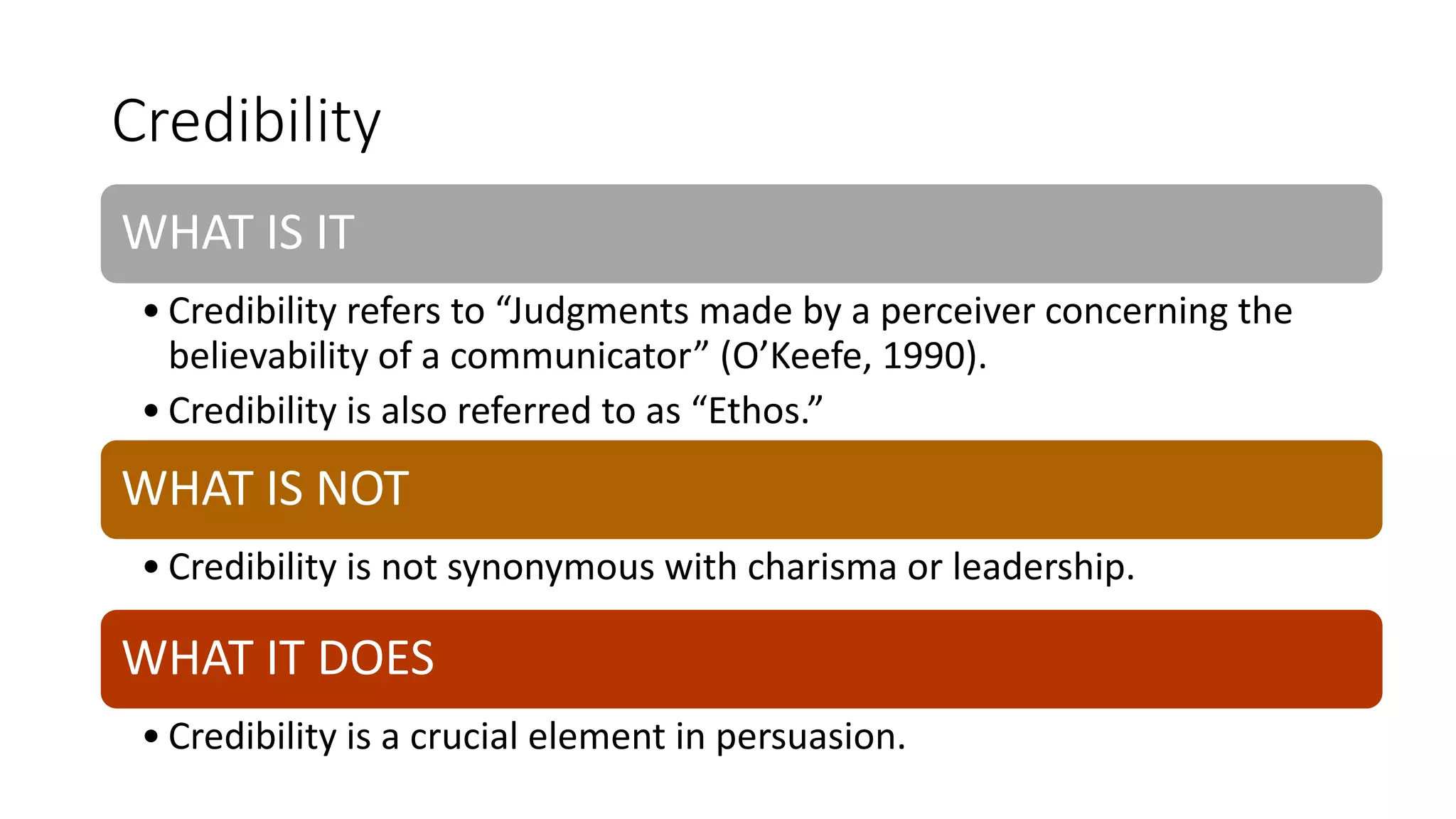
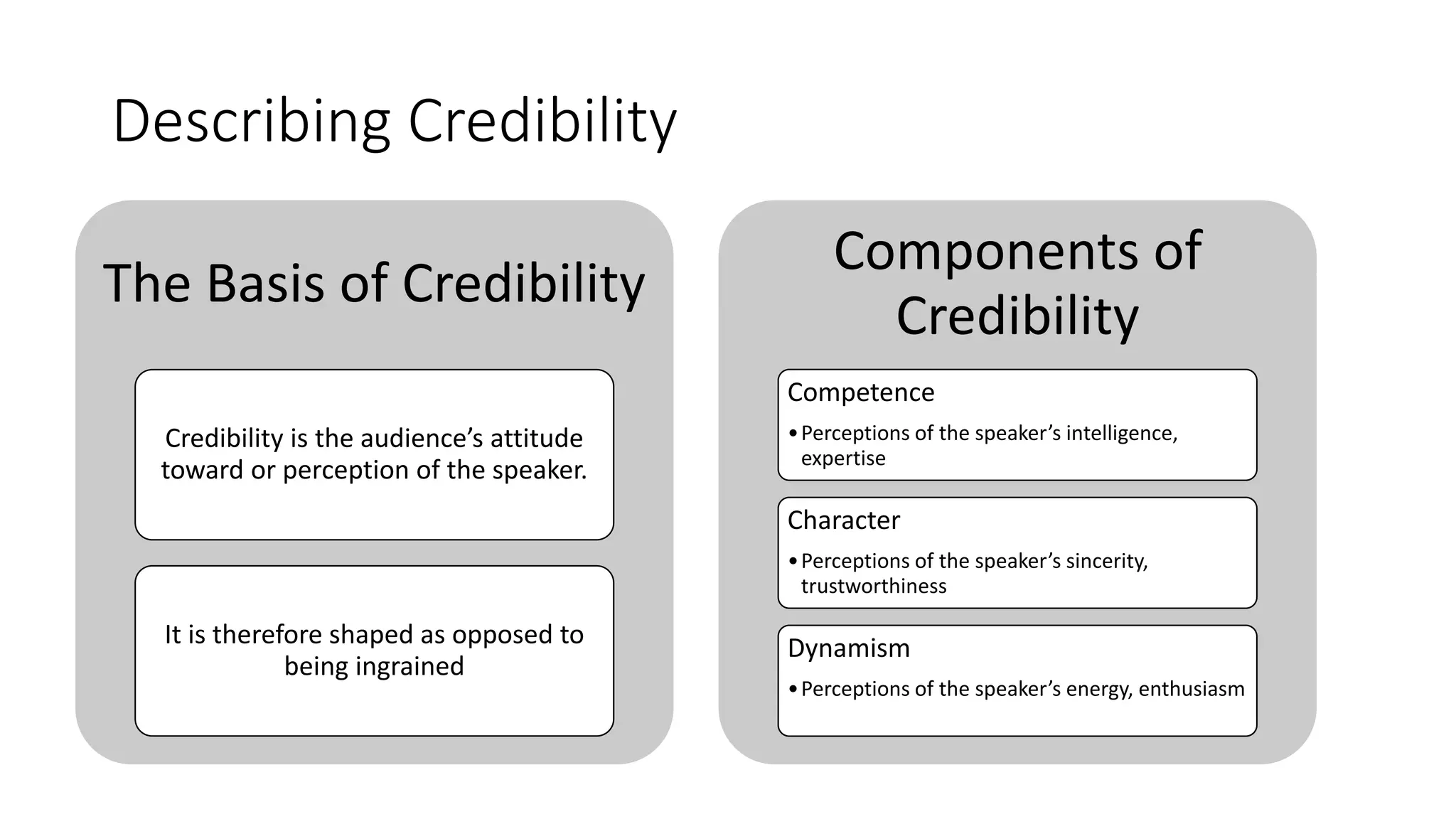
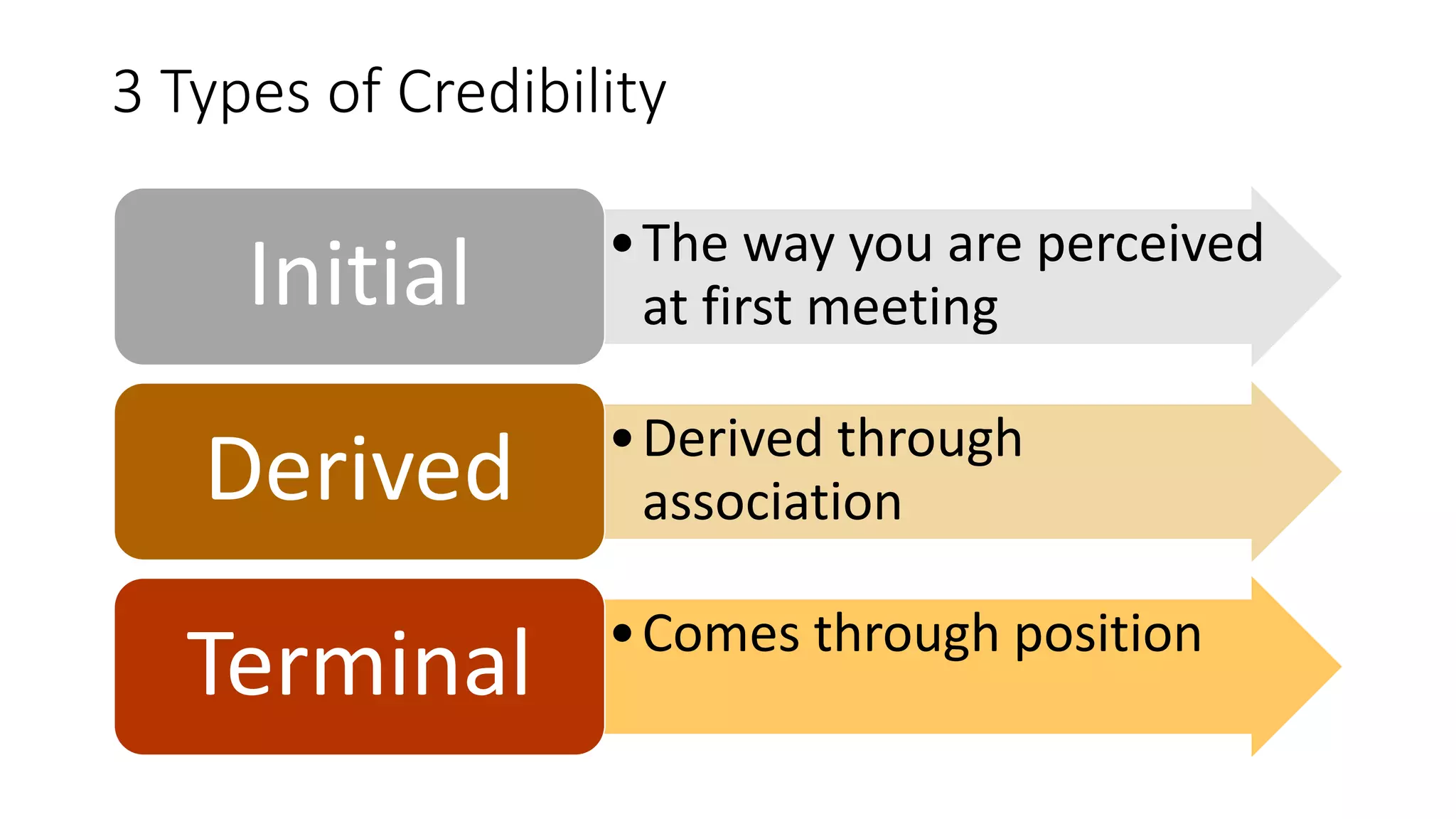
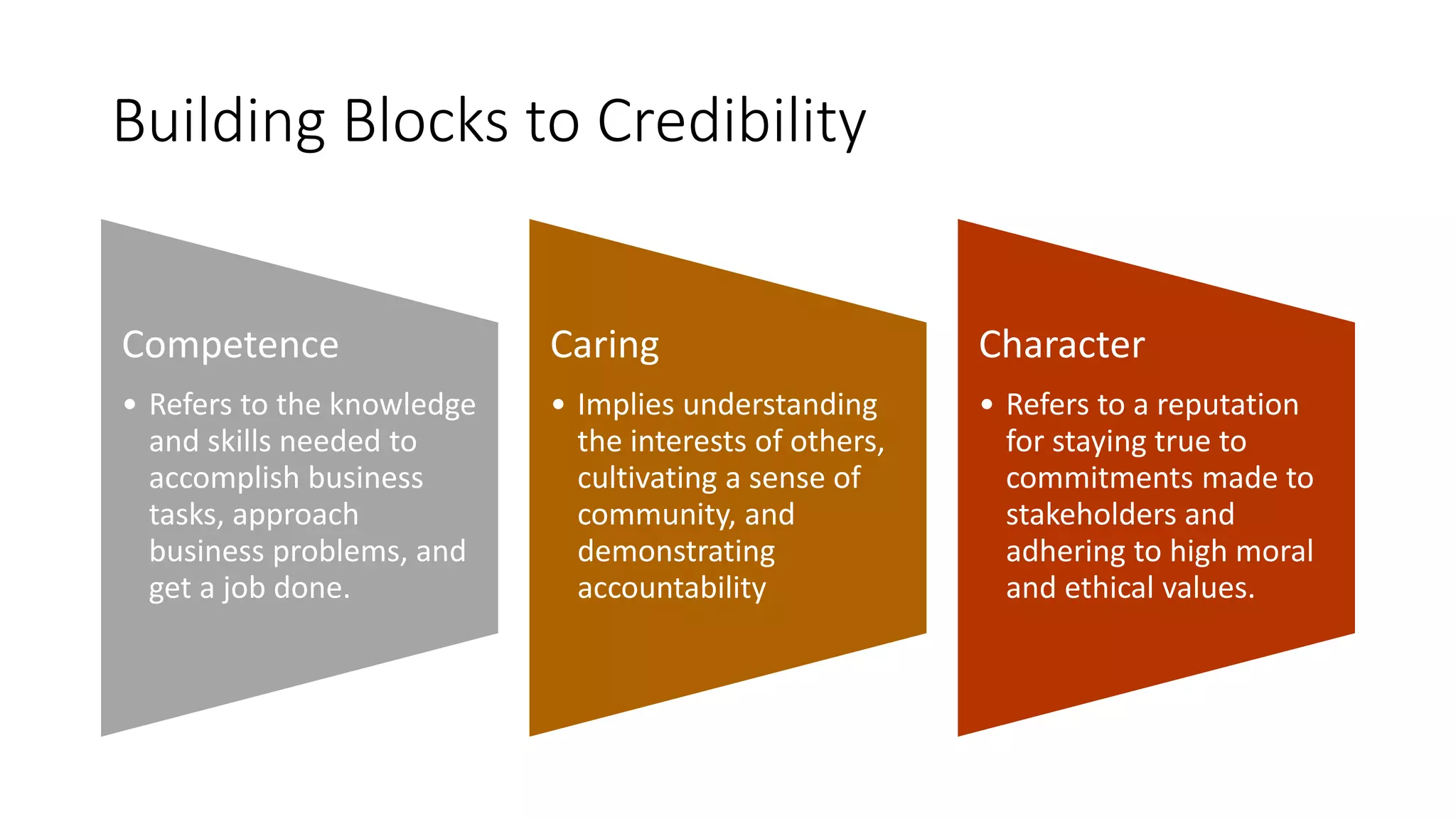
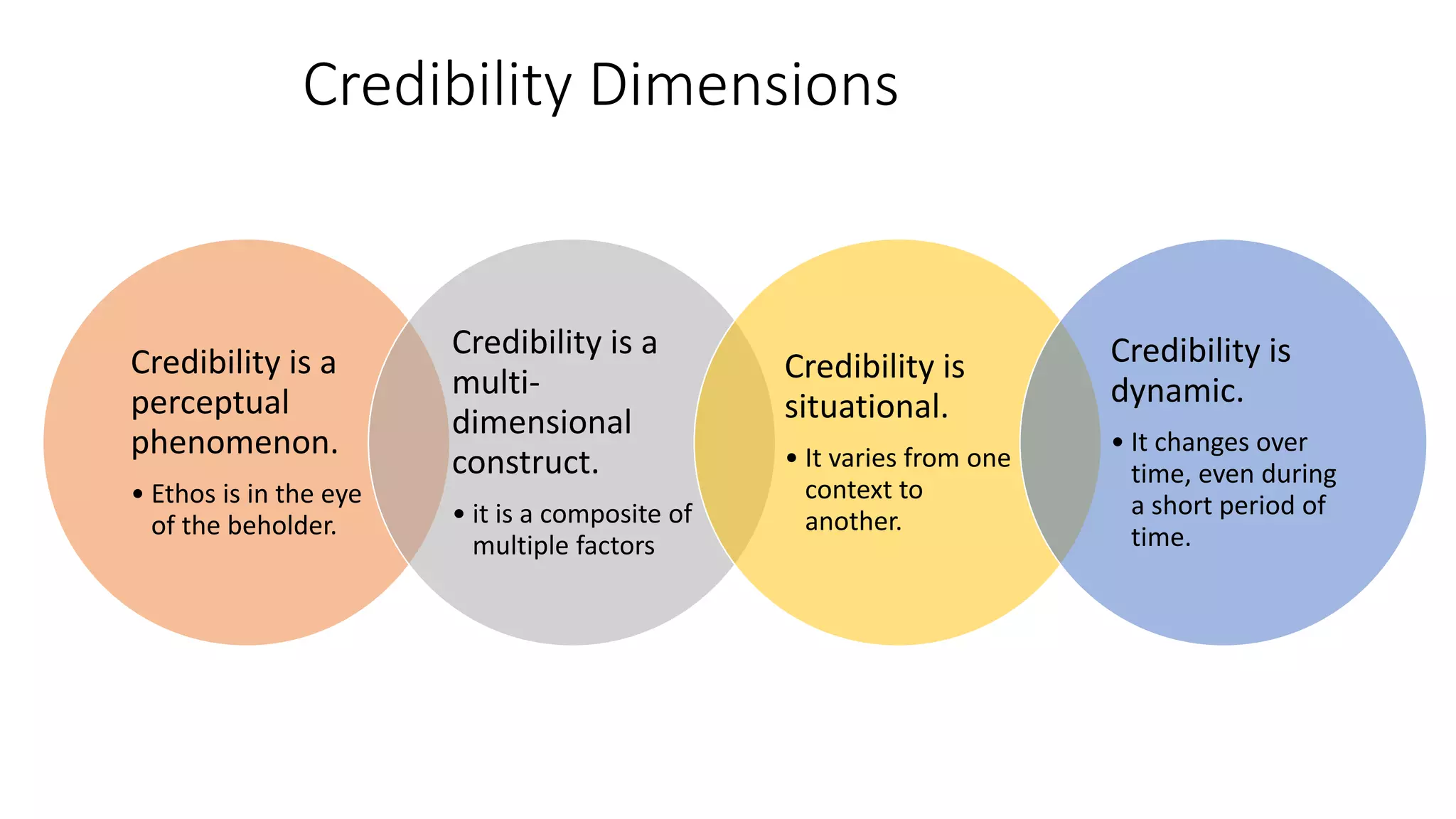
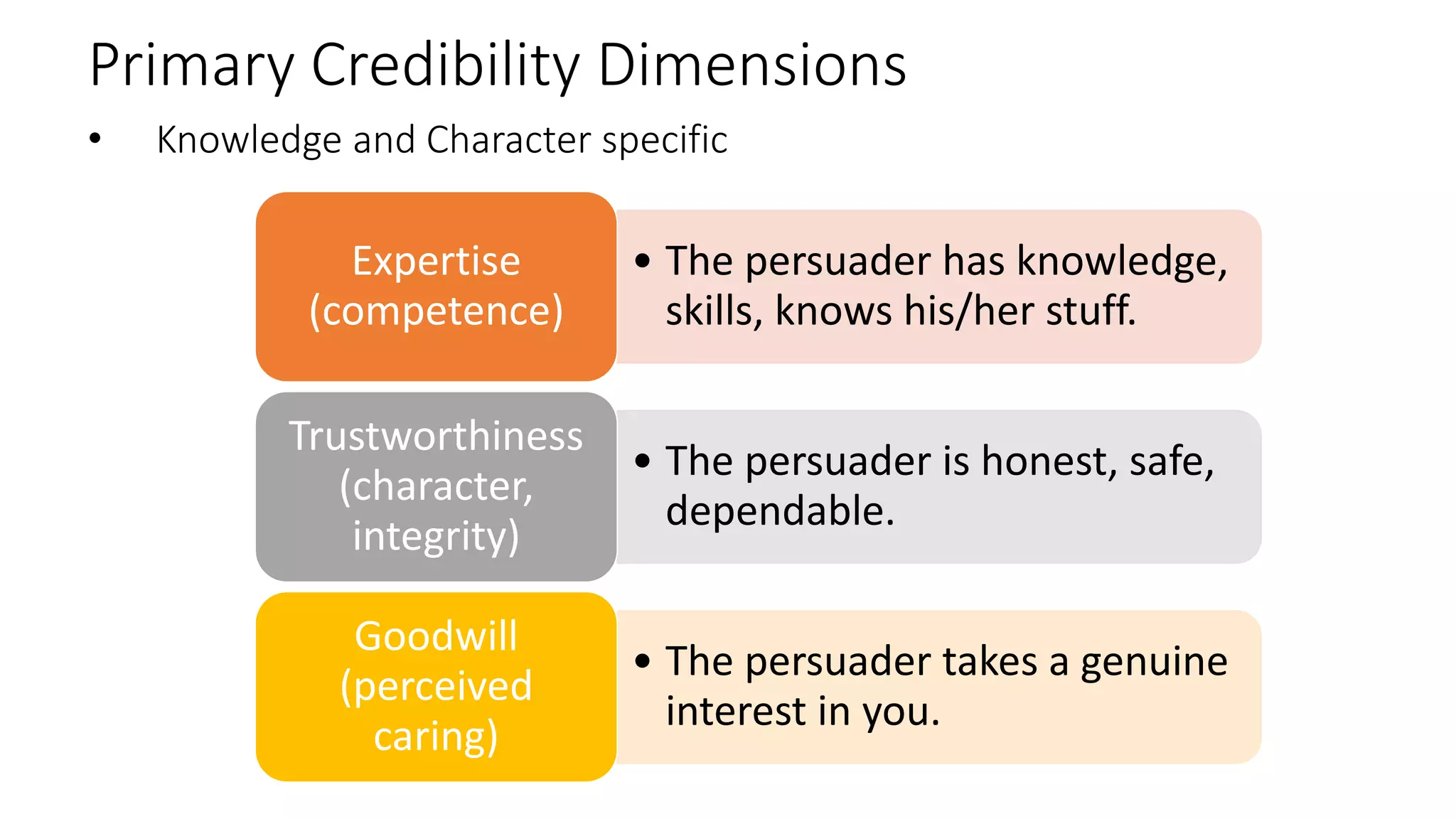
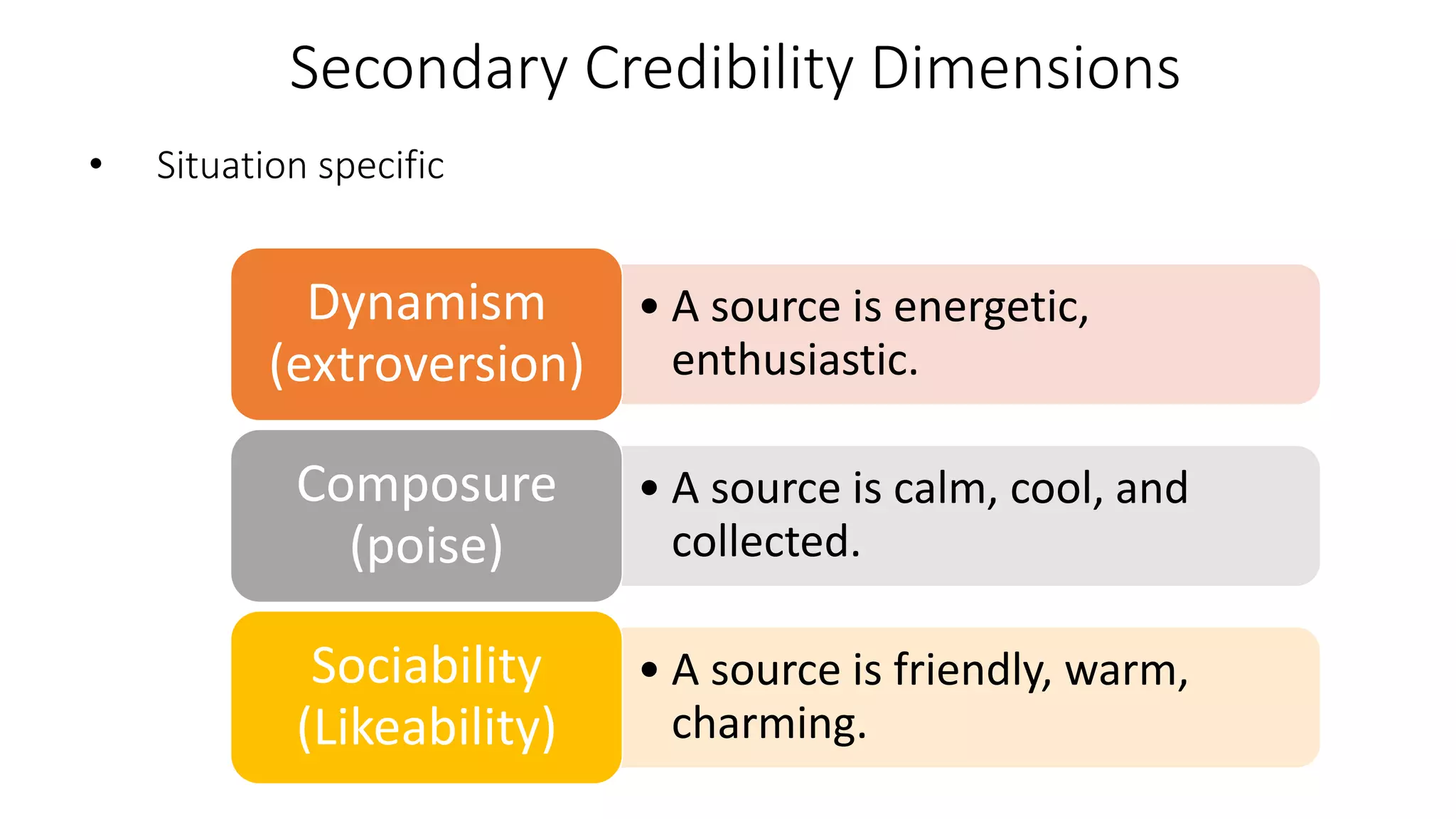
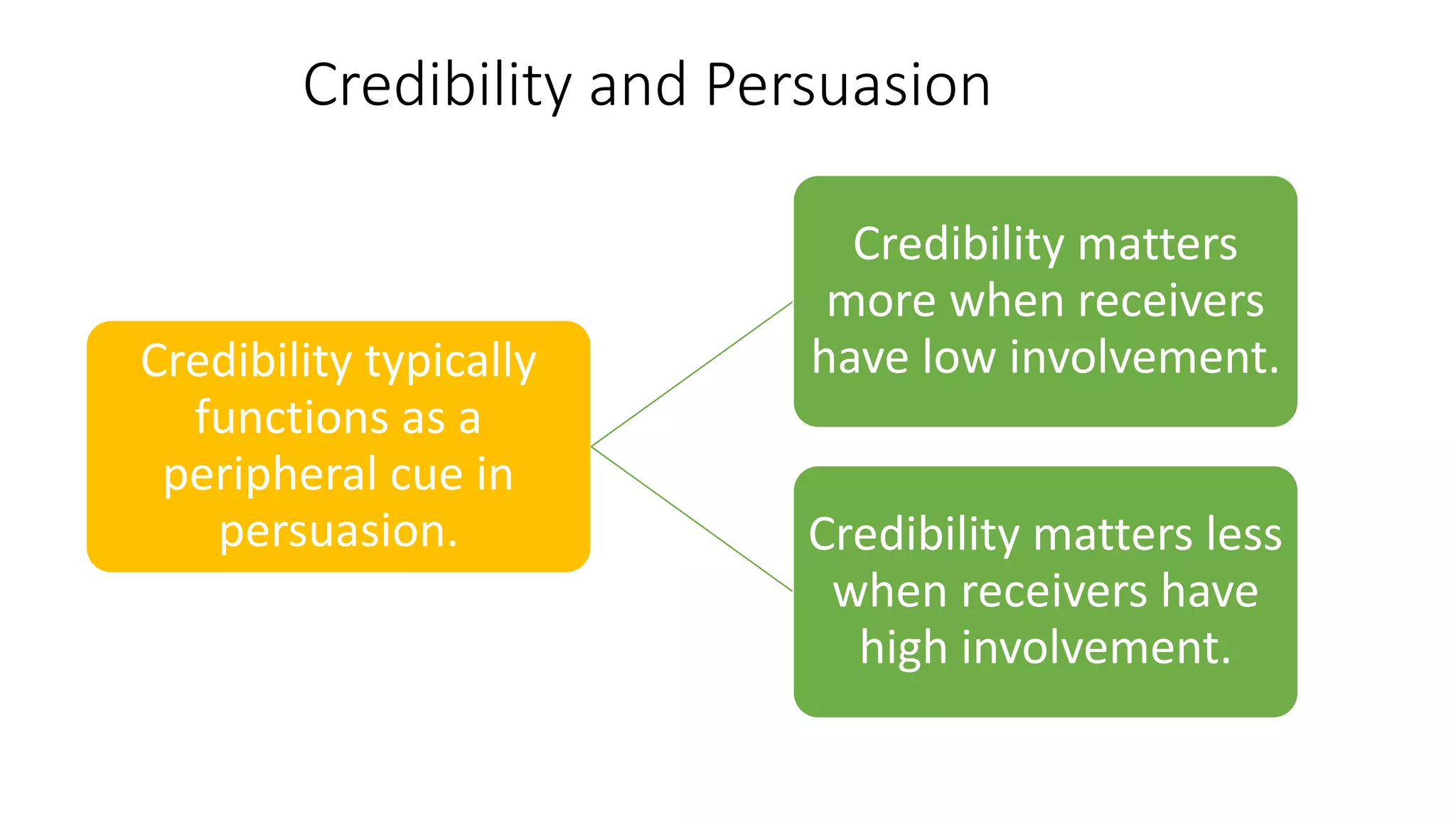
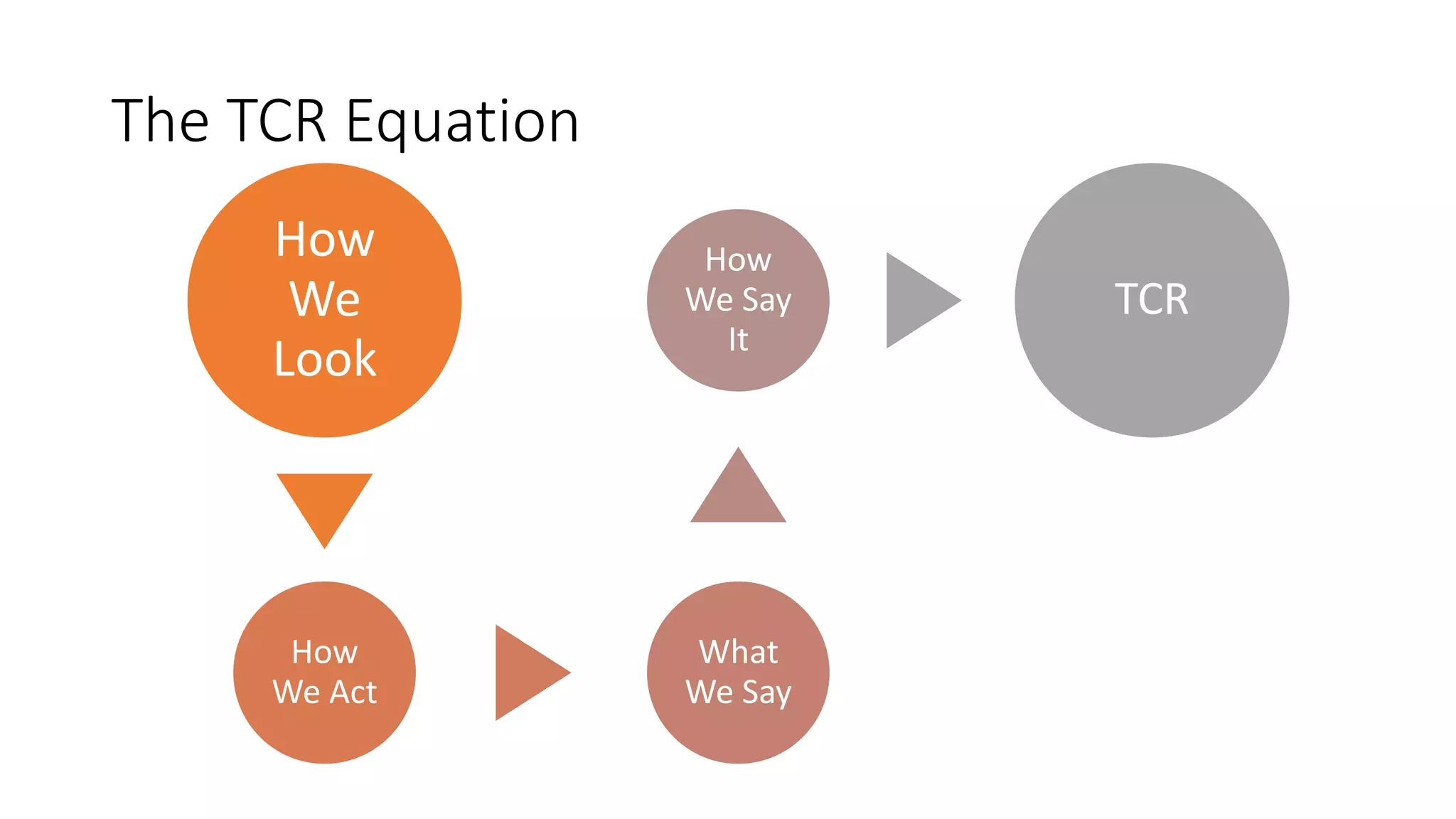
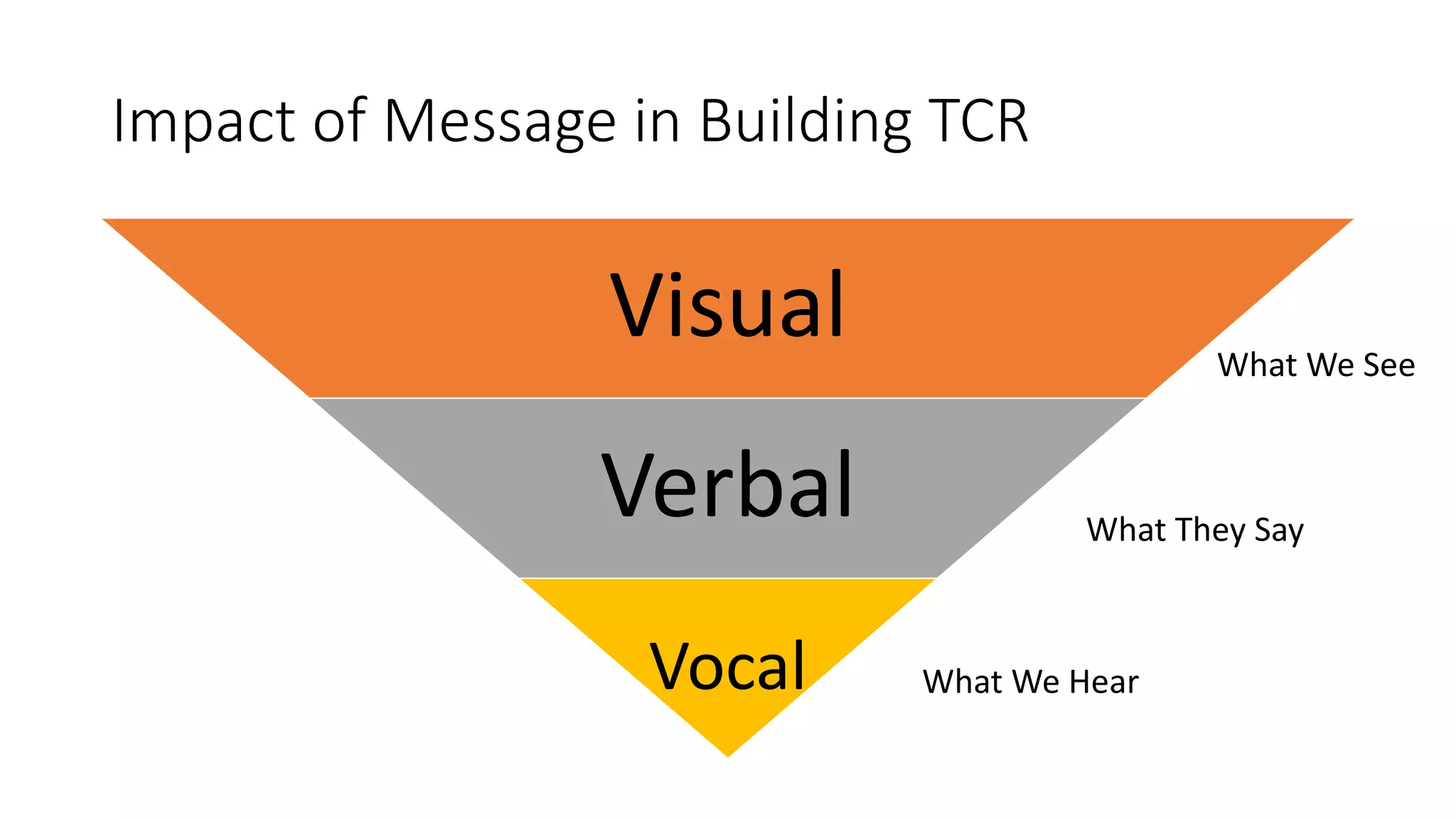
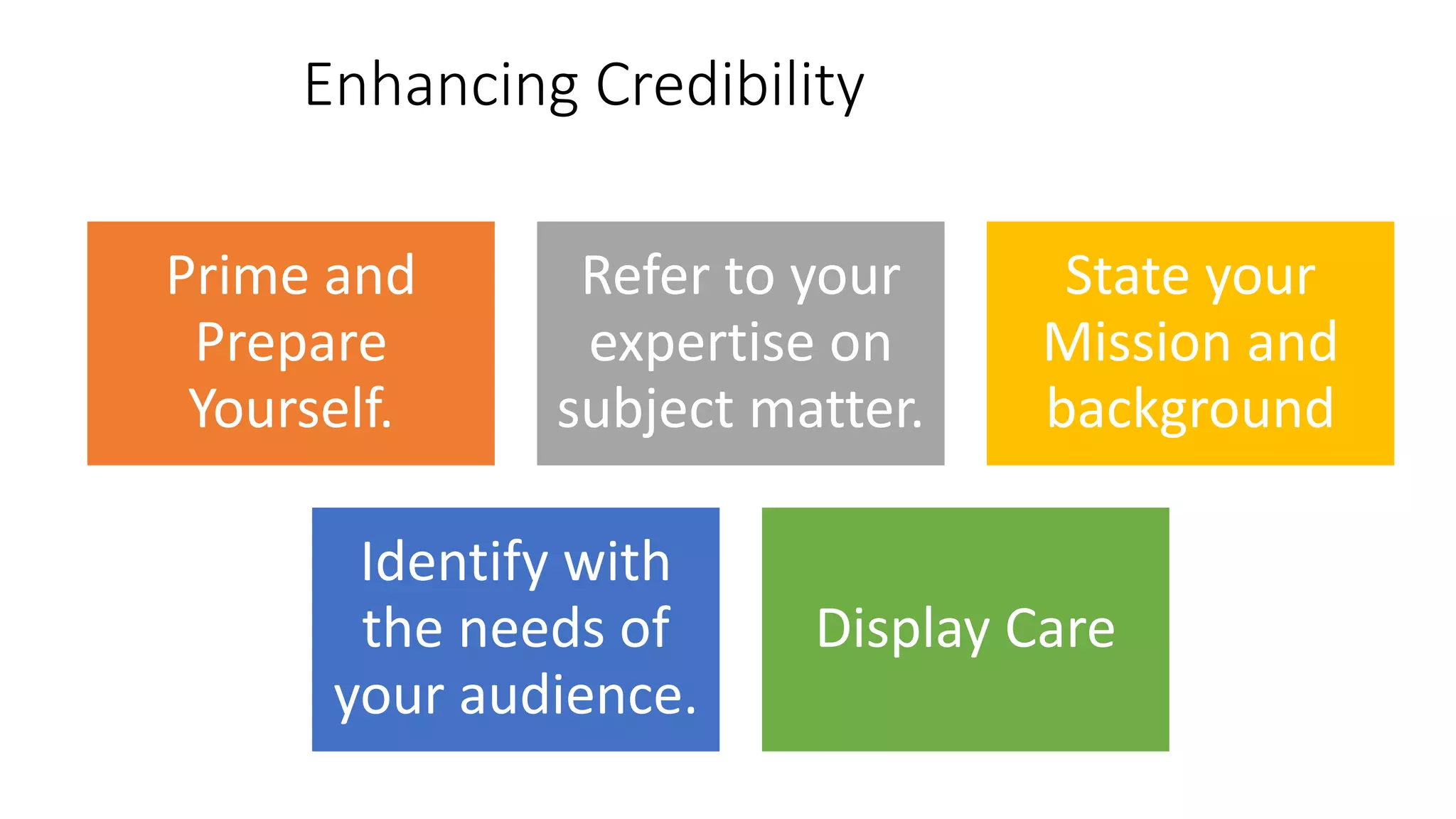
This document discusses the importance of thought leadership and how to build trust, credibility, and respect (TCR) to become an effective thought leader. It defines trust as dependability and consistency, and outlines ways to create trust through defining, nurturing, and creating "moments of truth." Credibility refers to perceptions of competence, character, and dynamism. It discusses initial, derived, and terminal credibility and how to build credibility through competence, caring, and character. The document also explains how credibility, trust, and respect interact in the "TCR equation" and the importance of message delivery through visual, verbal, and vocal channels in building TCR.