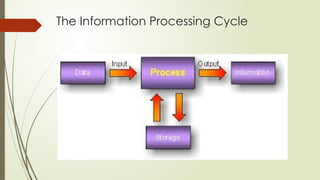
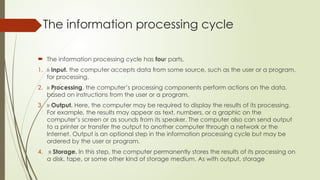
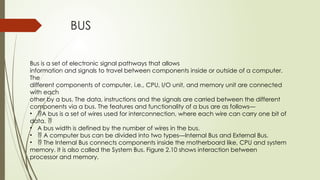
A complete computer system consists of hardware, software, data, and users, all of which work together in an information processing cycle that includes input, processing, output, and storage. The hardware is categorized into the processor, memory, input/output devices, and storage, with primary memory having volatile RAM and non-volatile ROM, while secondary memory offers long-term storage. The CPU, with its control unit and arithmetic logic unit, orchestrates data processing, supported by registers and cache memory for efficiency.