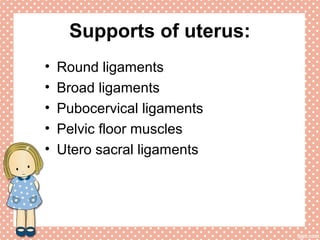
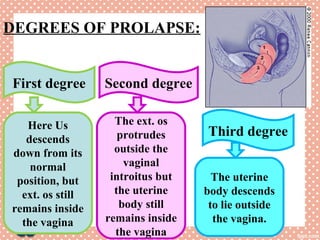
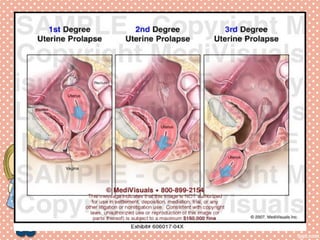
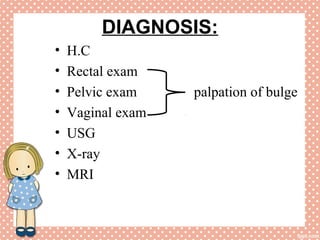
Uterine prolapse is a common condition where the uterus descends from its normal position, often seen in multiparous women. It is caused by weakening or overstretching of the ligaments and muscles that support the uterus. Symptoms include a feeling of pressure or fullness in the vagina, back pain, urinary problems, and difficulty with bowel movements. Diagnosis involves physical examination, ultrasound or MRI. Treatment options range from use of a pessary or surgery to correct or remove the prolapsed uterus, with surgery having a risk of complications like infection, incontinence, or injury to nearby organs.