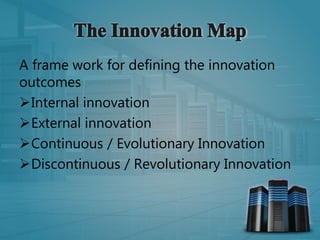
This document discusses creativity and innovation. It defines creativity as the generation of new ideas or concepts, while defining innovation as the application of creative ideas. It then discusses different types of innovation including operational, management, product/service, and strategic innovation. The document also covers innovation strategies such as inventive, adaptive, economic, and innovative application strategies. Overall, the document provides an overview of creativity, innovation, and how innovation strategies can be applied.