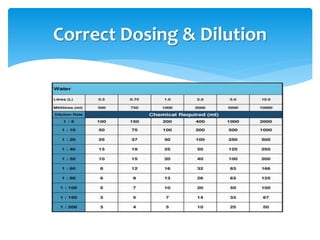
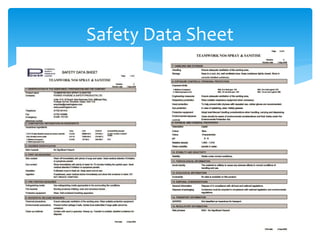
The document discusses the importance of following COSHH (Control of Substances Hazardous to Health) procedures when using chemicals for cleaning. It emphasizes that COSHH aims to protect workers' health from hazardous substances and is a legal requirement. It notes that COSHH involves identifying hazards and managing risks associated with chemicals. The document also discusses personal protective equipment and following safety instructions and procedures to safely handle chemicals.