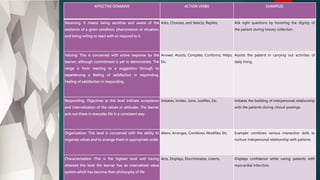
The document outlines the formulation of educational objectives, emphasizing their role in guiding teaching-learning processes and aligning with societal needs, student requirements, and available resources. It details Ralph Tyler's nine essential steps for creating these objectives, focuses on distinct domains of learning (cognitive, affective, psychomotor), and highlights specific criteria for writing measurable and effective objectives. The document aims to provide educators with a framework for developing clear, concise, and attainable educational goals that facilitate meaningful learning experiences.