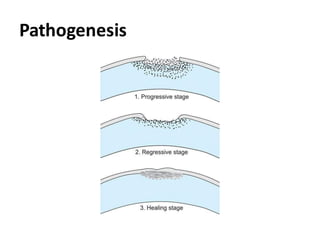
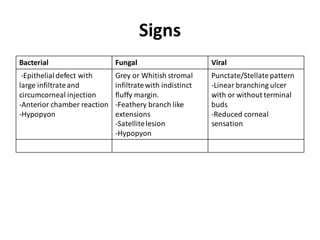
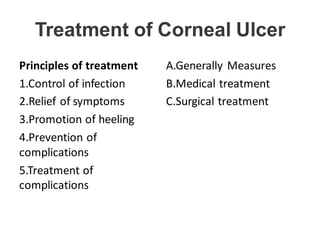
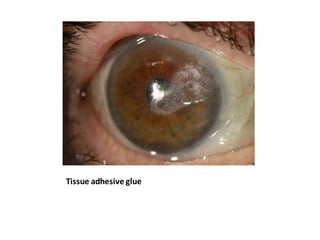
This document provides an overview of corneal ulcers, including their definition, classification, predisposing factors, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, investigations, management, and complications. Corneal ulcers are defined as excavations of the corneal tissue associated with an epithelial defect, usually with infiltration and necrosis. They can be classified based on etiology (infective vs. non-infective), location, or layer of cornea involved. Common predisposing factors include contact lens wear, trauma, dry eye, and malnutrition. Treatment involves controlling infection, relieving symptoms, promoting healing, and preventing/treating complications through various medical and surgical approaches depending on the specific type and severity of the ulcer.