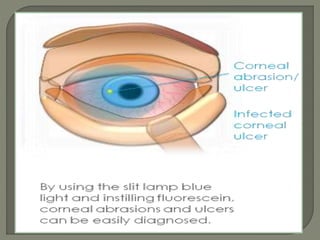
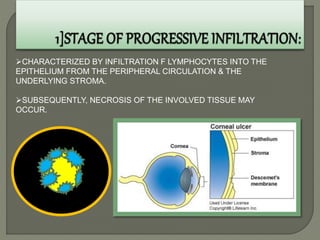
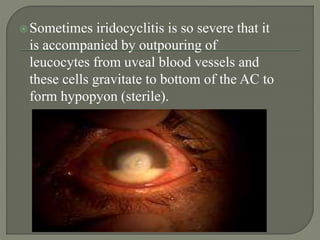
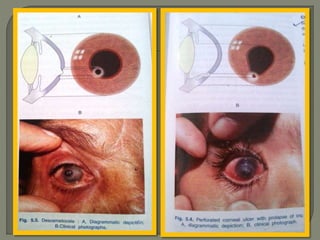
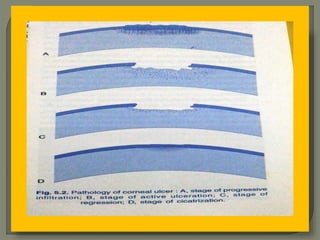
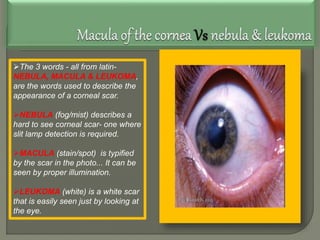
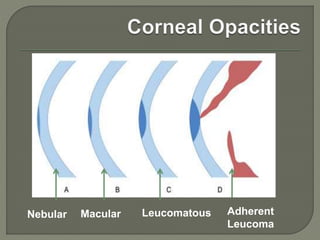
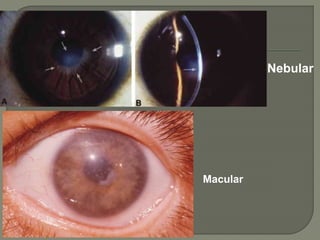
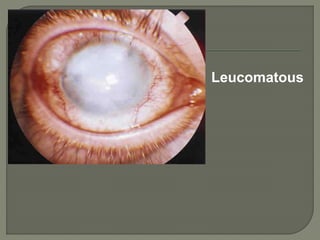
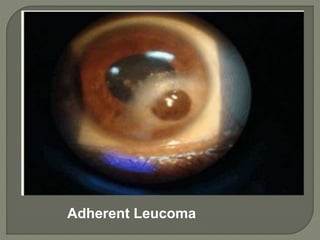
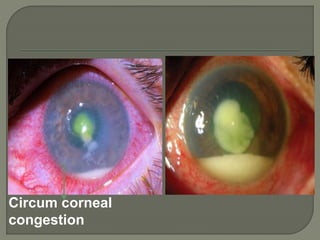
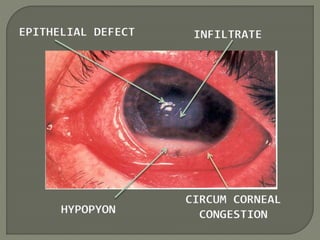
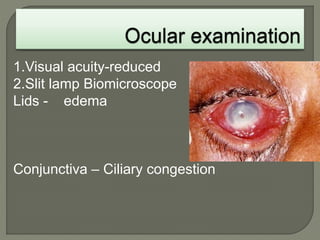
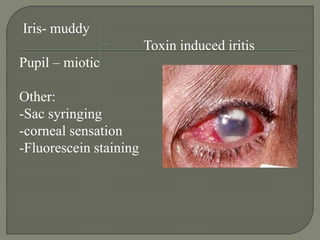
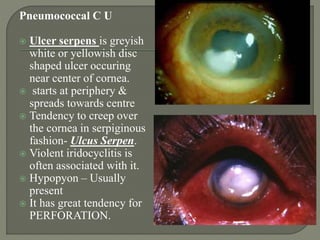
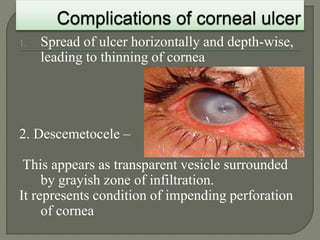
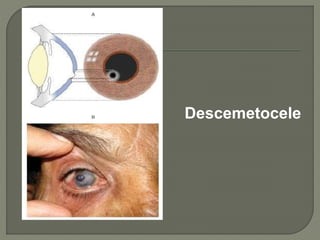
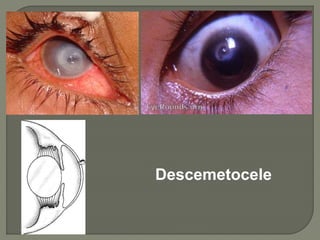
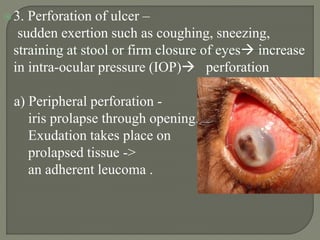
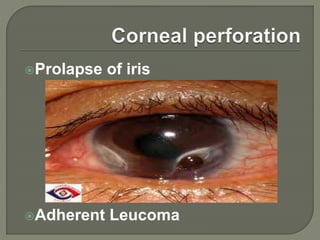
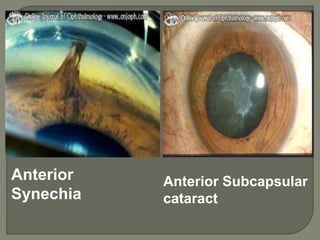
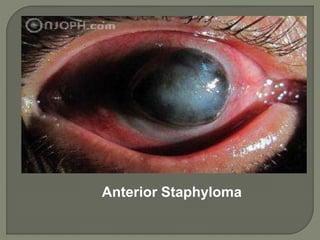
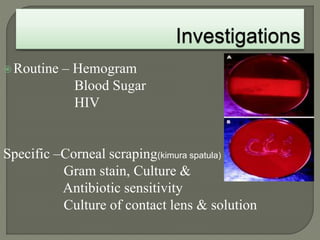
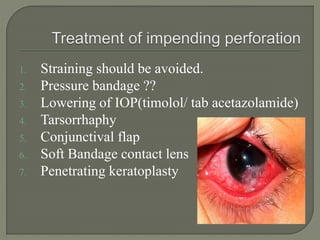
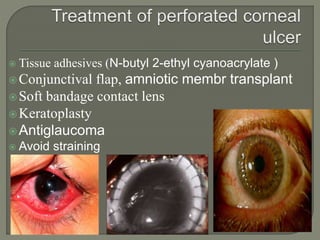
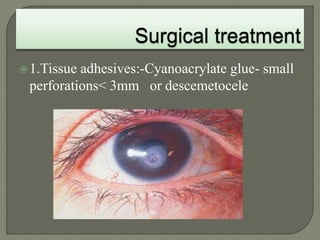
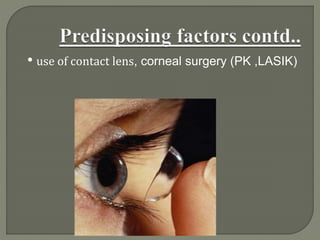
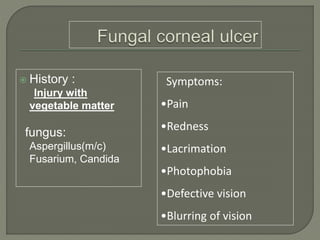
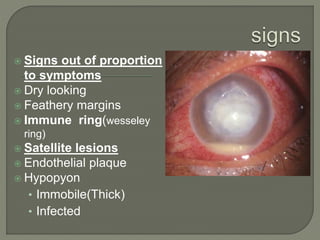
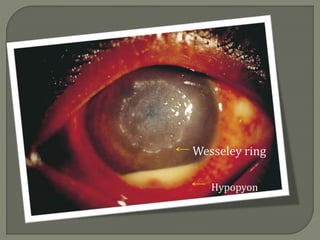
Dr. Atul Kumar Anand provides a detailed overview of corneal ulcers. He defines a corneal ulcer as a discontinuation of the normal corneal epithelial surface associated with necrosis and inflammation. Corneal ulcers are characterized by edema and cellular infiltration. The cornea is exposed and prone to infection, though protected by tear film defenses. Ulcers develop when these defenses are compromised, preexisting ocular diseases are present, or immunity is low. Treatment involves identifying predisposing factors, controlling infection with antibiotics, and addressing complications to promote healing and prevent worsening of the ulcer.



![THERE ARE 2 MAJOR FACTORS IN THE PRODUCTION OF A
PURULENT ULCER:-
A]CORNEAL
EPITHELIAL
DAMAGE
B]INFECTION
OF THE
ERODED AREA
HOWEVER, THE FOLLOWING 3
ORGANISMS CAN INVADE AN
INTACT CORNEAL EPITHELIUM AND
PRODUCE ULCERATION....
Neisseria gonorrhoea
N.meingitidis
Corynebacterium diptheriae.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cornealulcer-230502121028-2459e8ba/85/Corneal-Ulcer-pptx-5-320.jpg)