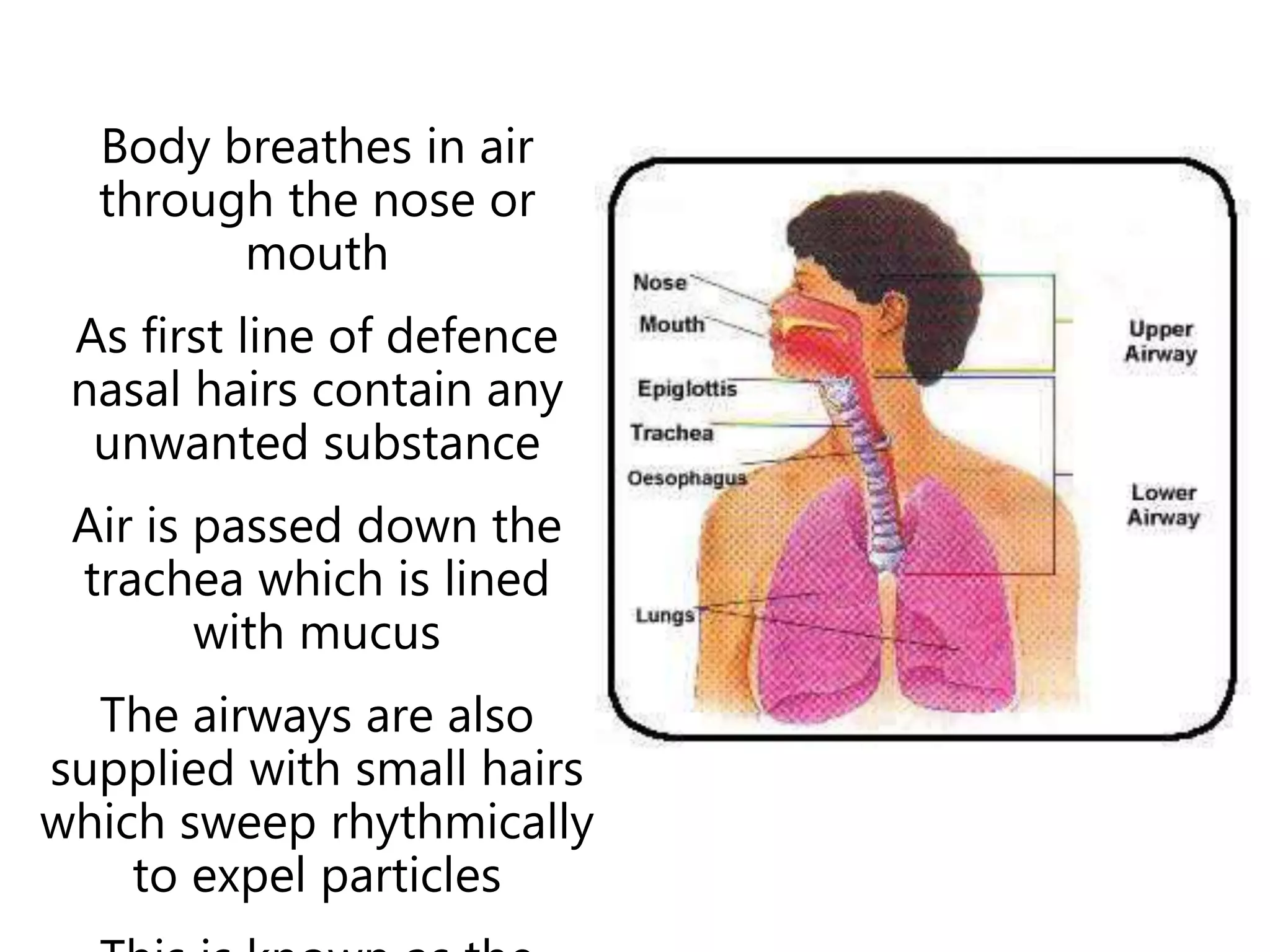
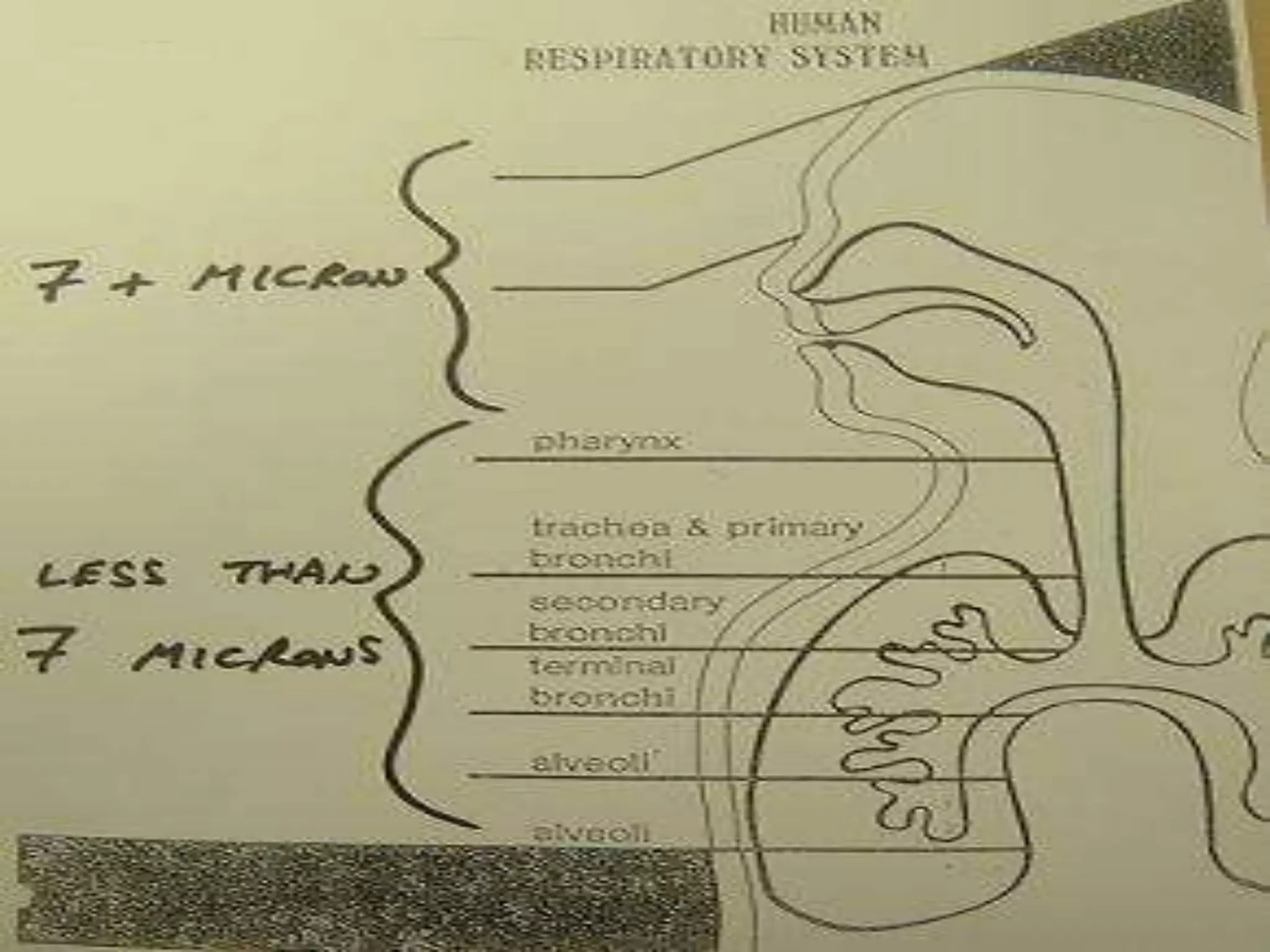
The document provides an overview of COSHH (Control of Substances Hazardous to Health) regulations, which require employers to assess and control exposure to hazardous substances. It outlines the key objectives of COSHH training to understand labeling/safety requirements and how to comply with regulations. It then details what constitutes a hazardous substance, employers' duties to assess risks and implement controls, and the steps involved in a full COSHH assessment.















![COSHH
2002
Skin, Eye irritants; unclassified. [A
Rated] Least Hazardous
Harmful on single exposure. [B
Rated]
Toxic, Corrosive. [C Rated]
Very toxic to reproduction [D Rated]
Asthma, Cancer, Genetic damage [E
Rated] Most Hazardous
L
TO
M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coshh-awareness-training-wecompress-230827075406-8935e658/75/COSHH-AWARENESS-TRAINING-wecompress-com_-ppt-16-2048.jpg)