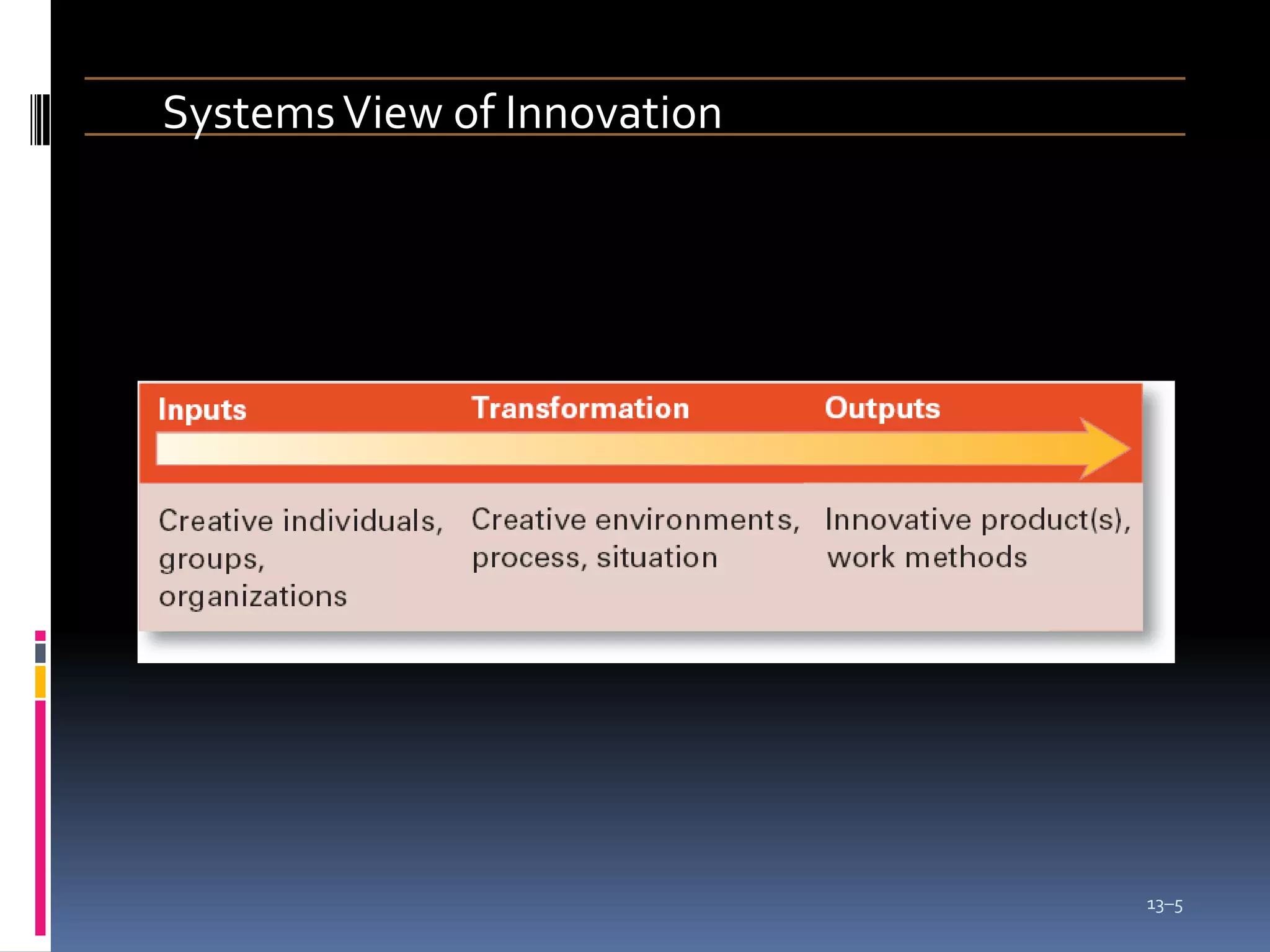
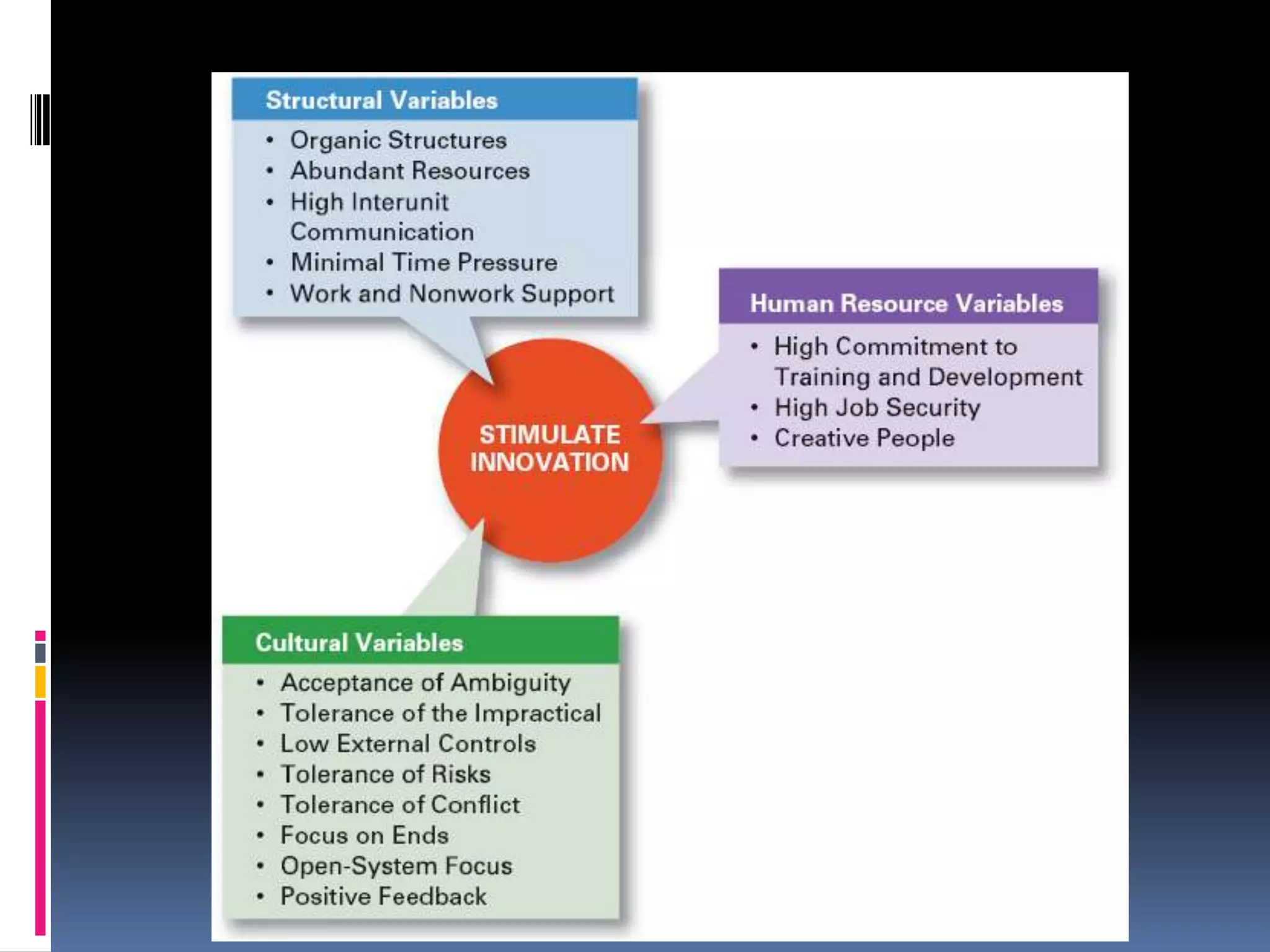
Creativity involves generating novel ideas, while innovation is implementing ideas to create useful products or services. Innovation can be measured more objectively than creativity. Creativity produces ideas, but innovation combines ideas with action. Organizations innovate to meet growing consumer demands and cope with uncertainty, ambiguity, diversity, and complexity. Innovation provides competitive advantage. Invention is a new product or process, while innovation is applying new knowledge to modify offerings. Fostering the right environment for innovation involves adopting structures, cultures, and human resource practices that support risk-taking, creativity, and change.