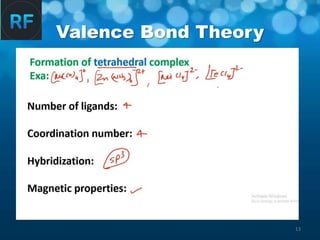
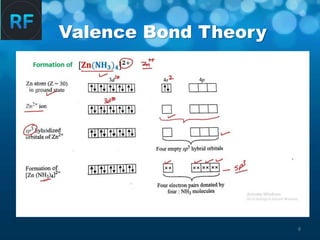
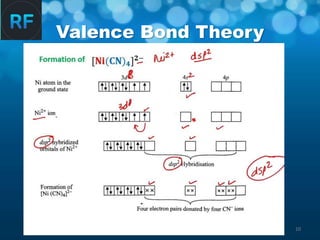
Valence Bond Theory (VBT) explains how chemical bonding occurs through the overlap of atomic orbitals, emphasizing the need for vacant orbitals and hybridization in metal-ligand complexes. It outlines the formation of different geometric structures such as octahedral, tetrahedral, and trigonal planar complexes based on factors like coordination number and hybridization. However, VBT has limitations, including its inability to explain certain magnetic behaviors and the complexities of ligand interactions.









![12
Valence Bond Theory
1) Misleading magnetic behavior.
2) Why some complex of same metal in a particular
oxidation state are low spin and high spin. For
example:[Co(NH3)6]3+ and [Co(F)6]3
3) Color of complex cannot explained.
4) Thermodynamic or kinetic stabilities of
complexes.
5) Not explain about weak and strong Ligands.
Limitations of VBT:-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbtvalancebondtheory-220221060929/85/VBT-valance-bond-theory-12-320.jpg)