Embed presentation
Downloaded 10 times


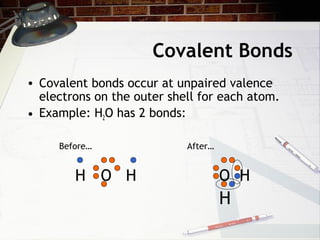



Covalent bonds occur when atoms share pairs of electrons to form molecules. Atoms form covalent bonds by sharing unpaired valence electrons, with examples being water (H2O) forming two covalent bonds and molecular oxygen (O2) forming a double covalent bond by sharing two pairs of electrons. Properties of covalent bonds include low melting and boiling points with poor conductivity.





