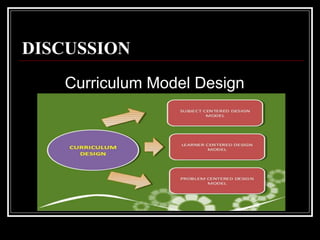
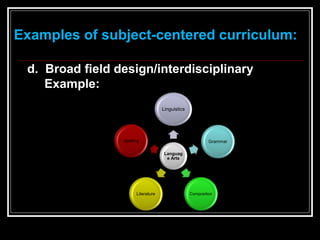
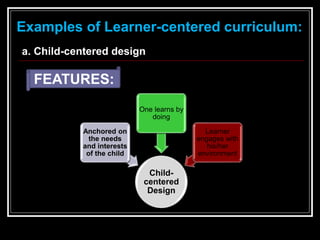
This document discusses different models for curriculum design: subject-centered, learner-centered, and problem-centered. The subject-centered model focuses on academic content and can organize curriculum around specific subjects, disciplines, or broad fields. The learner-centered model places students' needs, interests, and experiences at the center. Examples include child-centered and experience-centered designs. The problem-centered model structures curriculum around real-world problems for students to solve, such as in life situations or core designs. Effective curriculum design considers students' backgrounds and needs flexibility. The conclusion advocates exploring different models to design coherent educational experiences for students and teachers.