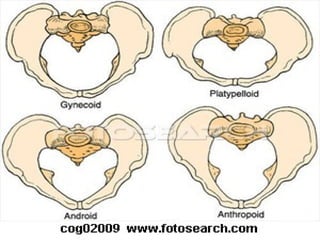
Cephalopelvic disproportion (CPD) refers to a disparity between the fetal head size and the mother's pelvic size that can impact labor and delivery. It is defined as the essential diameters of the pelvis being shortened by at least 0.5 cm. CPD can be caused by conditions like rickets, osteomalacia, or injuries that impact pelvic development. It increases risks during labor like prolonged labor, operative delivery, maternal injuries, and fetal hazards. Management options include preterm induction, elective c-section, or a trial of labor depending on the individual case.