This document discusses hot work permits, including:
1) A hot work permit is required for welding, cutting, grinding, or other activities that produce heat, flames, or sparks to prevent fires.
2) The permit process involves preparing the work area, inspecting it, conducting the hot work, and providing a fire watch after.
3) A permit must be completed before hot work, posted, and the work area made safe by removing combustibles, covering openings, and ensuring fire extinguishers are available.
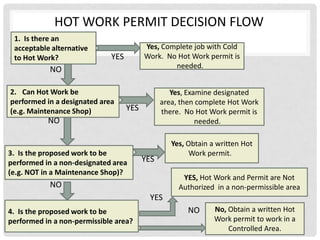
4) Alternatives to hot work like cold work should be considered, and hot work should be done in designated areas if possible to avoid needing a permit.