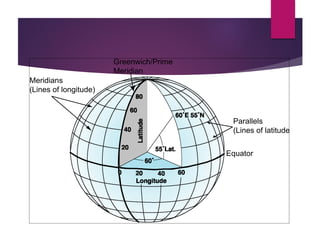
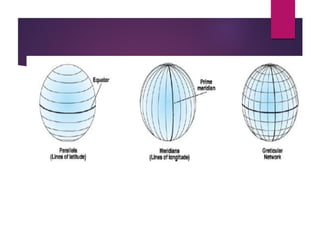
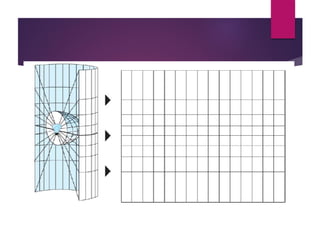
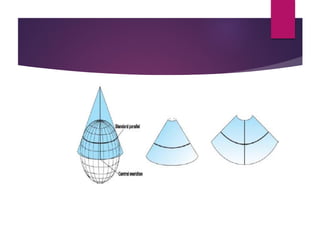
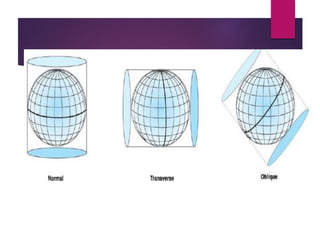
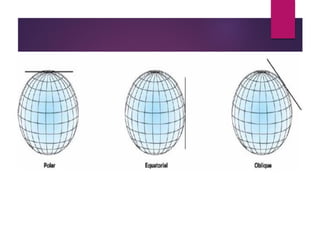
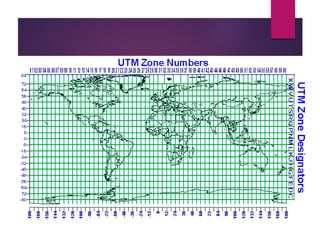
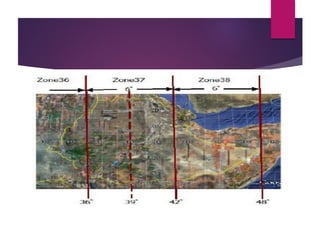
This document discusses coordinate systems and map projections. It defines projection as representing the curved Earth on a flat surface, which inevitably causes distortions. It describes geographic and projection coordinate systems, and how Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) divides the world into zones to allow for linear measurements. Datums define precise starting points for coordinate systems and projections.