Embed presentation
Downloaded 54 times


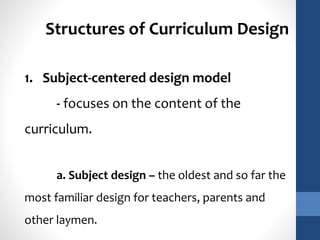
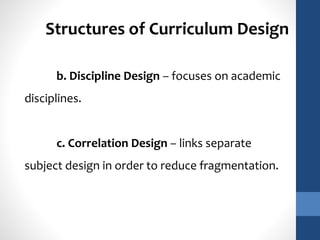
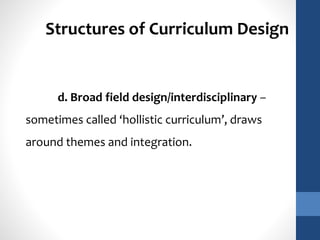
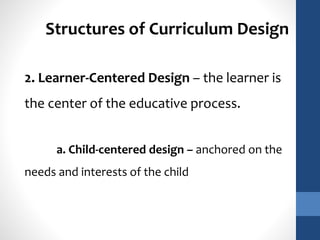
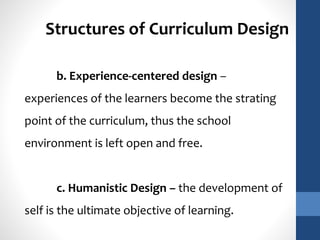
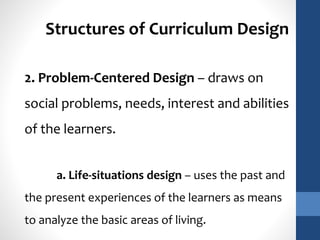
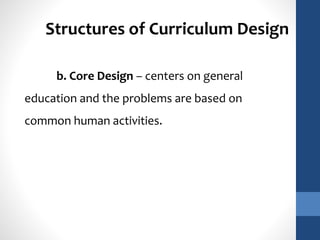

The document discusses the role of teachers as curriculum designers, implementors, and evaluators. It outlines different structures of curriculum design, including subject-centered models focused on content; learner-centered models centered on the needs and interests of students; and problem-centered designs drawing on social issues. The subject-centered structures include subject, discipline, correlation, and interdisciplinary designs. Learner-centered structures comprise child-centered, experience-centered, and humanistic designs. Problem-centered structures involve life-situations and core designs.








