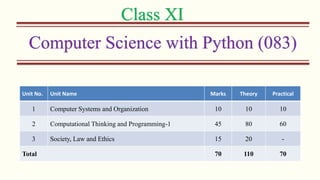
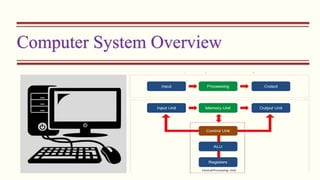
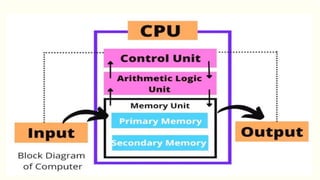
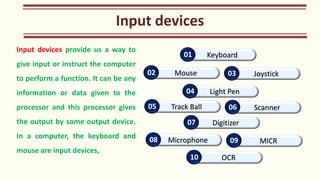
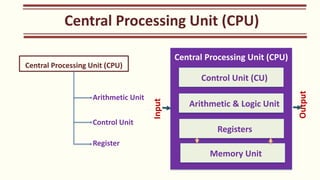
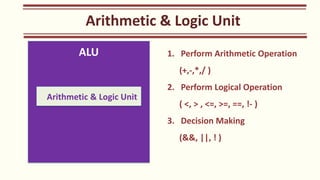
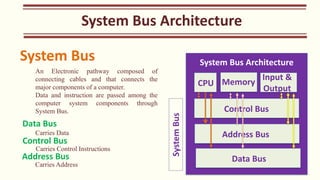
The document outlines the Class XI Computer Science curriculum focused on Python, including units on computer systems, programming, and ethical considerations. It explains fundamental concepts such as hardware, software, peripheral devices, and the CPU's role in processing instructions. Additionally, it details types of operating systems and language processors involved in programming and system functionality.