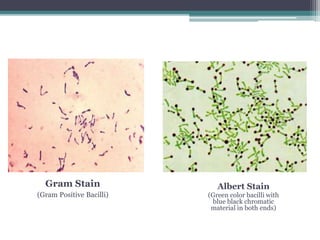
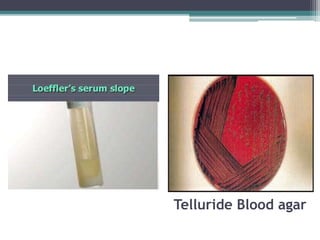
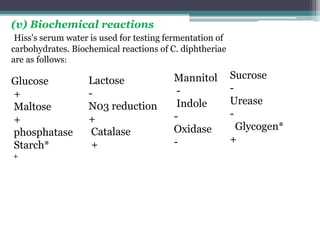
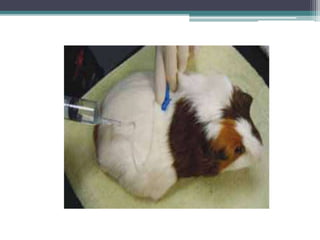
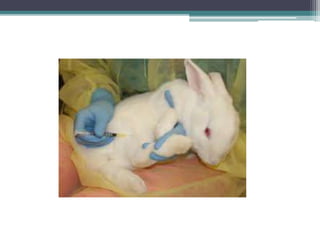
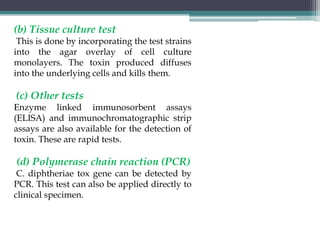
Corynebacterium, particularly C. diphtheriae, is a gram-positive bacillus responsible for diphtheria in humans. Laboratory diagnosis involves immediate treatment, specimen collection from lesions, and various staining and culture techniques, including gram staining, tellurite blood agar, and biochemical tests. Virulence tests, both in vivo and in vitro, demonstrate the production of exotoxin and include methods like the Elek's gel precipitation test and PCR for detecting the tox gene.