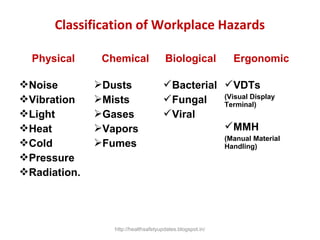
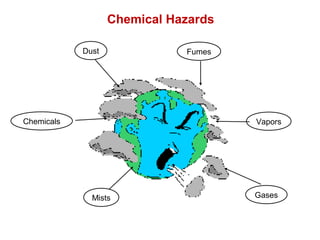
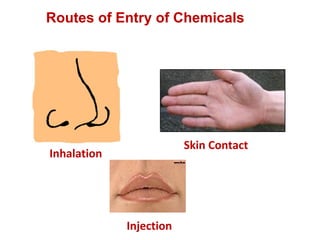
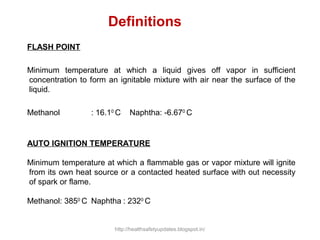
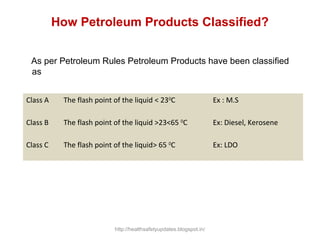
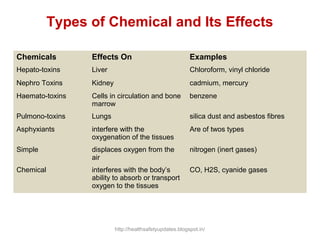
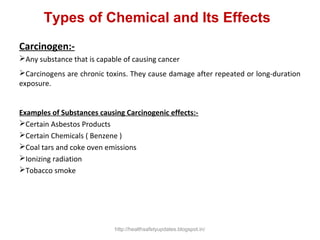
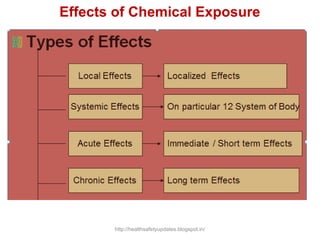
This document provides an overview of chemical hazards and safety. It discusses the classification of workplace hazards including physical, chemical, biological and ergonomic. It defines key terms like flash point, auto ignition temperature, threshold limit values and IDLH. It describes routes of chemical entry, health effects of chemicals on different organs, and carcinogens. The document provides guidance on personal protective equipment, respiratory protection, and controlling chemical exposure through engineering controls, hygiene and proper storage. It emphasizes the importance of material safety data sheets and following standard operating procedures to safely handle chemicals.