This document provides an overview of computers including:
1. A computer is an electronic device that takes in data as input, processes it, and provides output. It gets its name from the Latin word "compute" meaning to calculate.
2. Computers are used in many fields like banking, education, business, science and more. They can also have drawbacks like physical or mental health issues if overused.
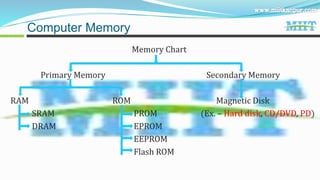
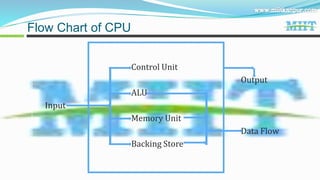
3. Computers have great speed, accuracy and storage capacity. Key components include the CPU, memory, hardware and different types of software.