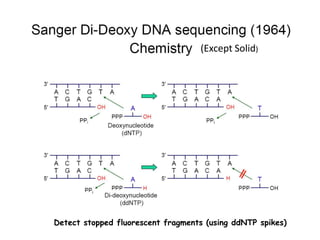
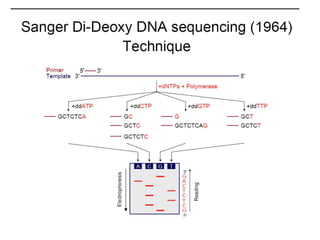
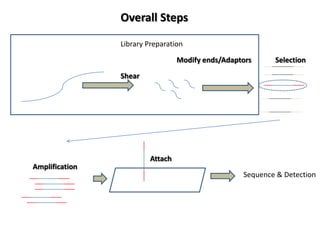
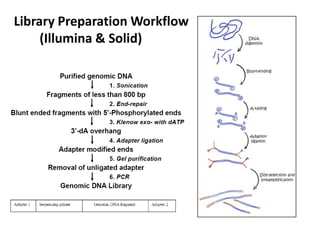
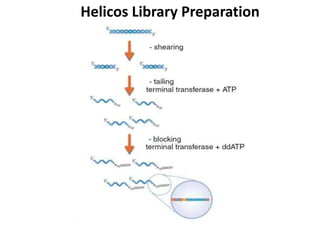
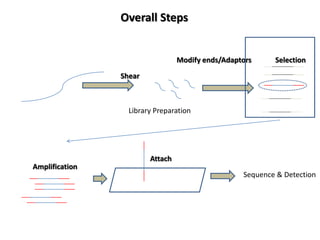
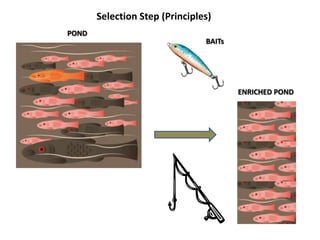
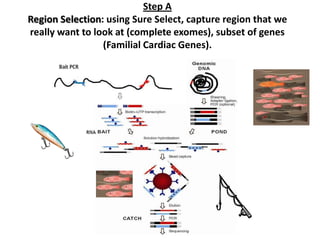
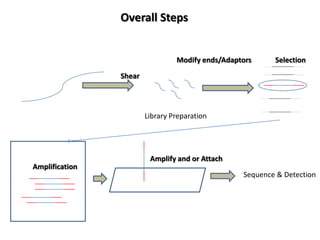
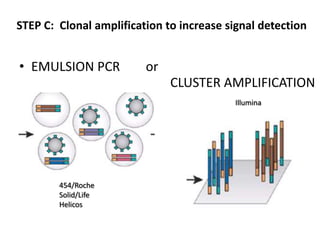
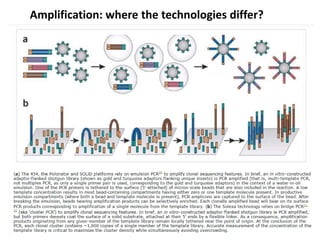
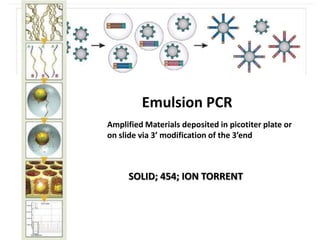
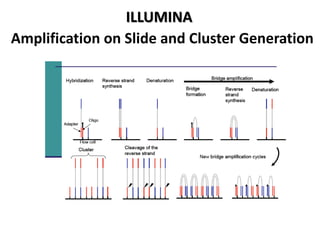
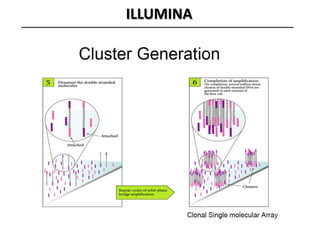
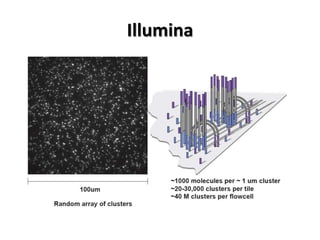
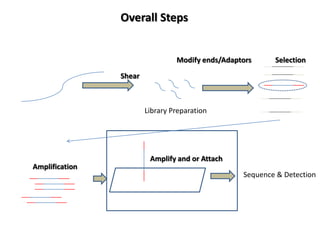
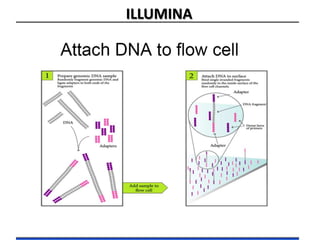
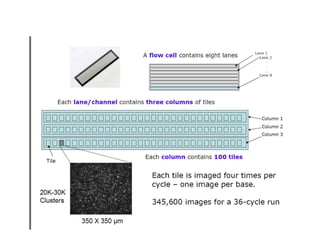
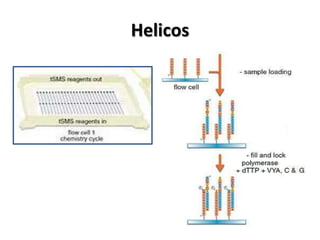
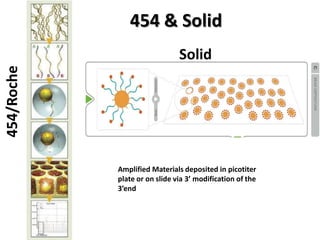
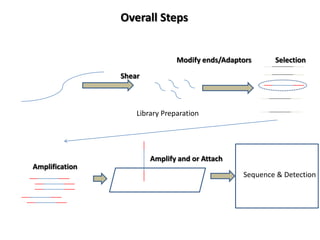
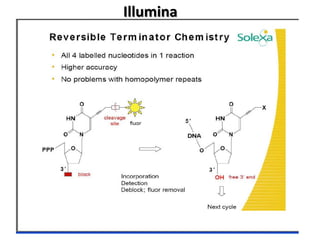
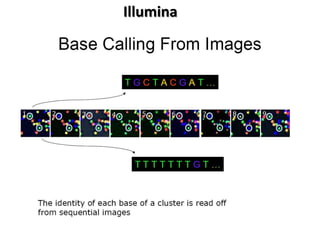
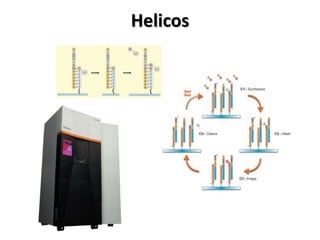
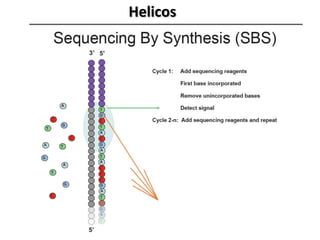
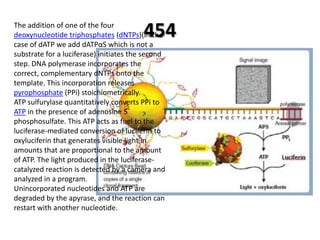
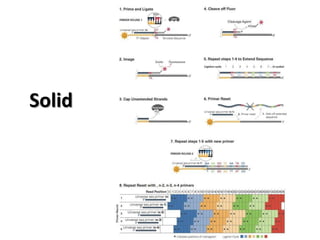
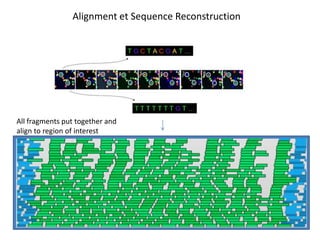
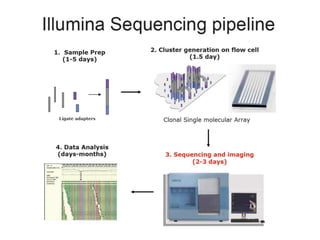
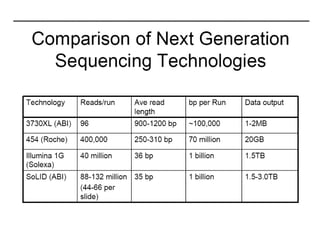
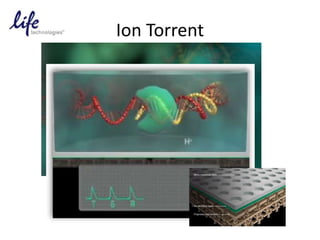
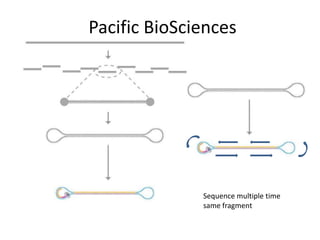
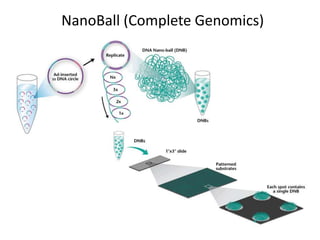
The document discusses past, current, and next generation sequencing technologies. It provides an overview of Illumina, Helicos, and Solid sequencing, describing the common steps of library preparation, amplification, attachment to a flow cell matrix, sequencing and detection, and interpretation. The technologies differ in their approaches to amplification and detection of incorporated nucleotides. Next generation sequencing is now current generation sequencing and is having an impact in life sciences and clinical diagnostics.