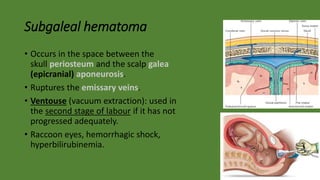
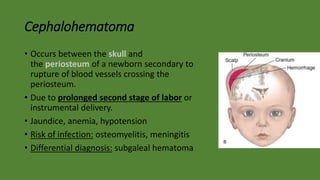
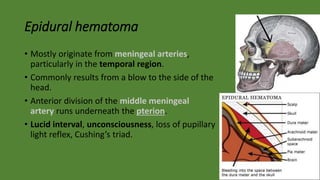
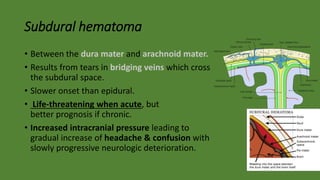
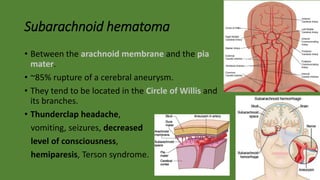
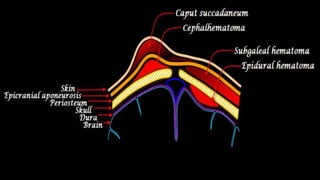
Cranial hematomas can be either extra-axial (outside the brain), occurring between membranes covering the brain, or intra-axial (inside the brain). The most common extra-axial hematomas are epidural, subdural, and subarachnoid hematomas. Epidural hematomas typically result from injuries that rupture the middle meningeal artery. Subdural hematomas are caused by tears in bridging veins, while subarachnoid hematomas usually stem from ruptured cerebral aneurysms. In newborns, common cranial hematomas include caput succedaneum, cephalohematoma, and subgaleal hematoma, which are usually due to difficult childbirth and