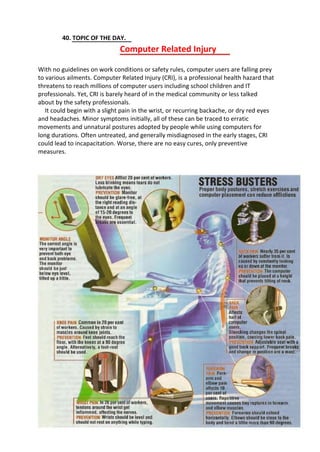
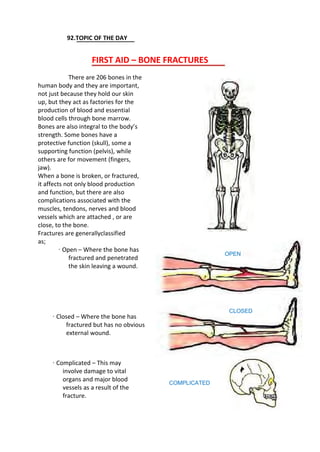
This document discusses pyrophoric iron fires, which occur when iron sulfide deposits inside refinery equipment are exposed to oxygen during maintenance. Iron sulfide forms as a corrosion product when iron oxide reacts with hydrogen sulfide. When iron sulfide is exposed to air, it rapidly oxidizes back to iron oxide in an exothermic reaction that generates enough heat to ignite nearby flammable gases. Distillation columns are most prone to these fires due to iron sulfide deposits accumulating on trays and packings. Proper cleaning of equipment before opening is needed to prevent pyrophoric iron oxidation from igniting combustible materials and causing fires or explosions during maintenance.













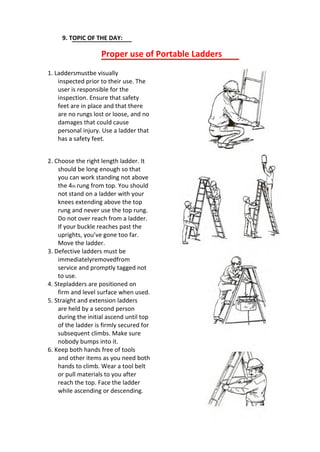












































































































![·
·
·
·
Do not use butter or other ointments (Example, Vaseline).
Avoid using local anesthetic sprays and creams. They can slow healing and
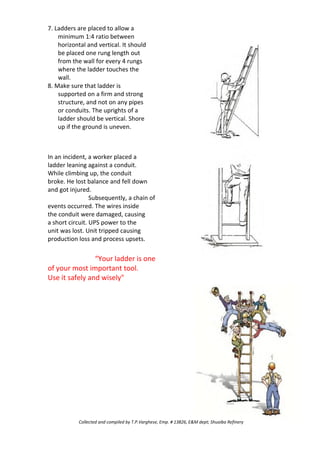
may lead to allergic reactions in some people.
Call your doctor if after 2 days you show signs of infection (fever of 101،F or
higher, chills, increased redness, swelling, or pus in the infected area) or if the
affected area is still painful.
Take aspirin, acetaminophen, or ibuprofen, or naproxen sodium to relieve
pain. [Note: Do not give aspirin or any medication containing salicylates to
anyone 19 years of age or younger, unless directed by a physician, due to its
association with Reye's Syndrome, a potentially fatal condition.]
For Second Degree Burns (that are not extensive and less than 3" in diameter)
·
·
·
·
·
Immerse the affected area in cold (not ice) water until the pain subsides.
Dip clean cloths in cold water, wring them out and apply them over and over
again to the burned area for as long as an hour. Blot the area dry. Do not
rub.
Do not break any blisters that have formed.
Avoid applying antiseptic sprays, ointments, creams.
Once dried, dress the area with a single layer of loose gauze that does not
stick to the skin. Hold in place with bandage tape that is placed well away
from the burned area.
Change the dressing the next day and every two days after that.
Prop the burn area higher than the rest of the body, if possible.
Call your doctor if there are signs of infection (fever of 101º F or higher,
chills, increased redness and swelling, and pus) or if the burn shows no sign
of improvement after 2 days.
·
·
·
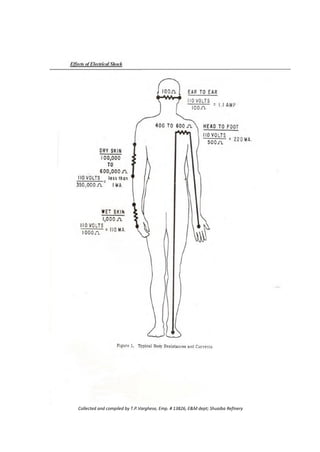
Collected and compiled by T.P.Varghese, Emp. # 13826, E&M dept; Shuaiba Refinery](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/100safetytopicsbook-230810084333-924504c3/85/100-Safety-topics-Book-pdf-135-320.jpg)












