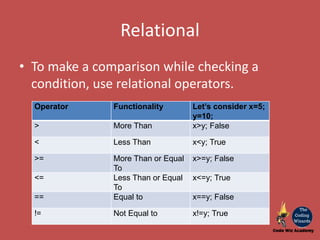
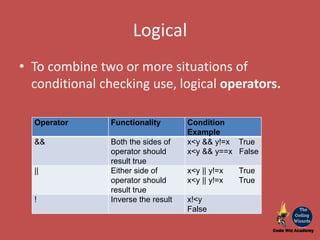
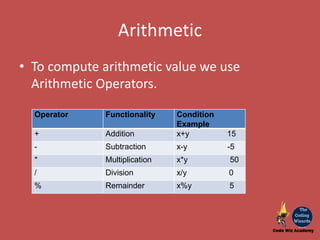
The document provides an overview of JavaScript as a programming language used for web development, detailing its interaction with HTML and CSS. It covers basics of JavaScript programming including storage (variables, constants, arrays), conditional constructs, and iterations like loops. Additionally, it introduces different types of operators used in conditional checks and arithmetic computations.