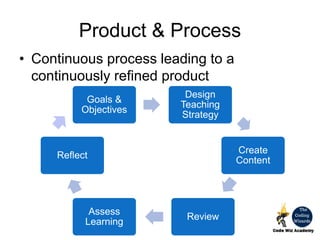
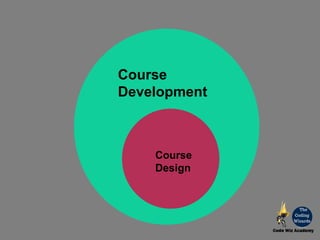
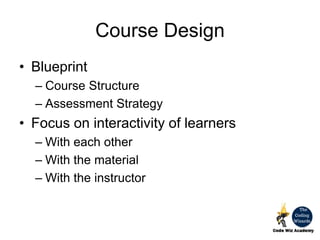
The document outlines the principles and processes involved in course development at CodeWiz Academy, emphasizing the importance of designing courses that foster creativity, critical thinking, and collaboration among learners. It discusses various pedagogical elements including the definition of goals and objectives, course design strategies, and methods for assessment to ensure effective learning outcomes. Additionally, it highlights the significance of understanding the psychological and sociological foundations of education to enhance the learning experience.