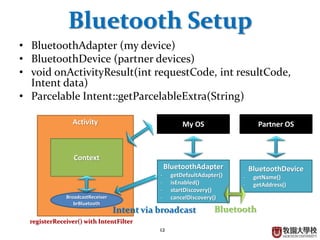
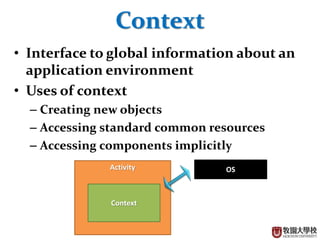
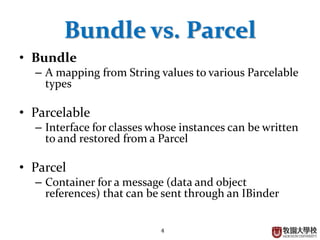
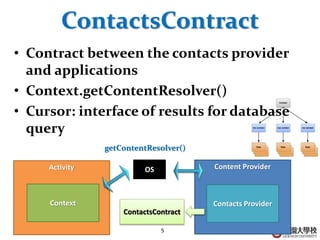
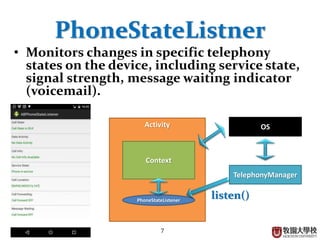
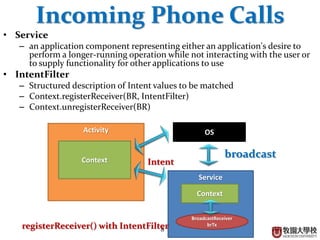
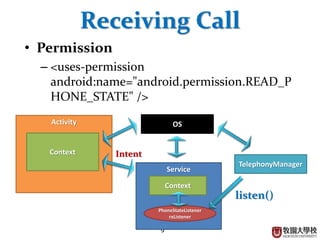
This document discusses various Android programming concepts including context, activities, bundles, contacts provider, telephony manager, phone state listener, incoming phone calls, sending and receiving SMS, and Bluetooth setup. Context provides information about the application environment and is used to access common resources and components. An activity extends context and views get their context usually from the activity context. Bundles are used to parcel data between components while the contacts provider and telephony manager provide APIs to access contacts and phone functions, respectively. Listeners can monitor phone states and incoming calls. SMS and Bluetooth functions also use contexts and intents to communicate between components.



![11
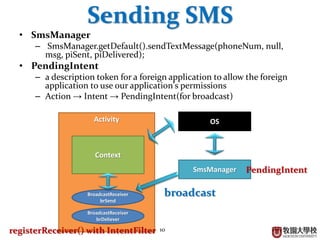
Receiving SMS
• Receiving process
– Broadcast → Intent → Bundle → PDU (Object[]) →
SmsMessage → String
• Bundle: a mapping (or dictionary) class from String
key to various types
• PDU: Protocol Description Unit
Activity
Context
BroadcastReceiver
brReceive
OS
SmsManager
Intent via broadcast
registerReceiver() with IntentFilter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidprogramming-161101094129/85/Android-Programming-11-320.jpg)