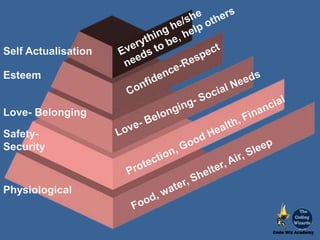
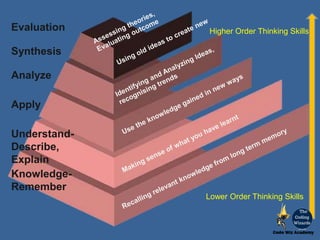
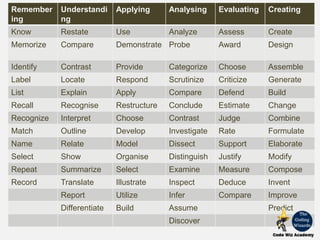
The document discusses educational taxonomies, specifically Maslow's hierarchy of needs and Bloom's taxonomy, as frameworks for understanding educational objectives and learning processes. It emphasizes that basic human needs must be met before engaging in higher-order cognitive skills and outlines various teaching approaches for active learning, including problem-based and project-based learning. The document also highlights the importance of the affective domain in education, detailing how students internalize values and behaviors through structured learning experiences.