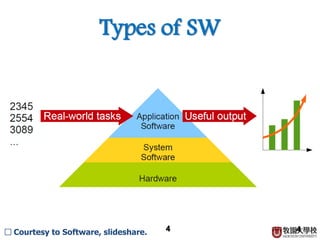
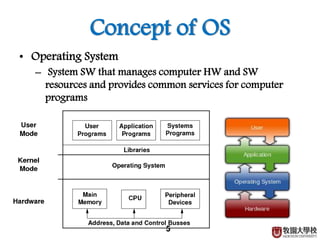
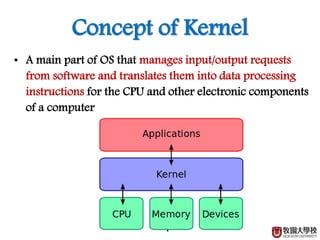
This document discusses CPU, software, and operating systems. It defines software as programs that run on computers and categorizes them into system software like operating systems, and application software. It describes operating systems as system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, providing common services. It outlines the requirements of operating systems, including shielding hardware details from applications, substituting abstract services for physical hardware services, and optimizing resource allocation.
![CPU and Software
Yong Heui Cho @ Mokwon University
Some of slides are referred to:
[1] Software, slideshare.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11-151120095453-lva1-app6891/75/CPU-and-Software-1-2048.jpg)