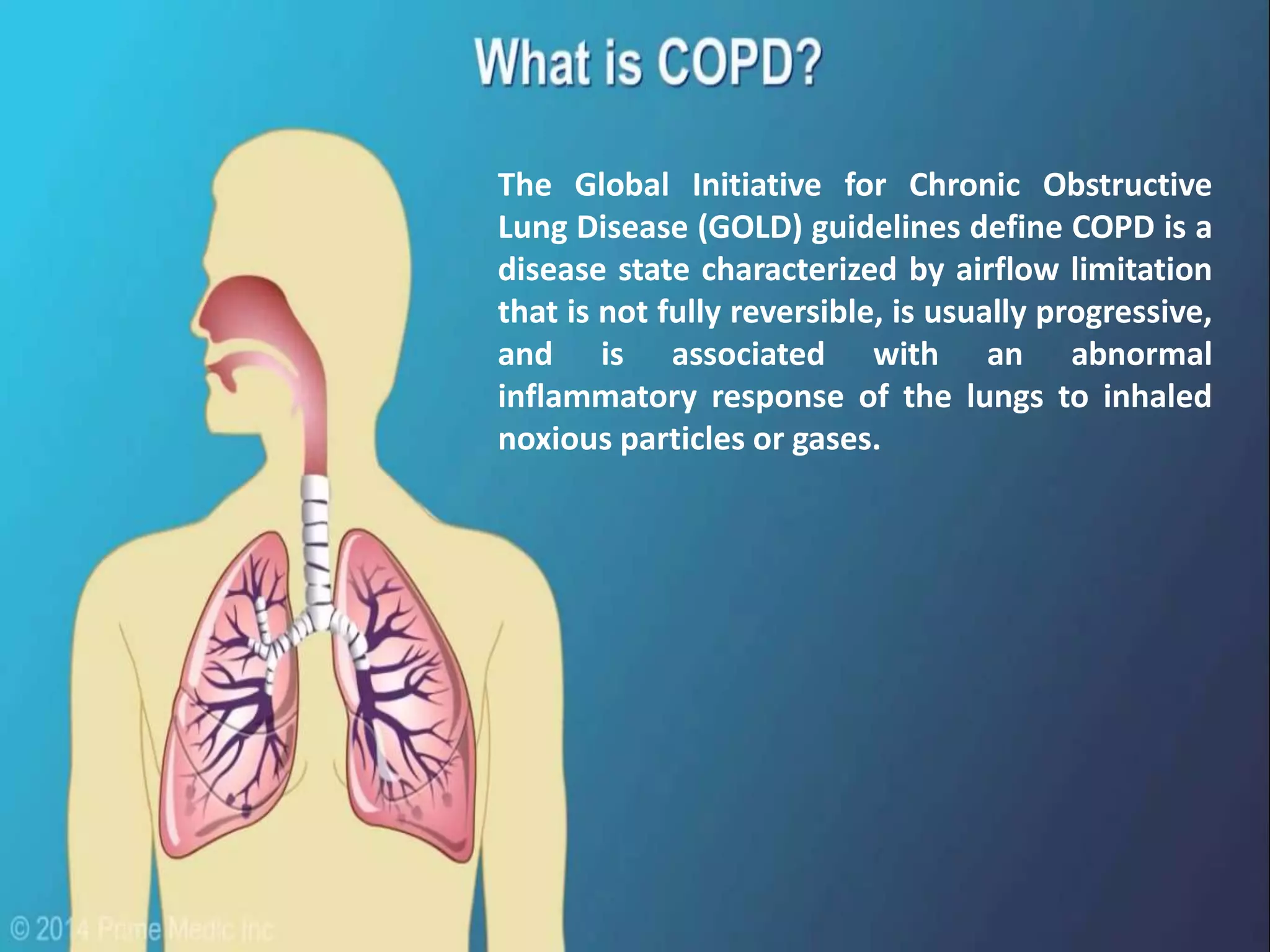
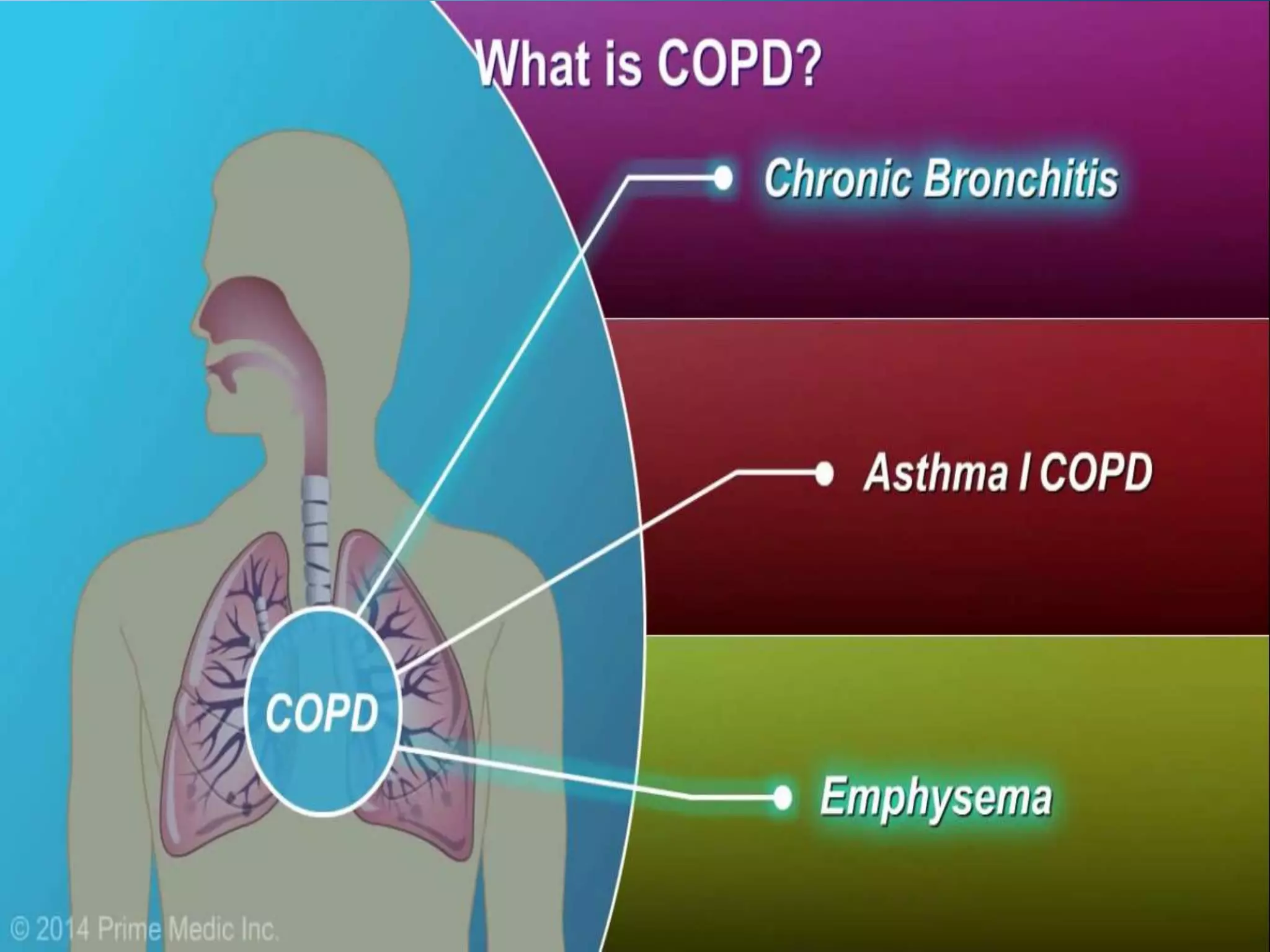
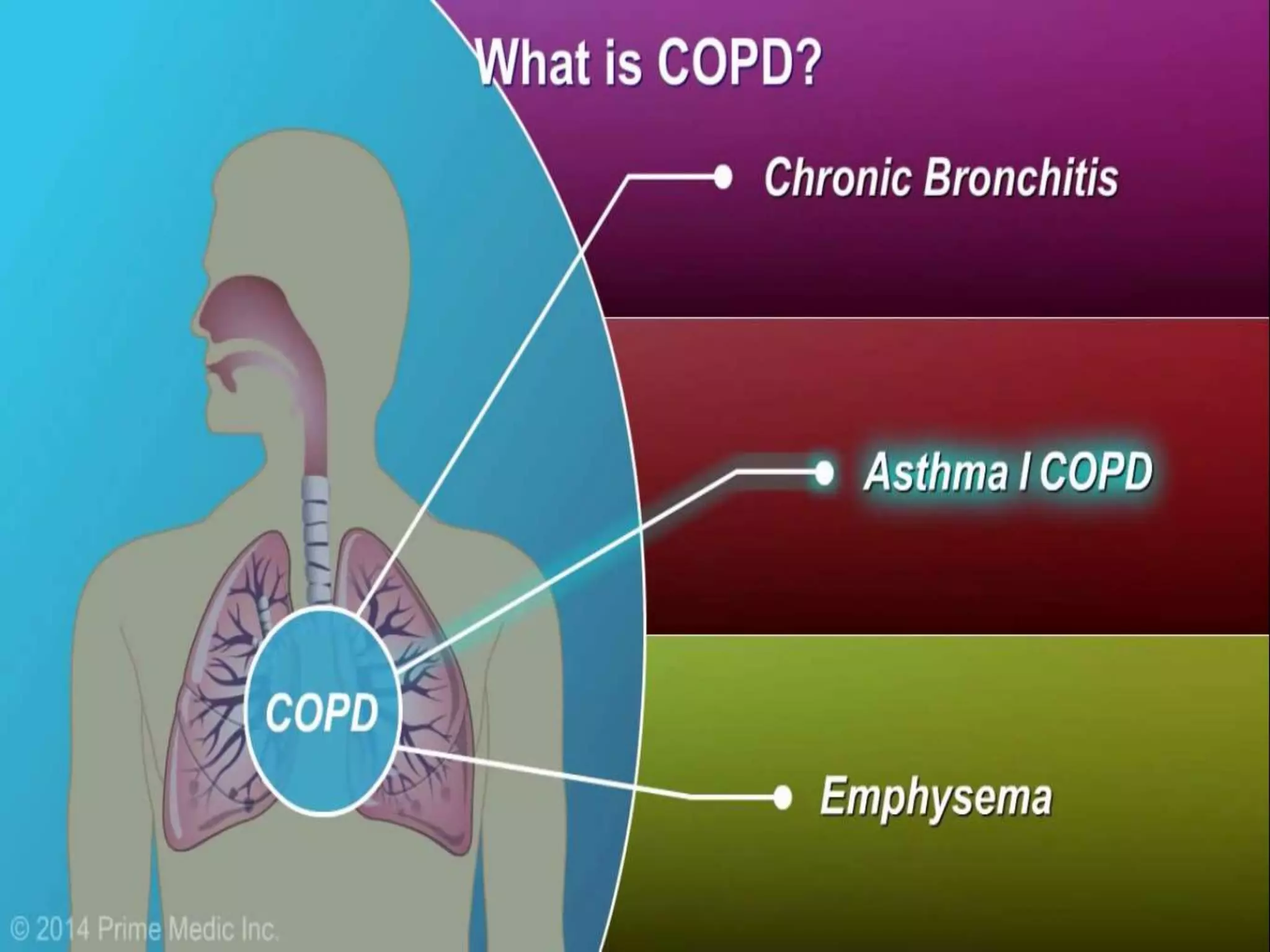
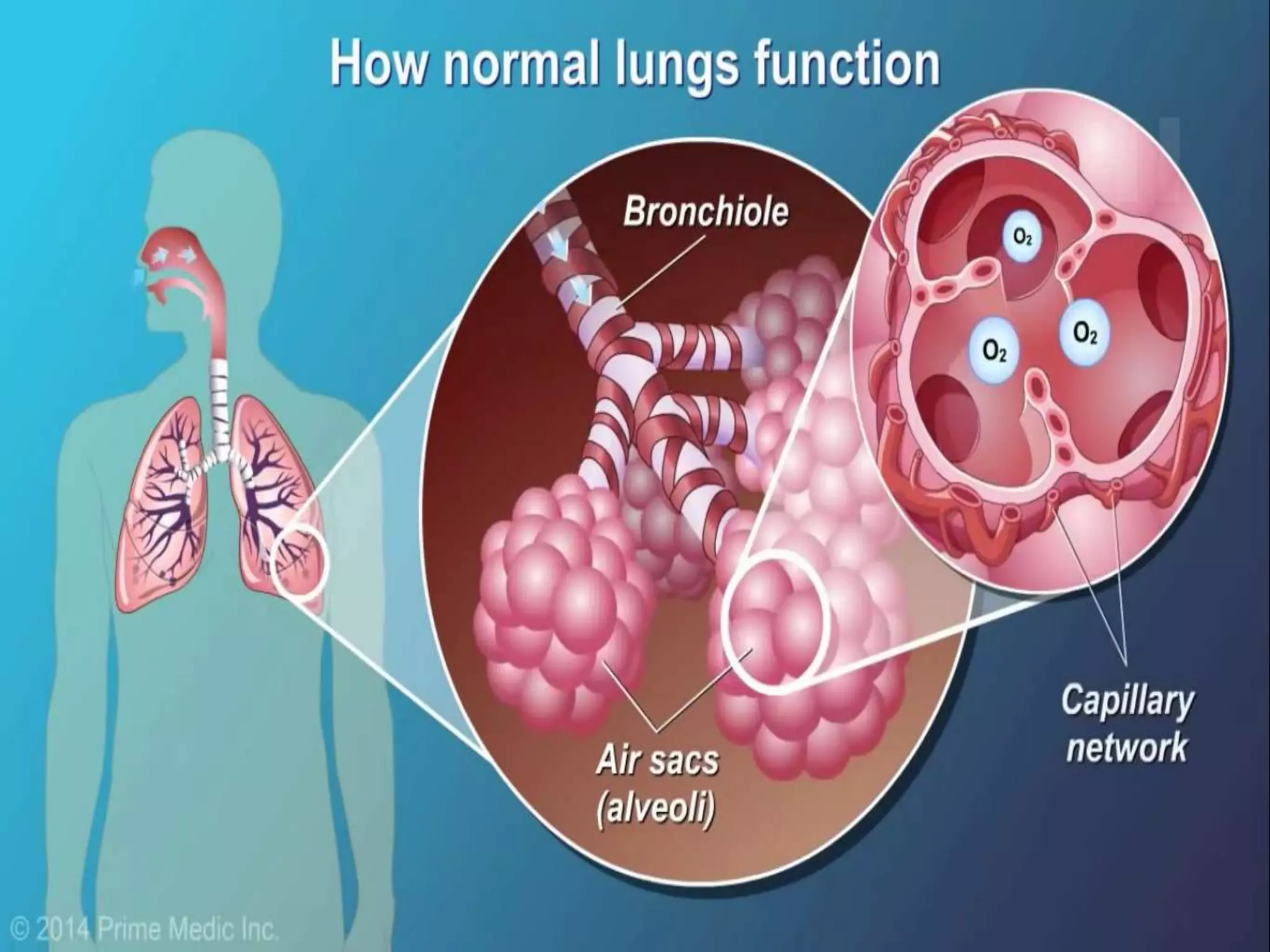
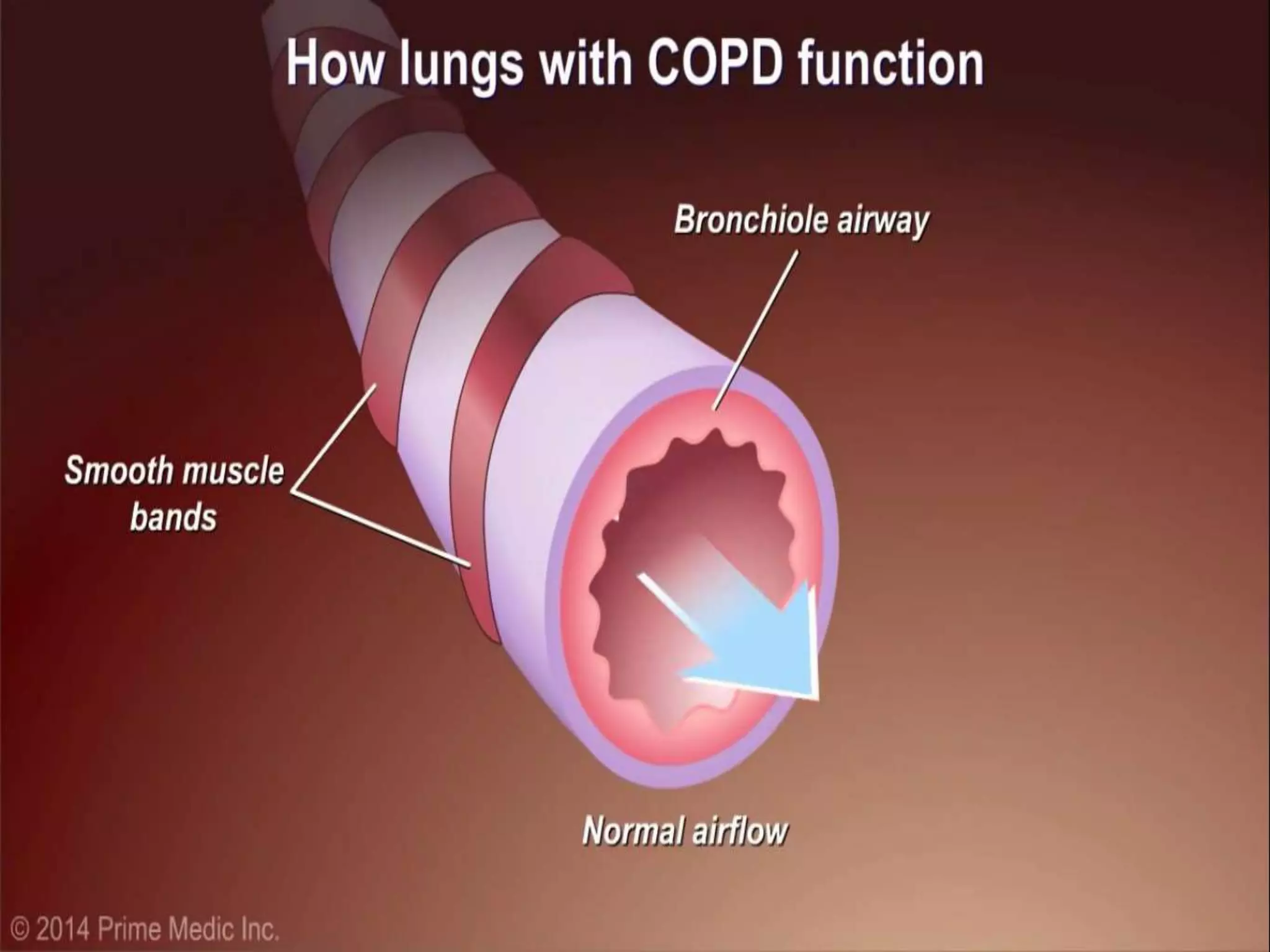
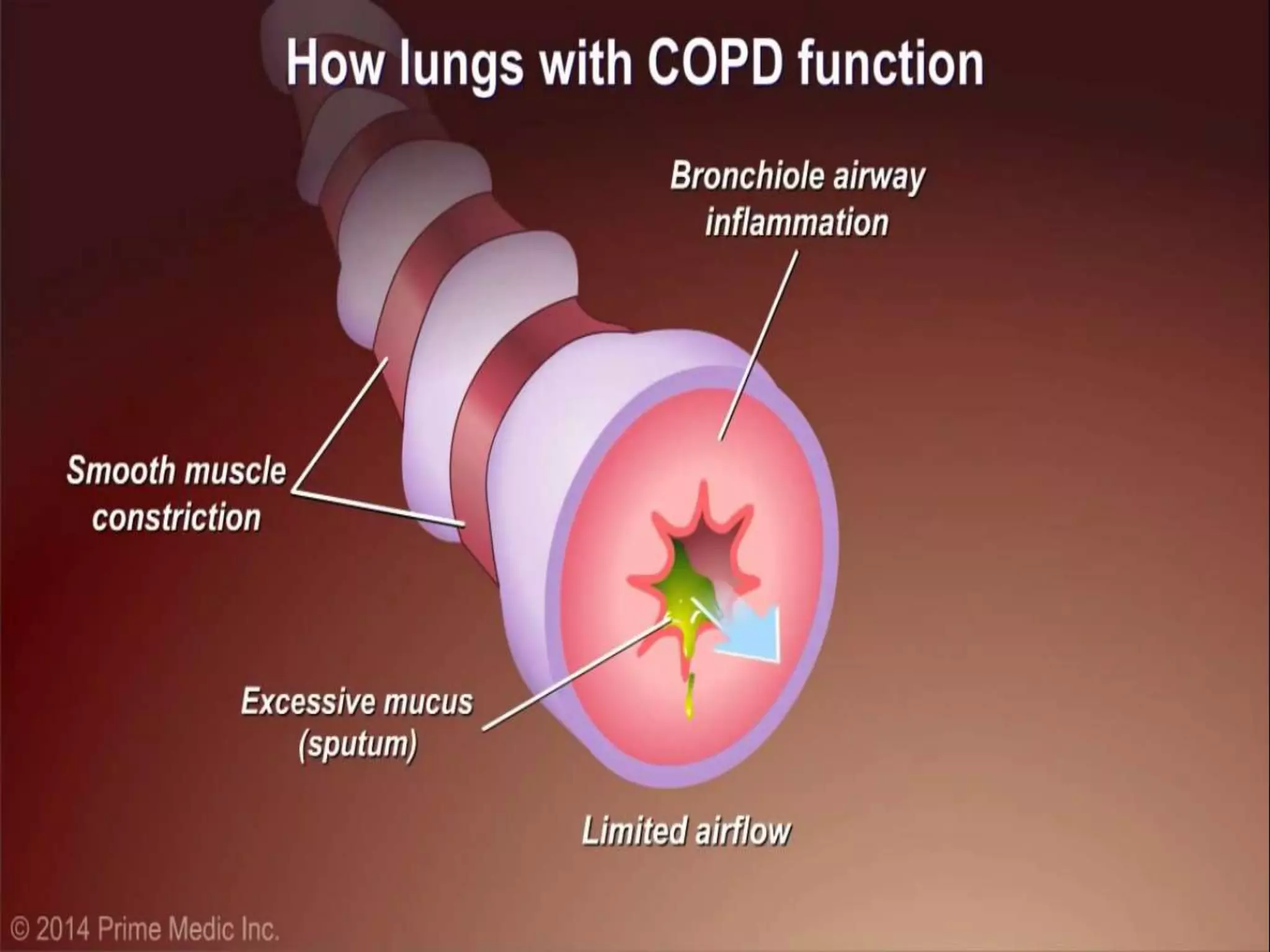
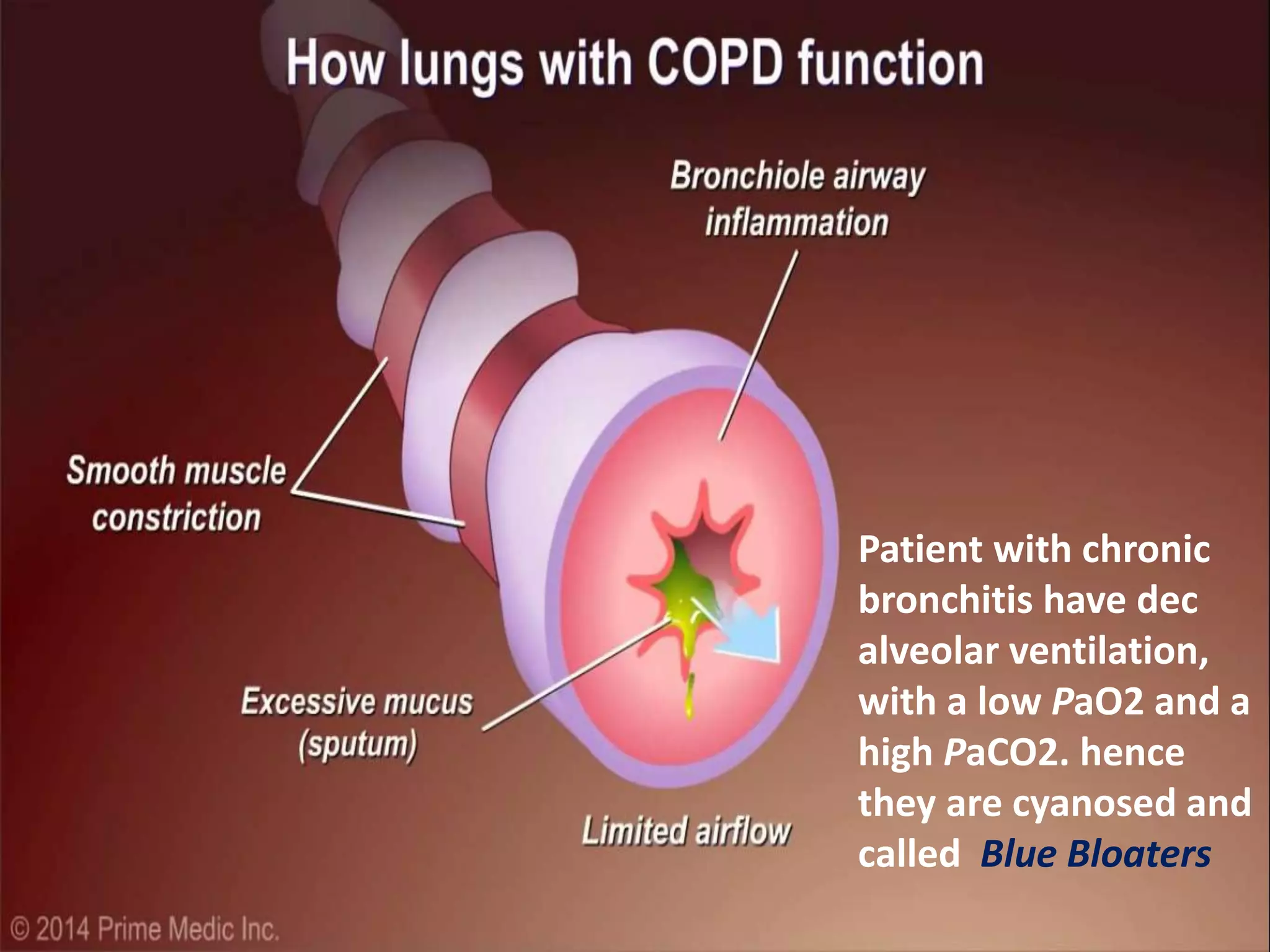
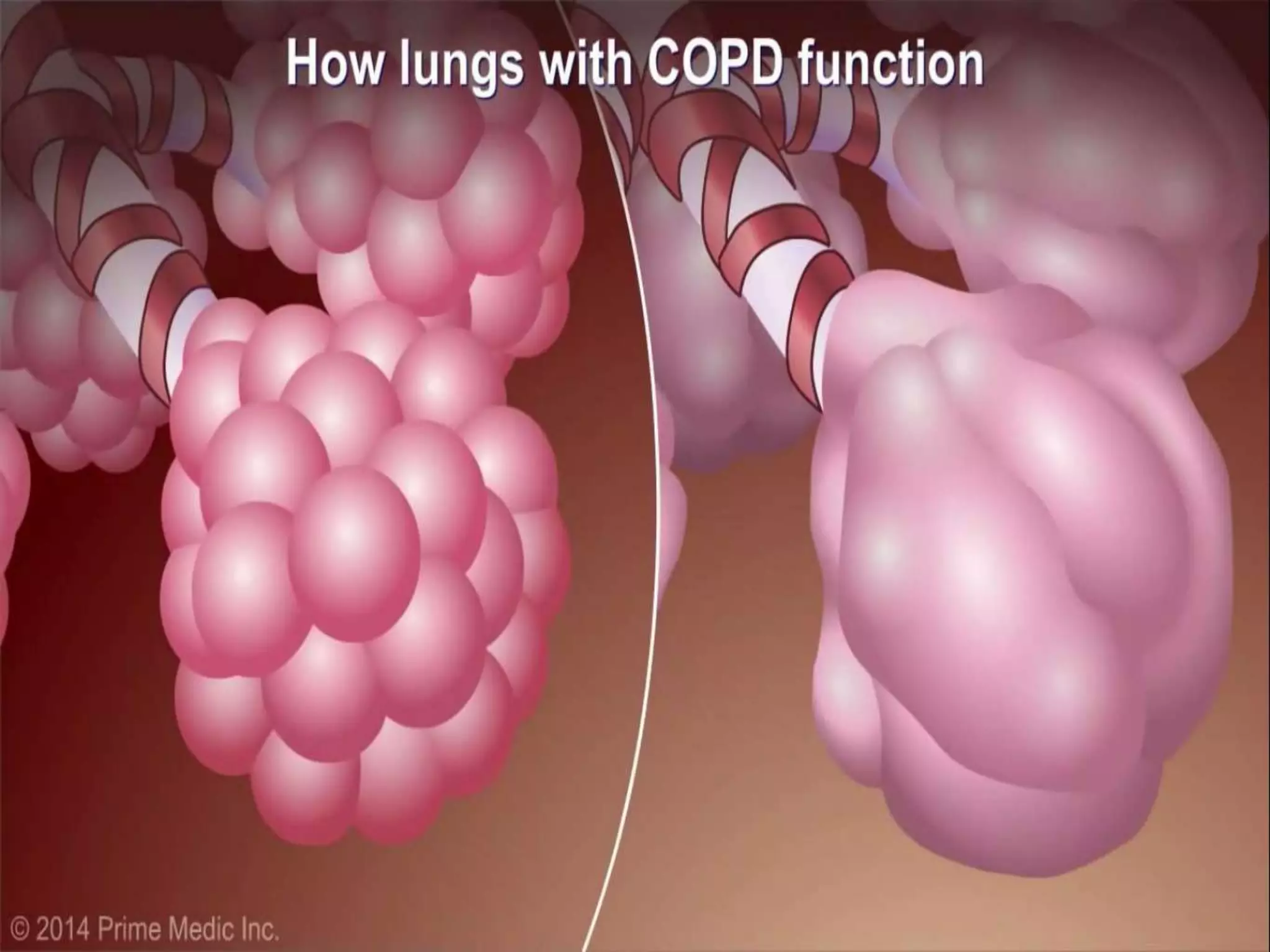
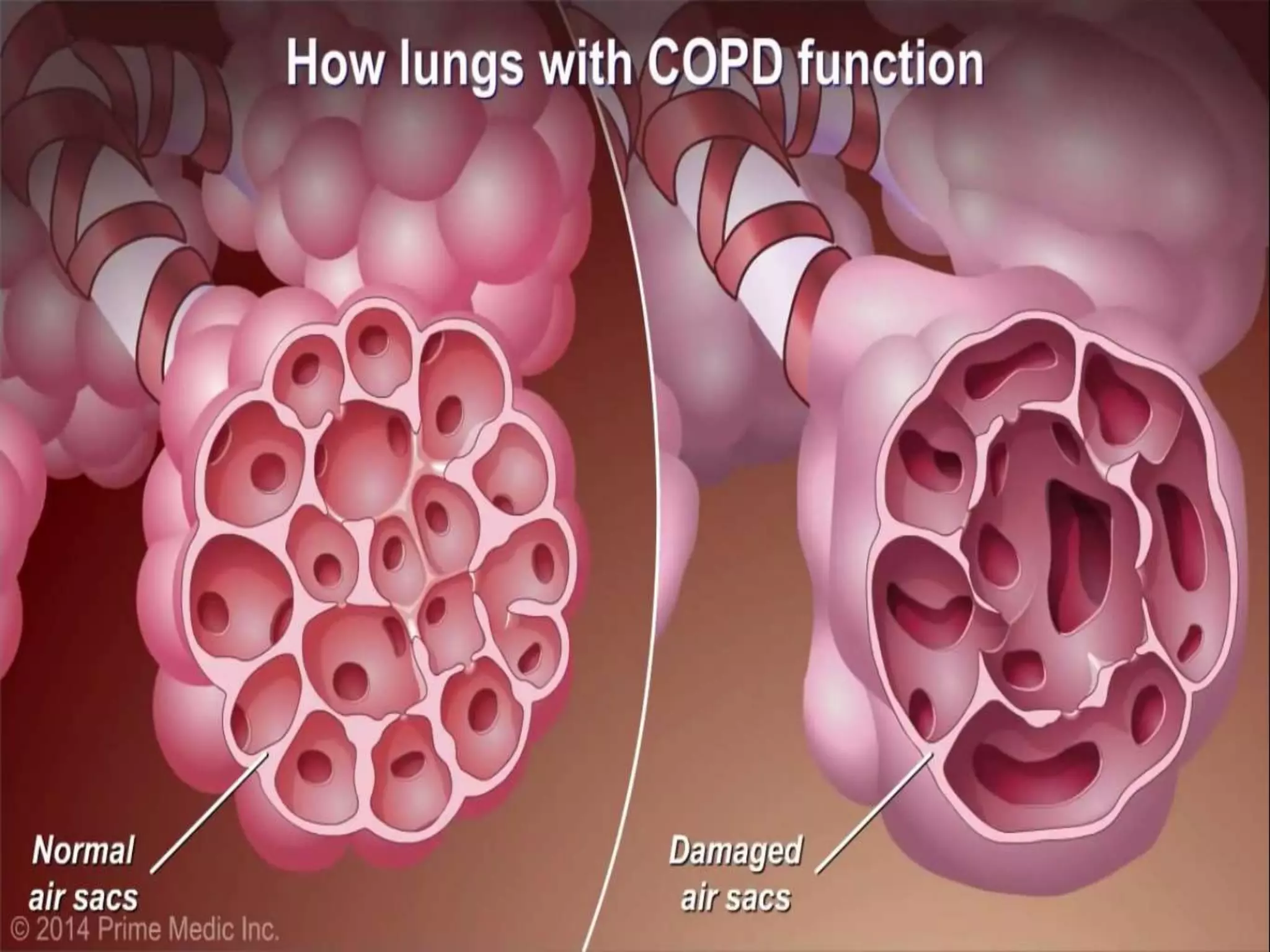
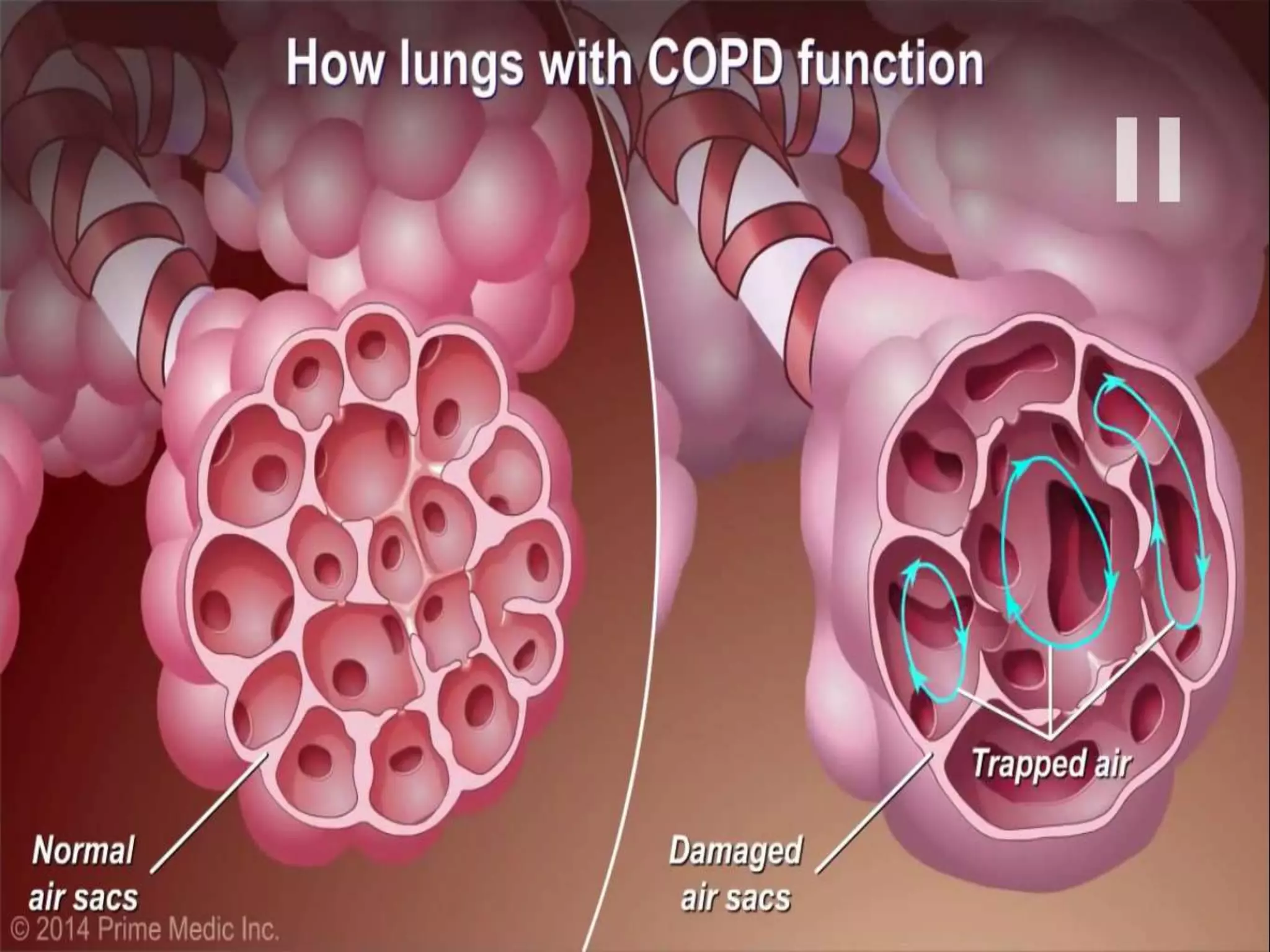
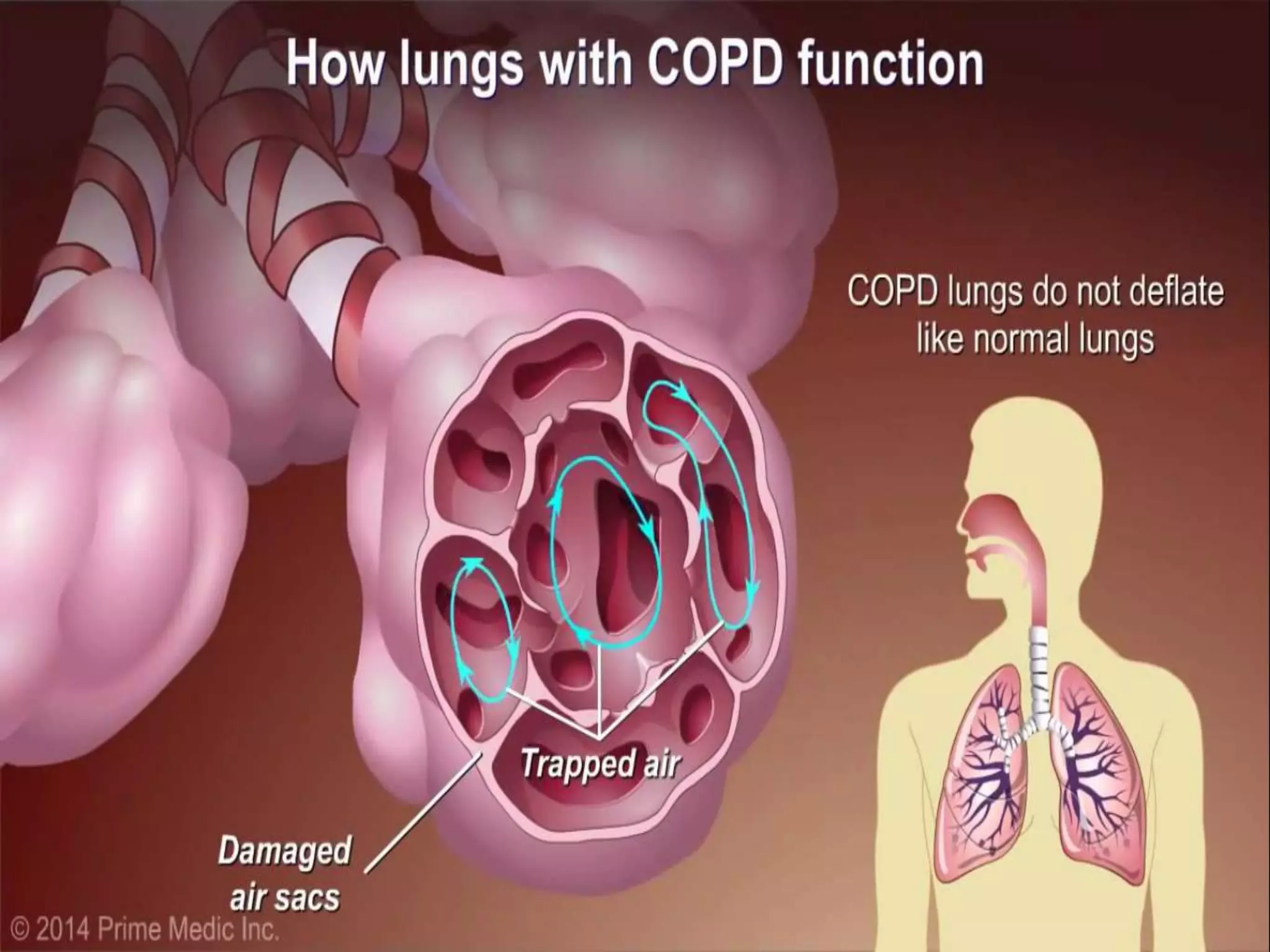
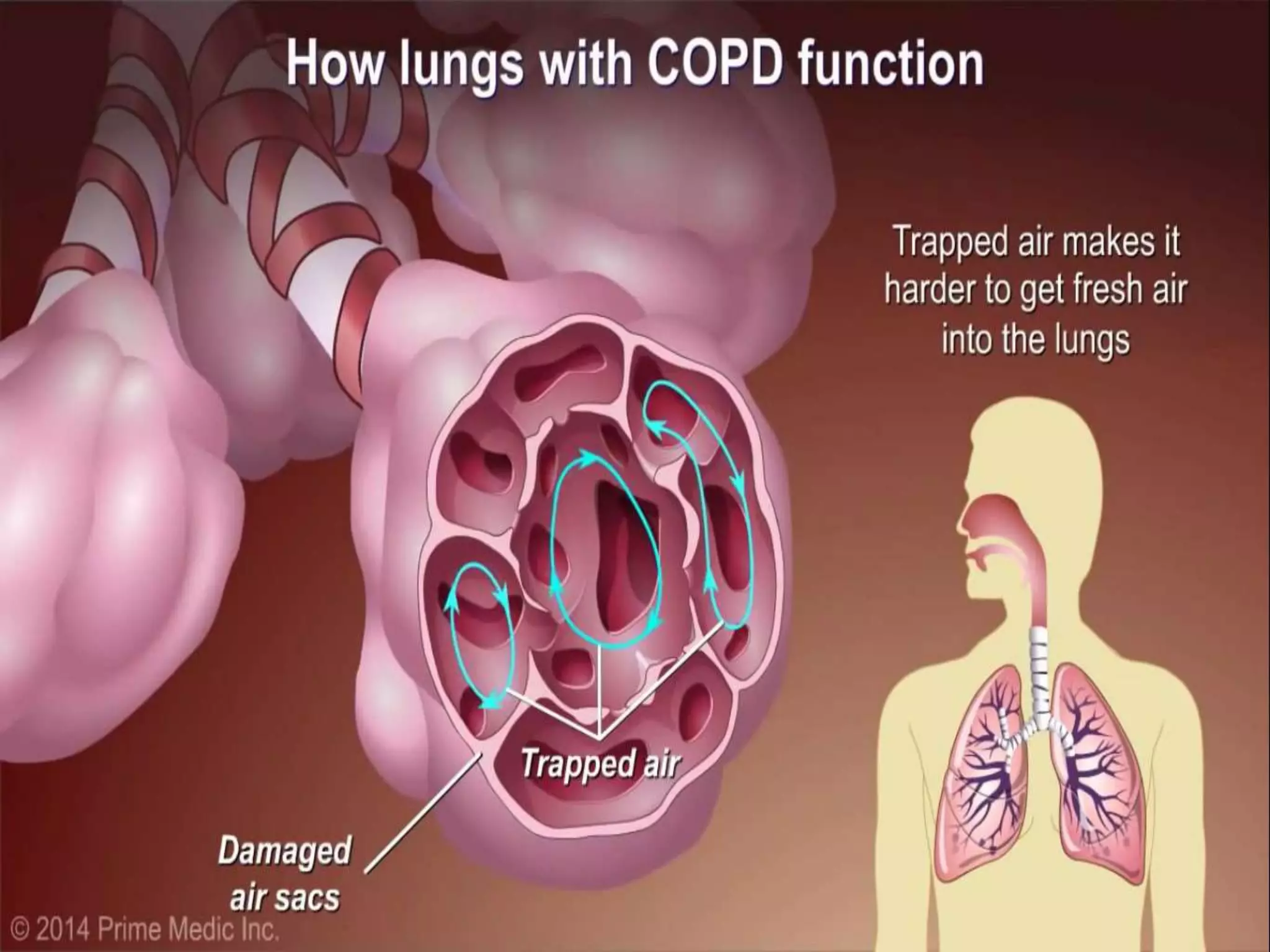
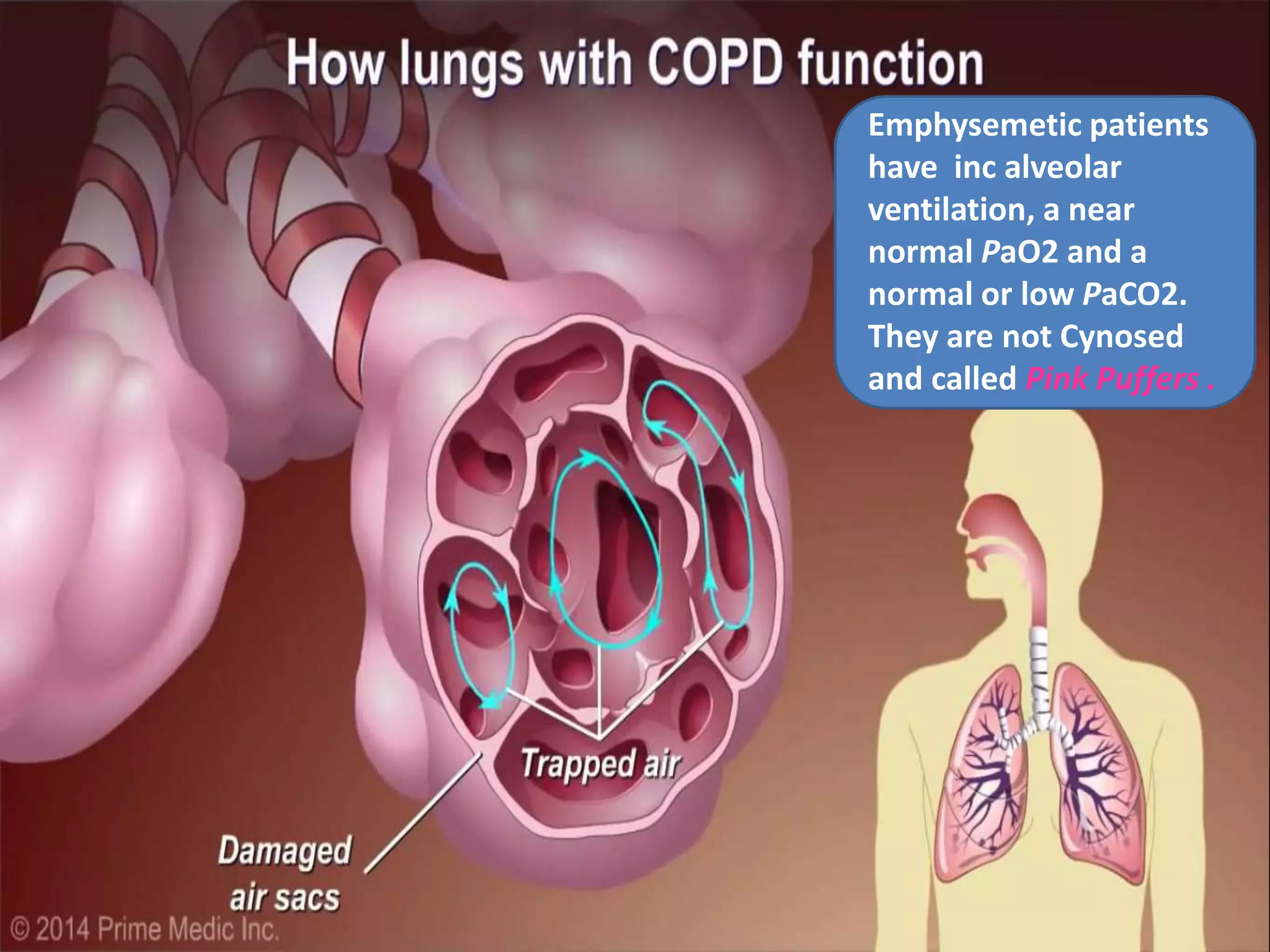
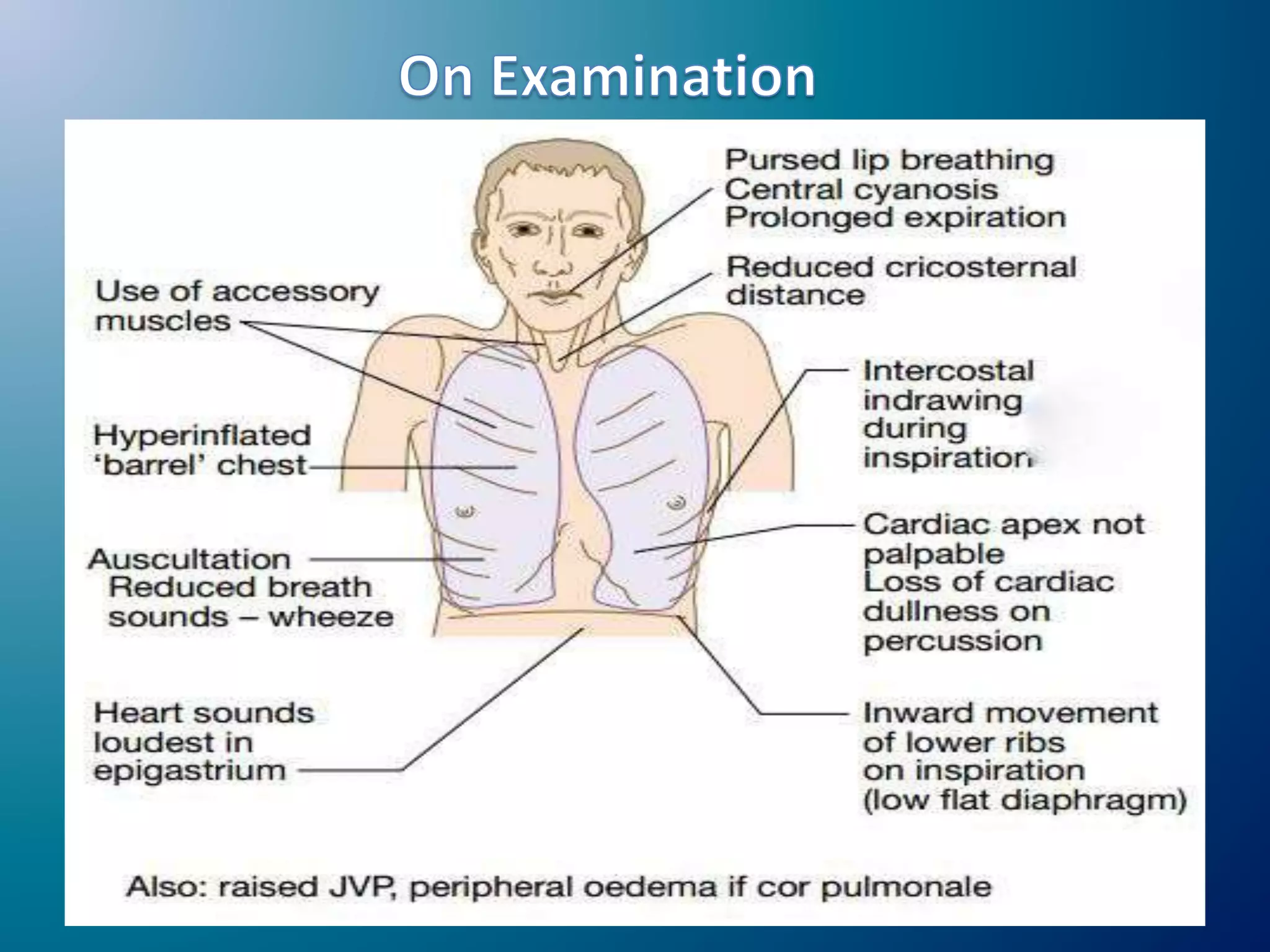
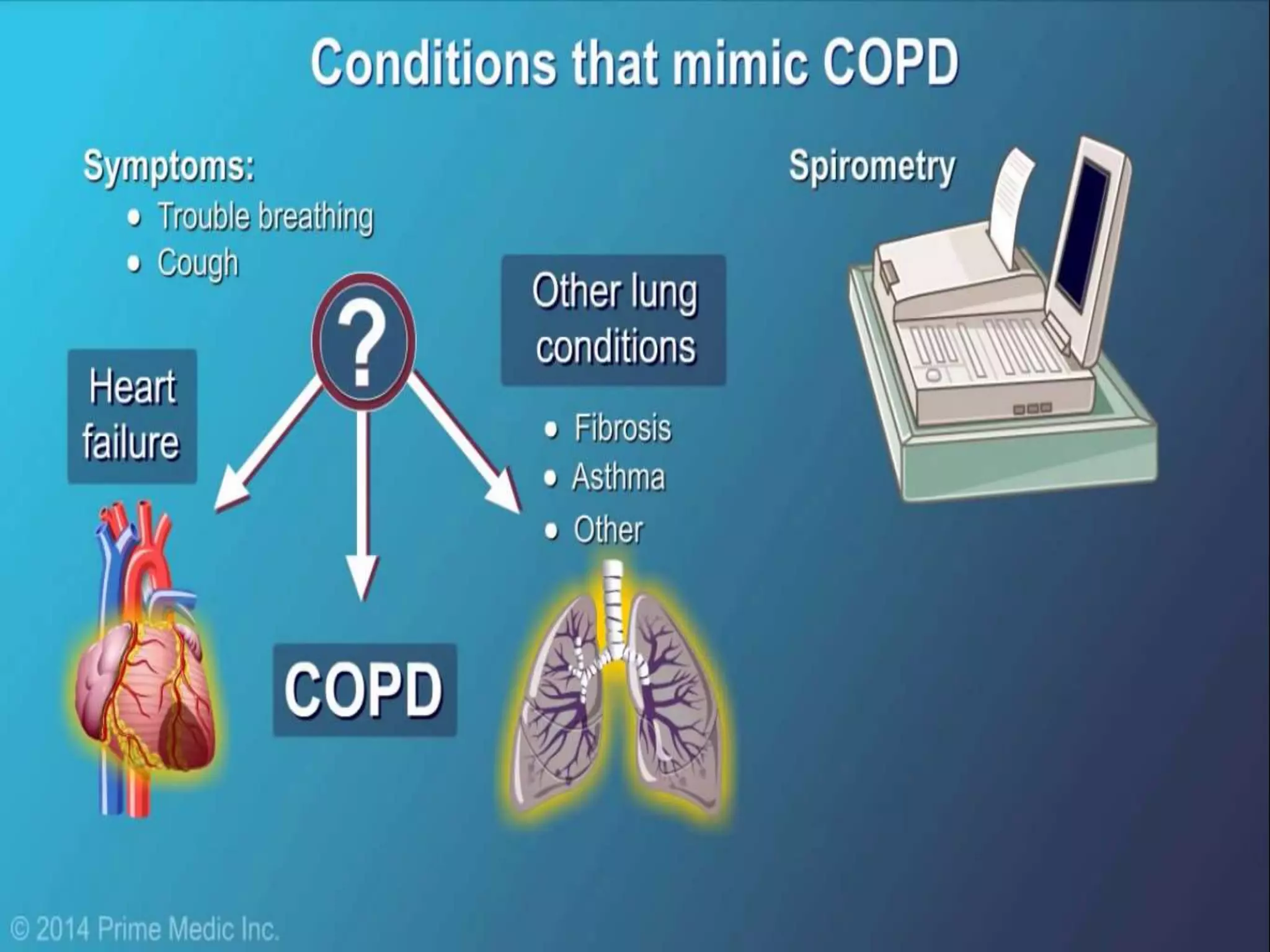
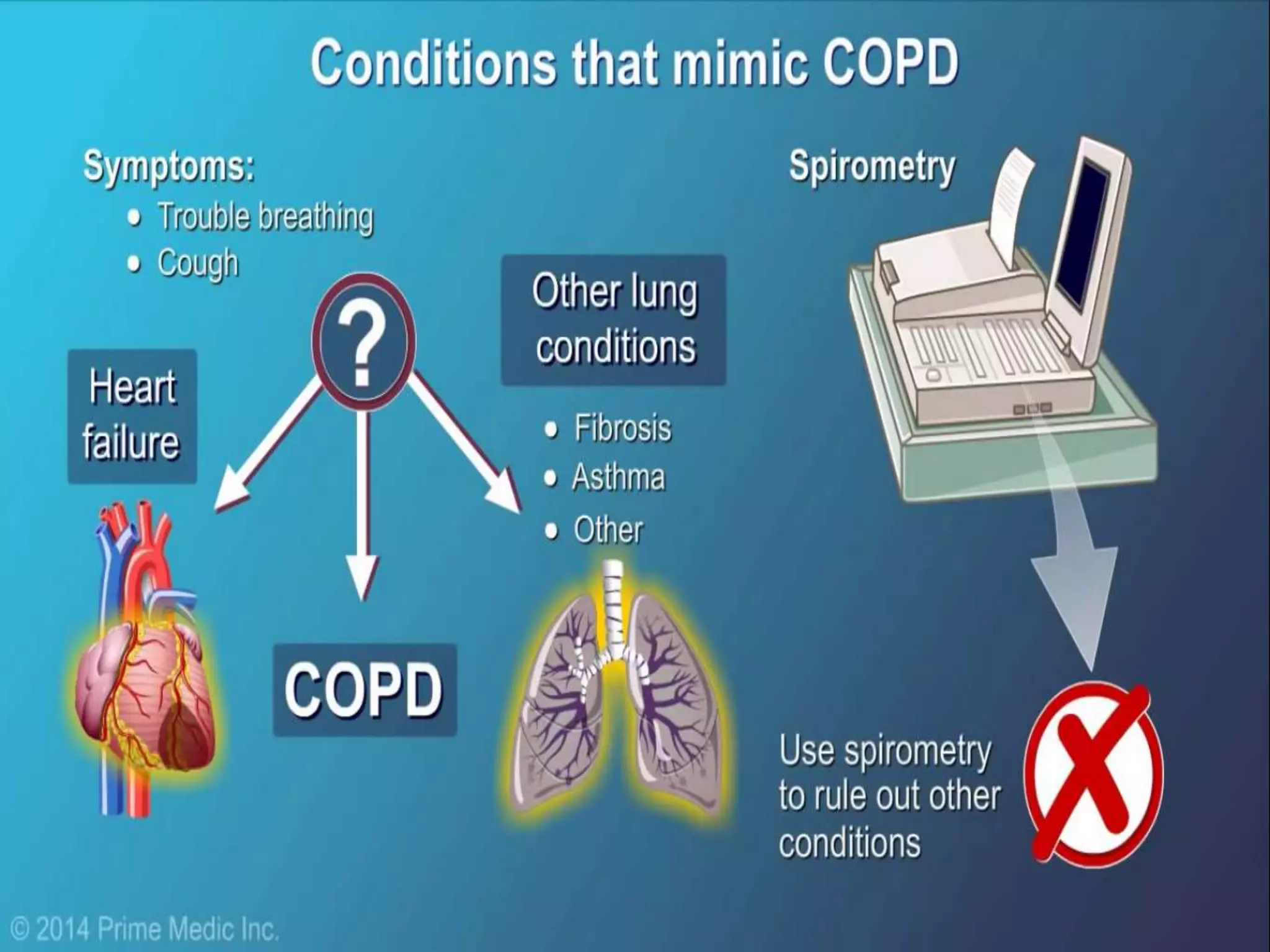
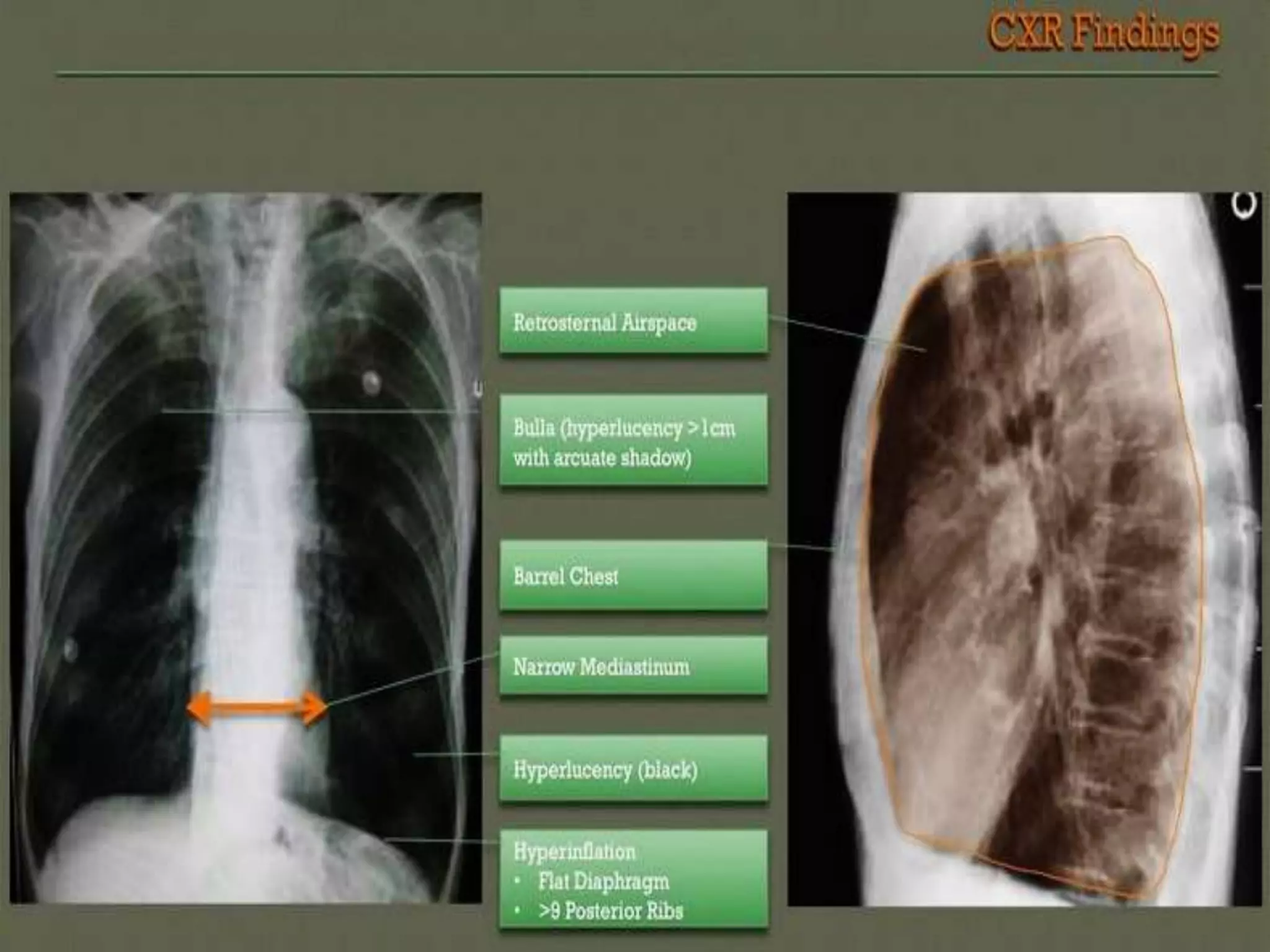
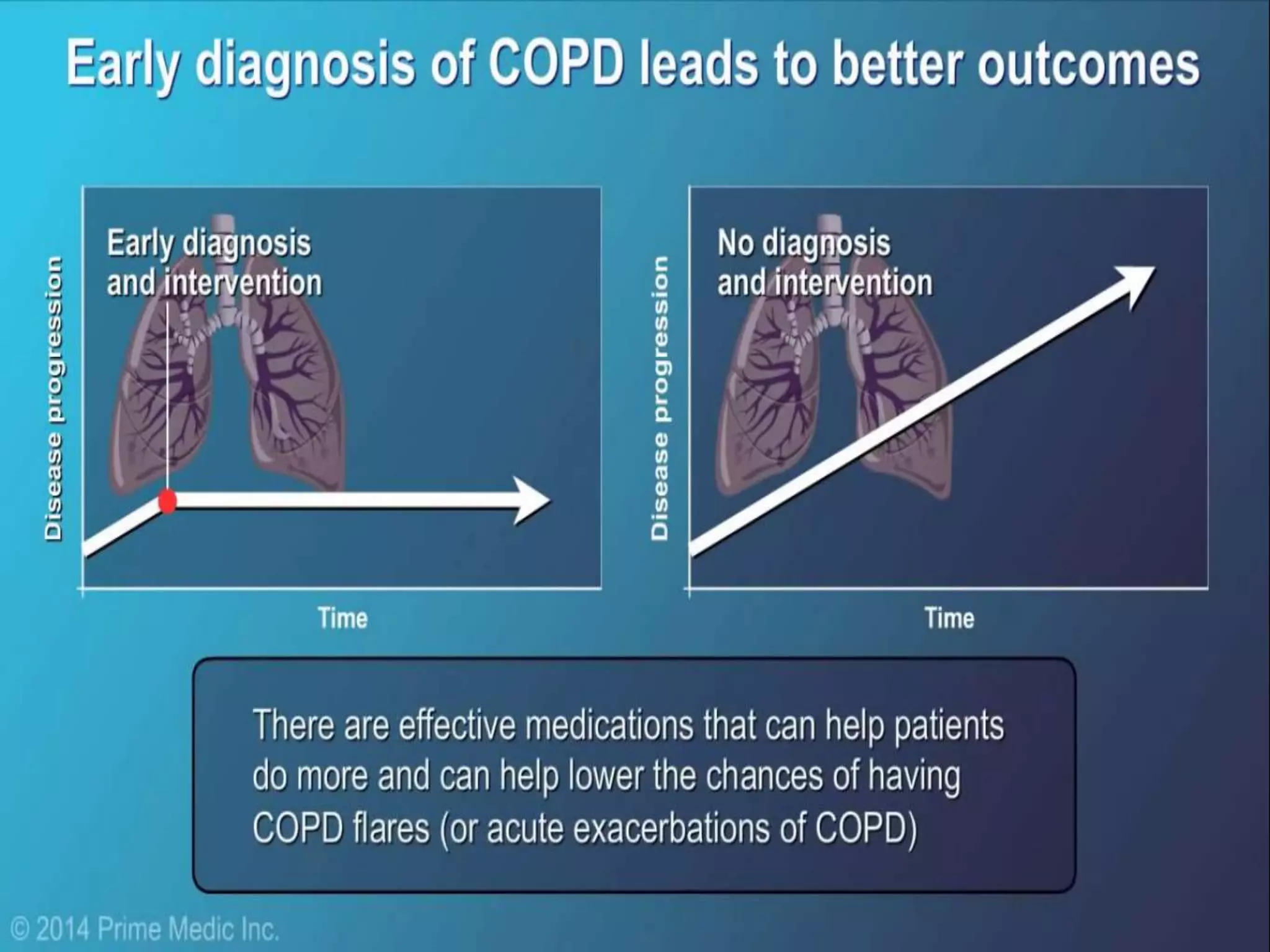
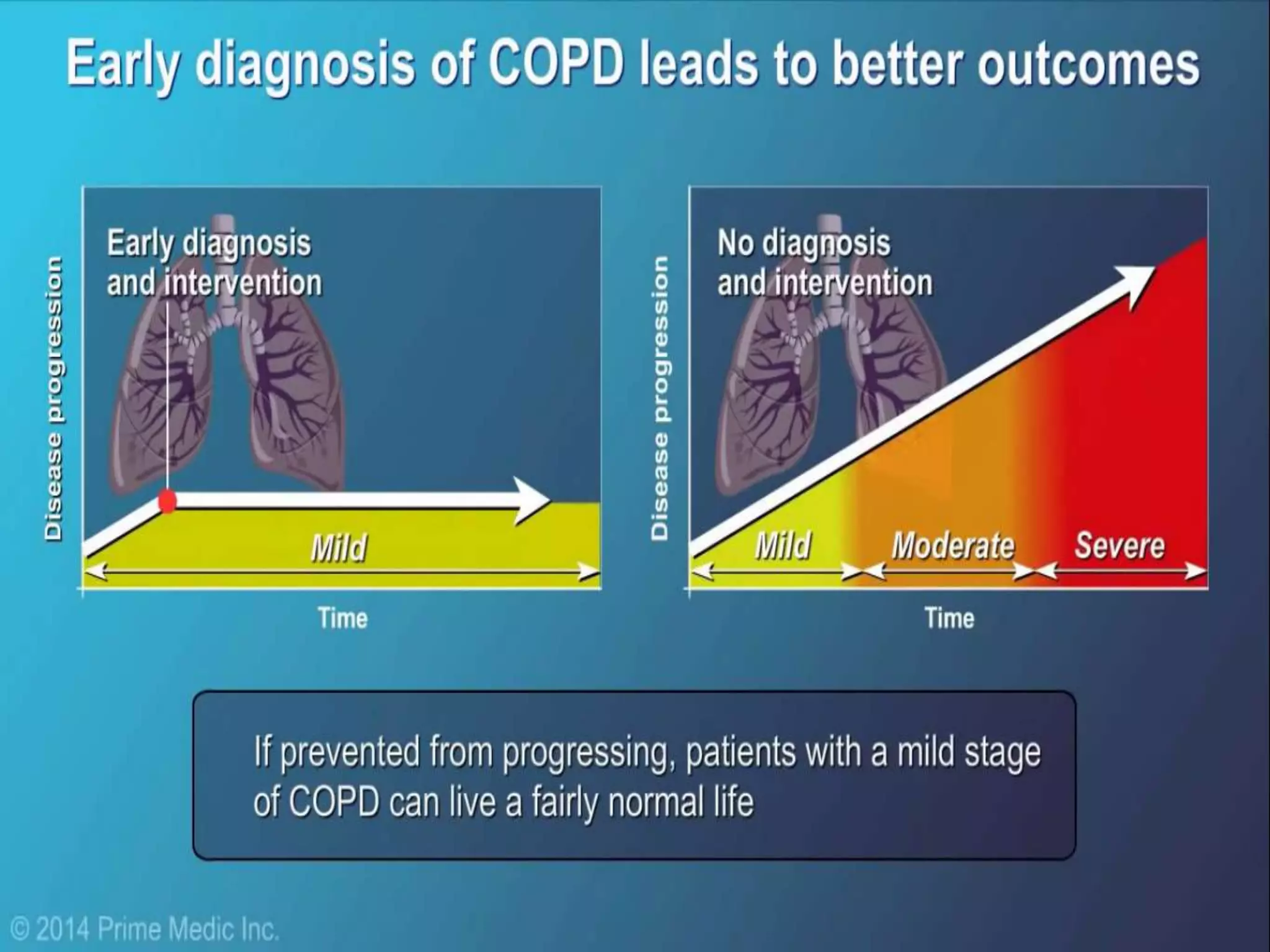
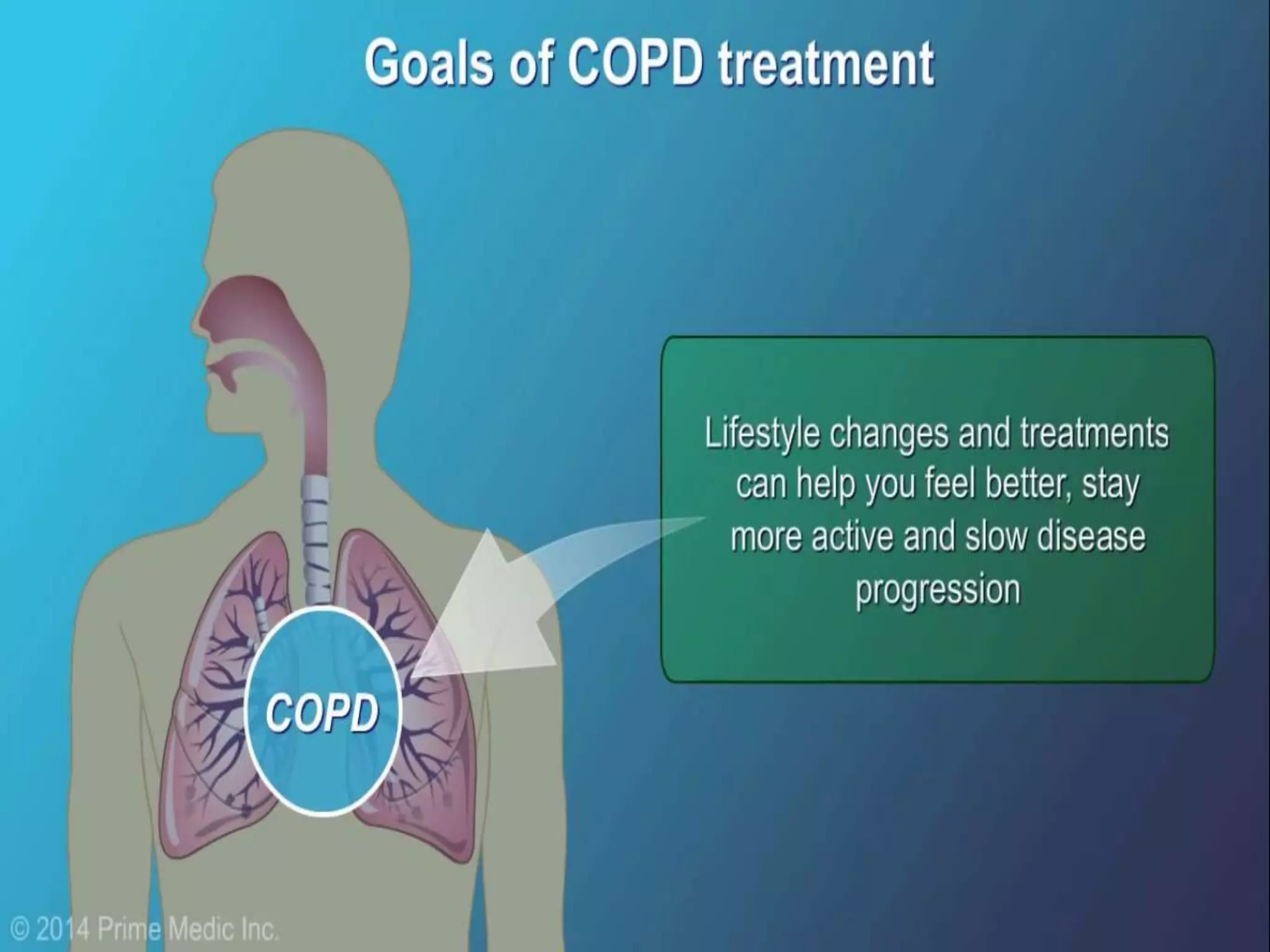
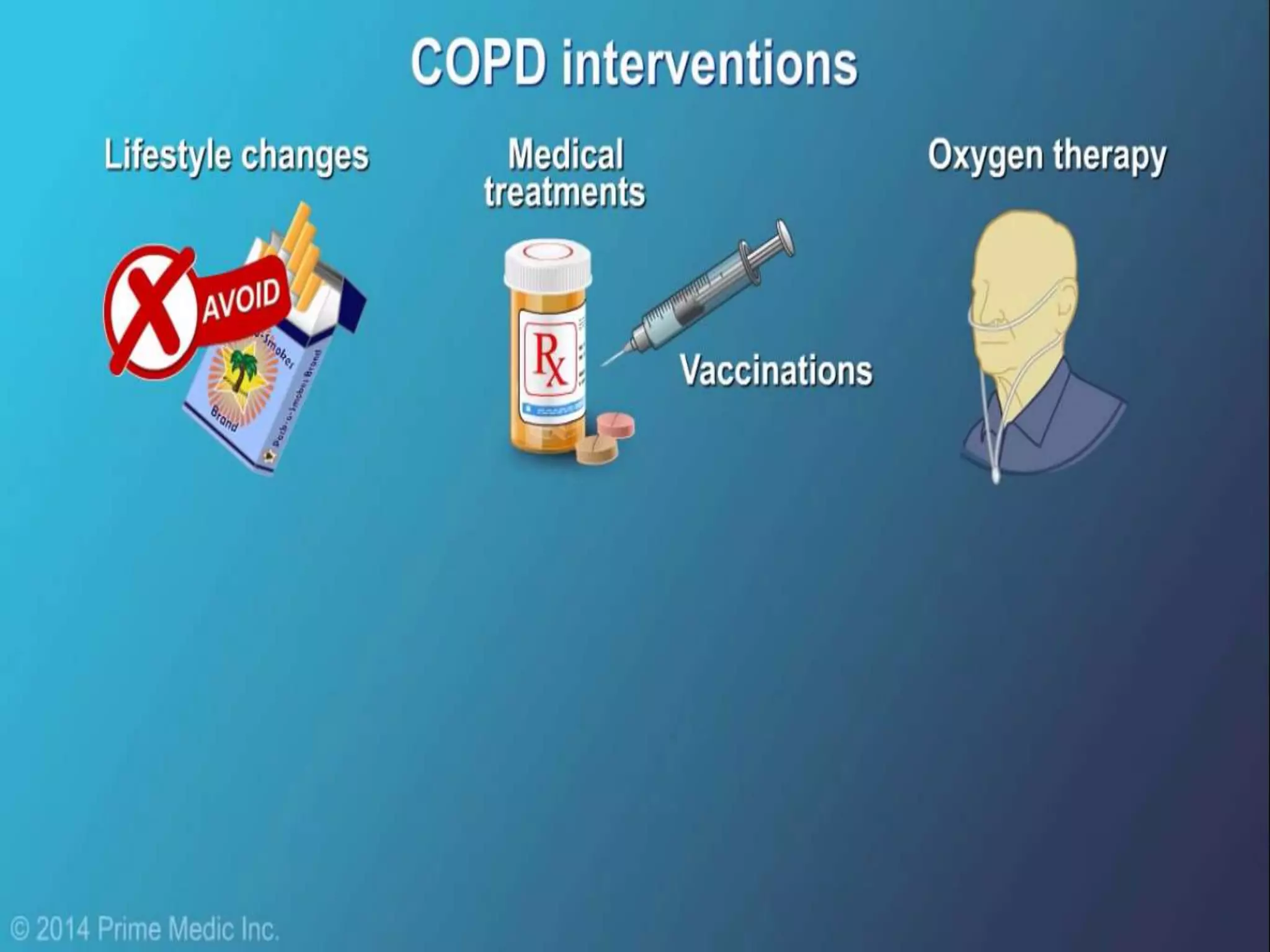
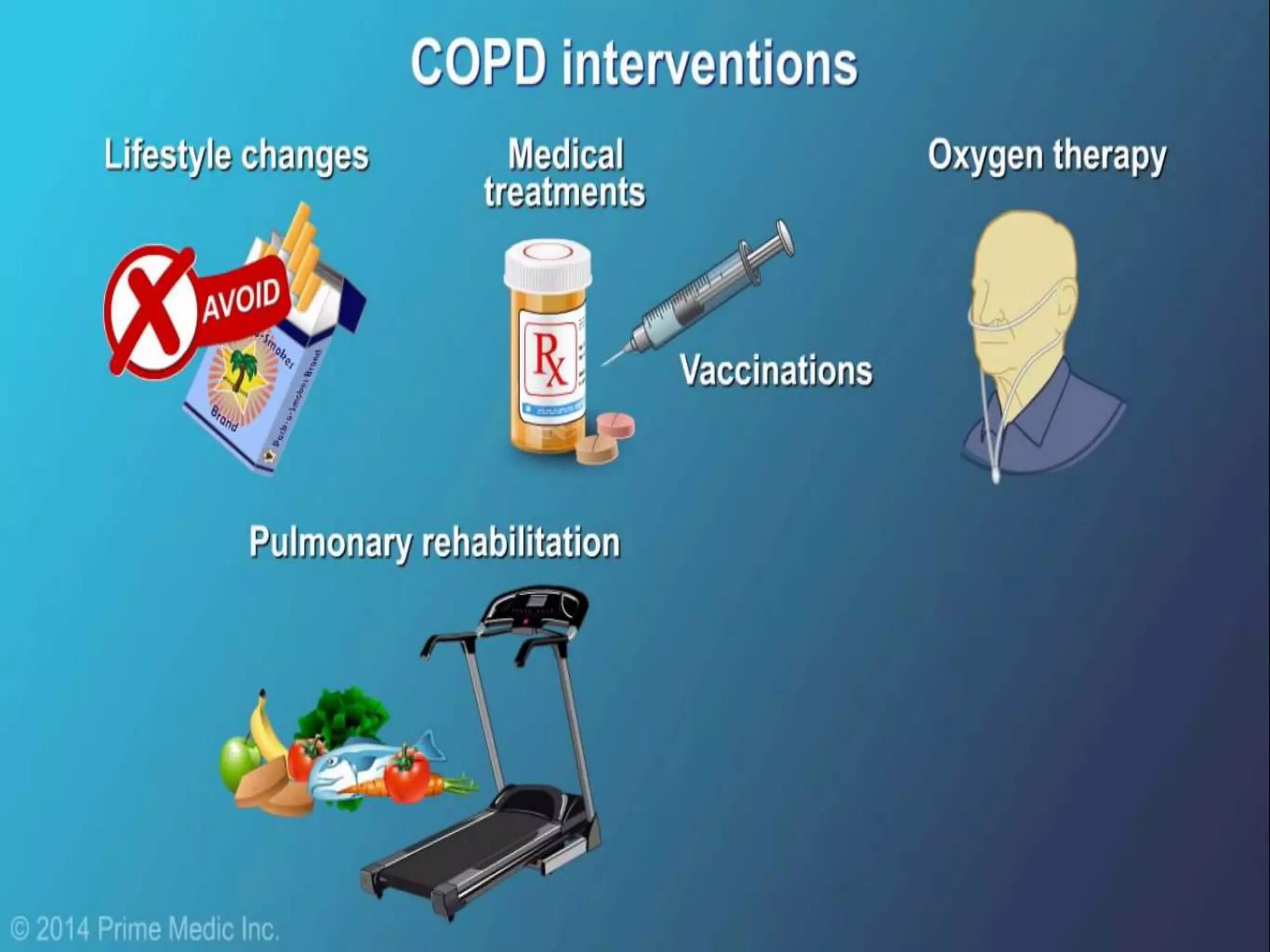
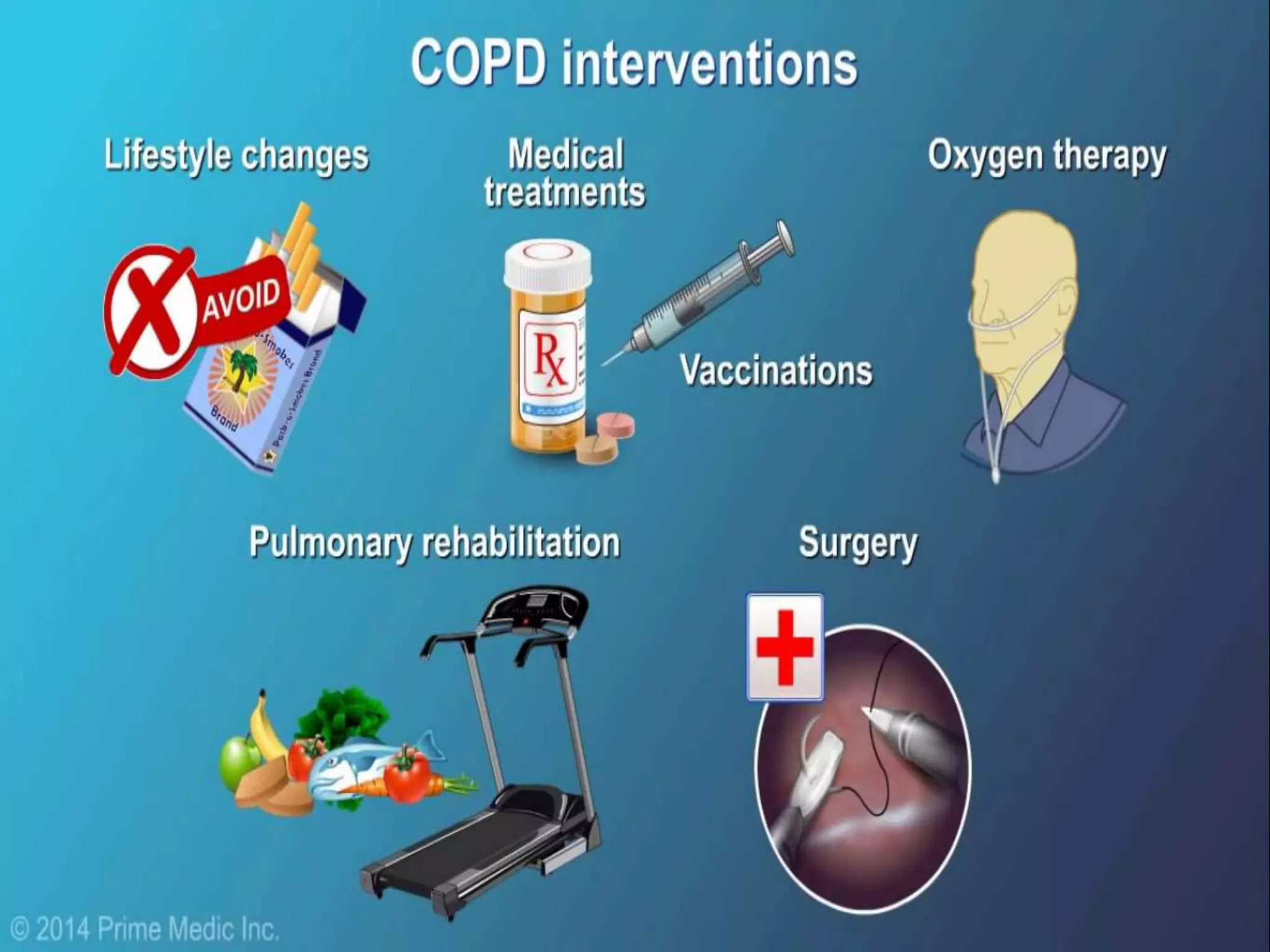
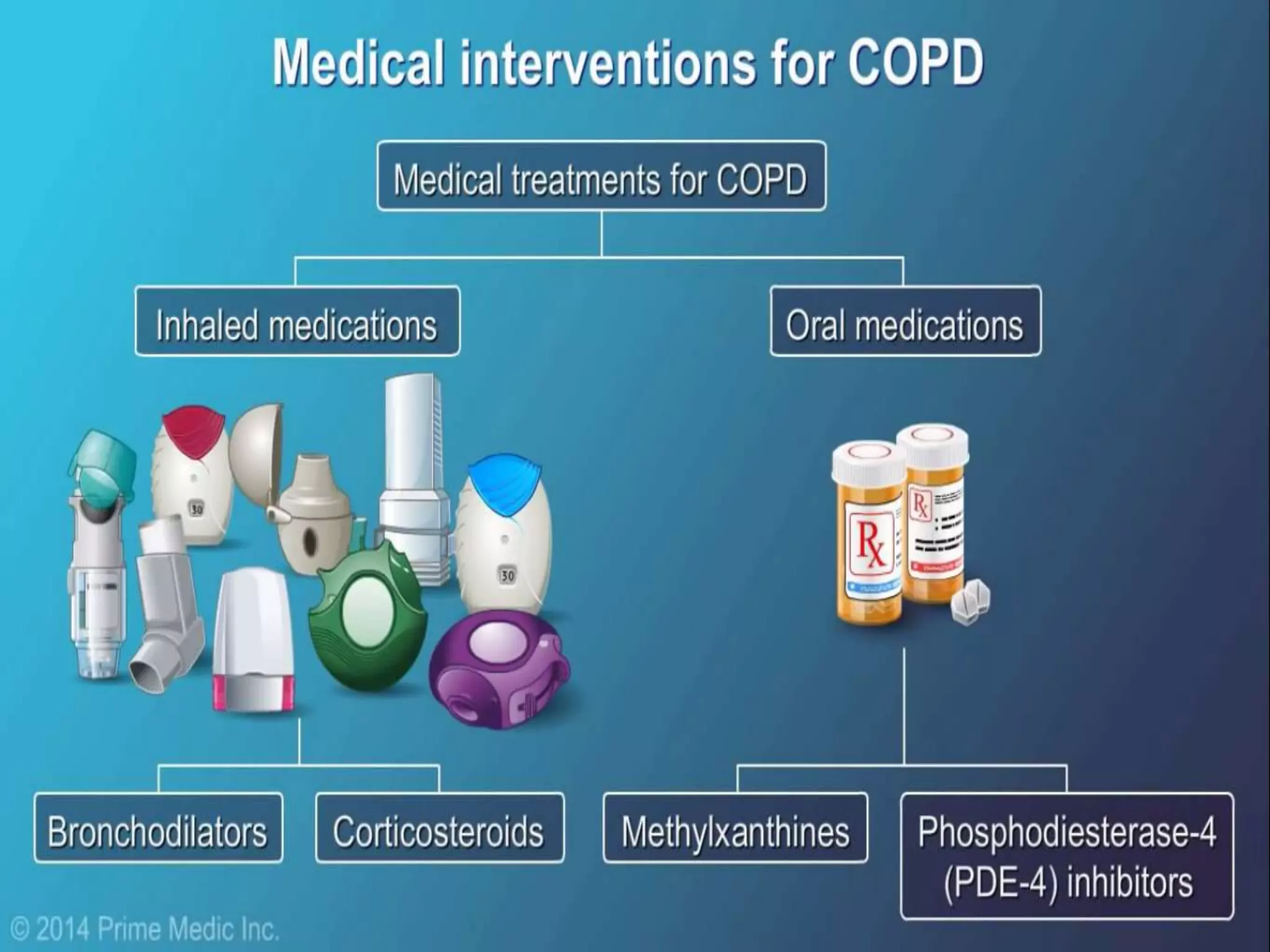
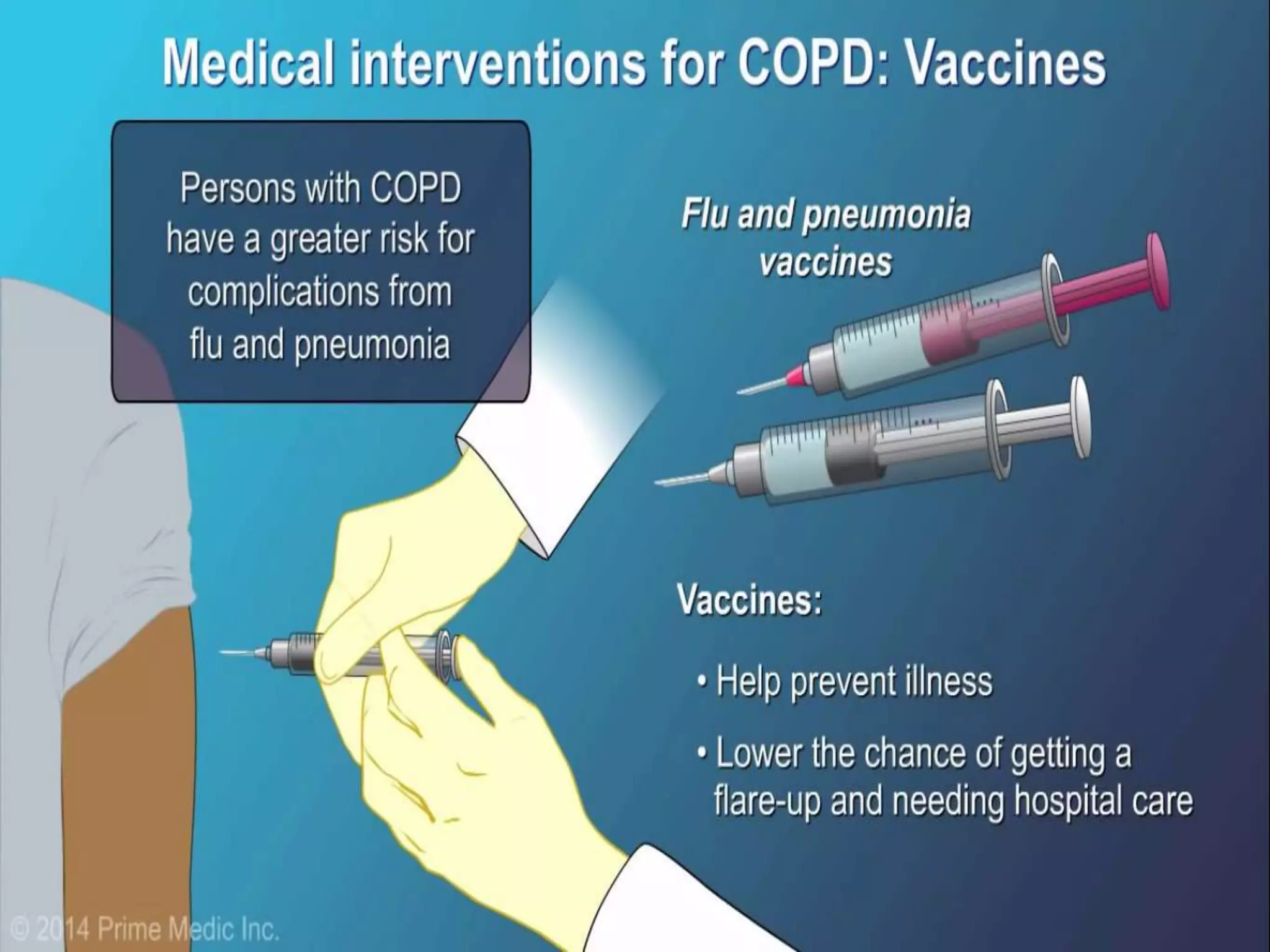
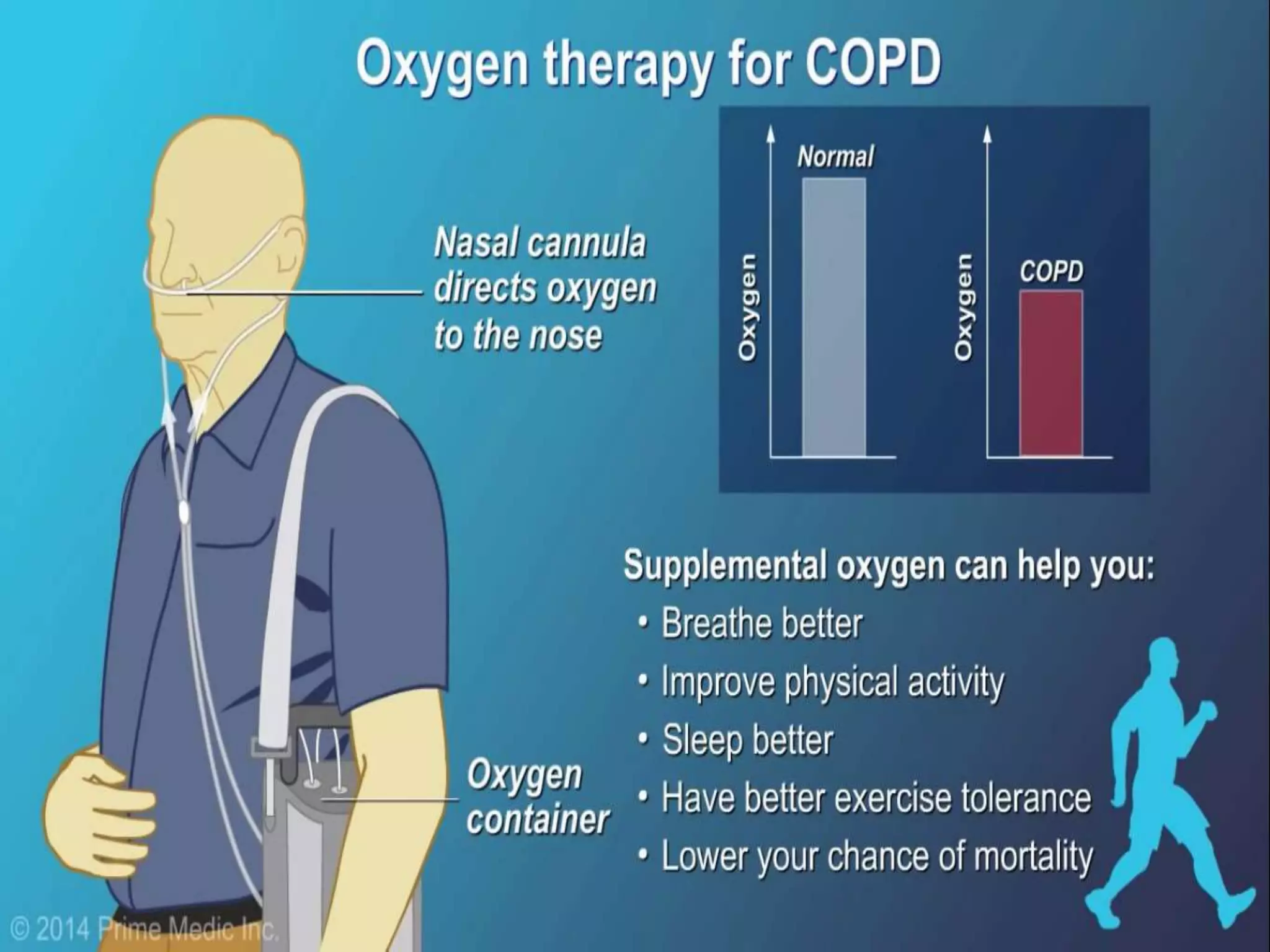
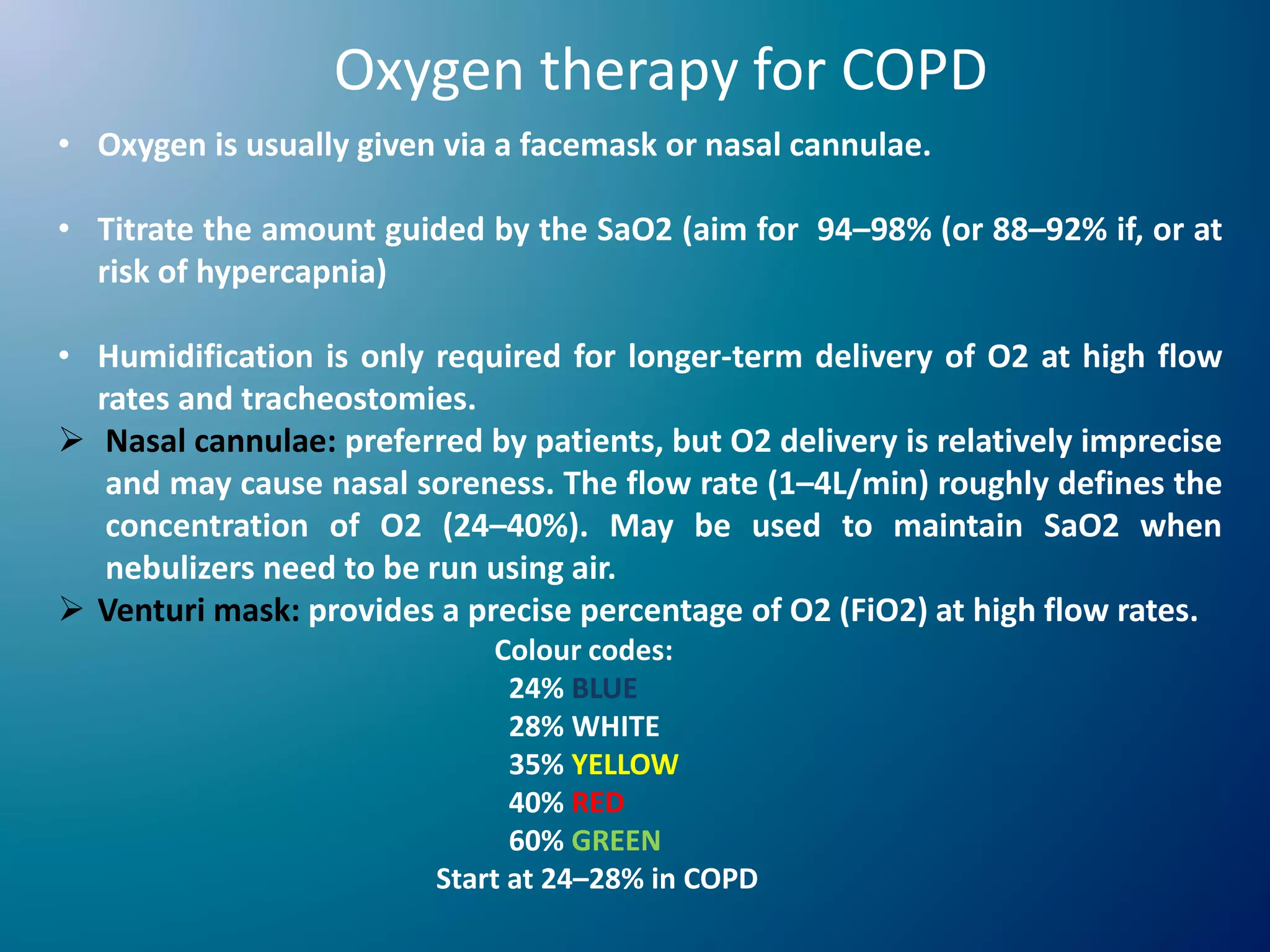
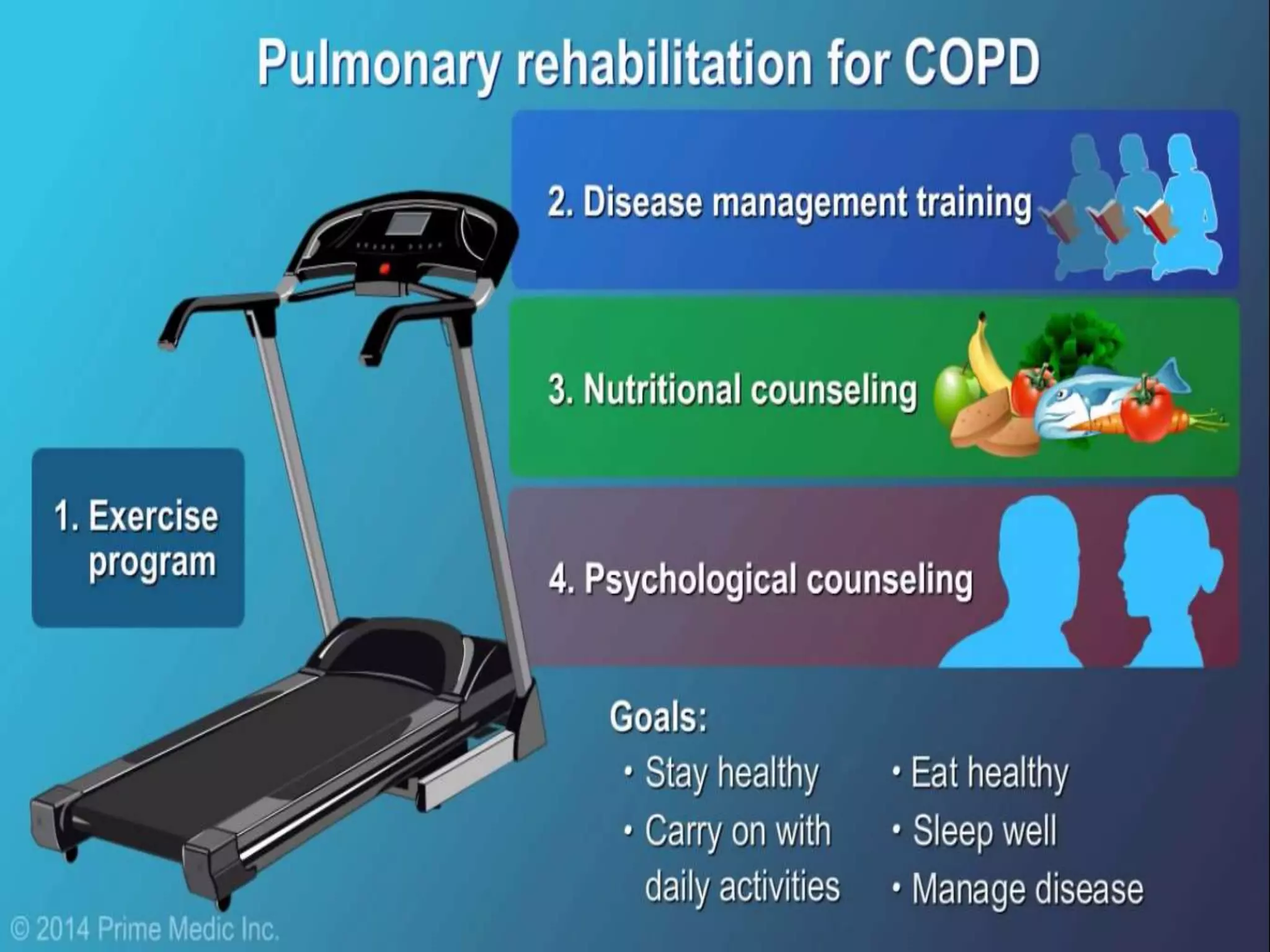
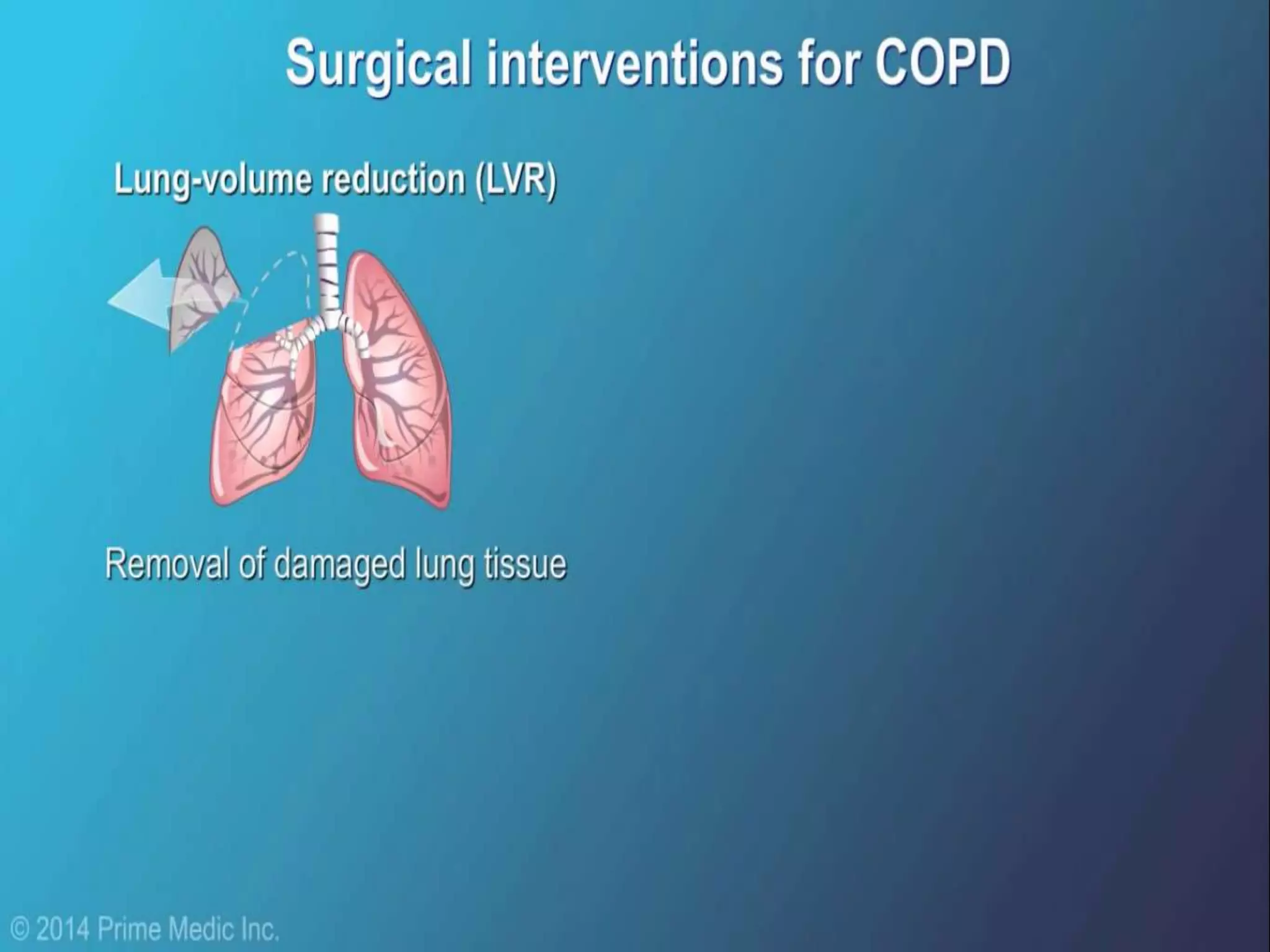
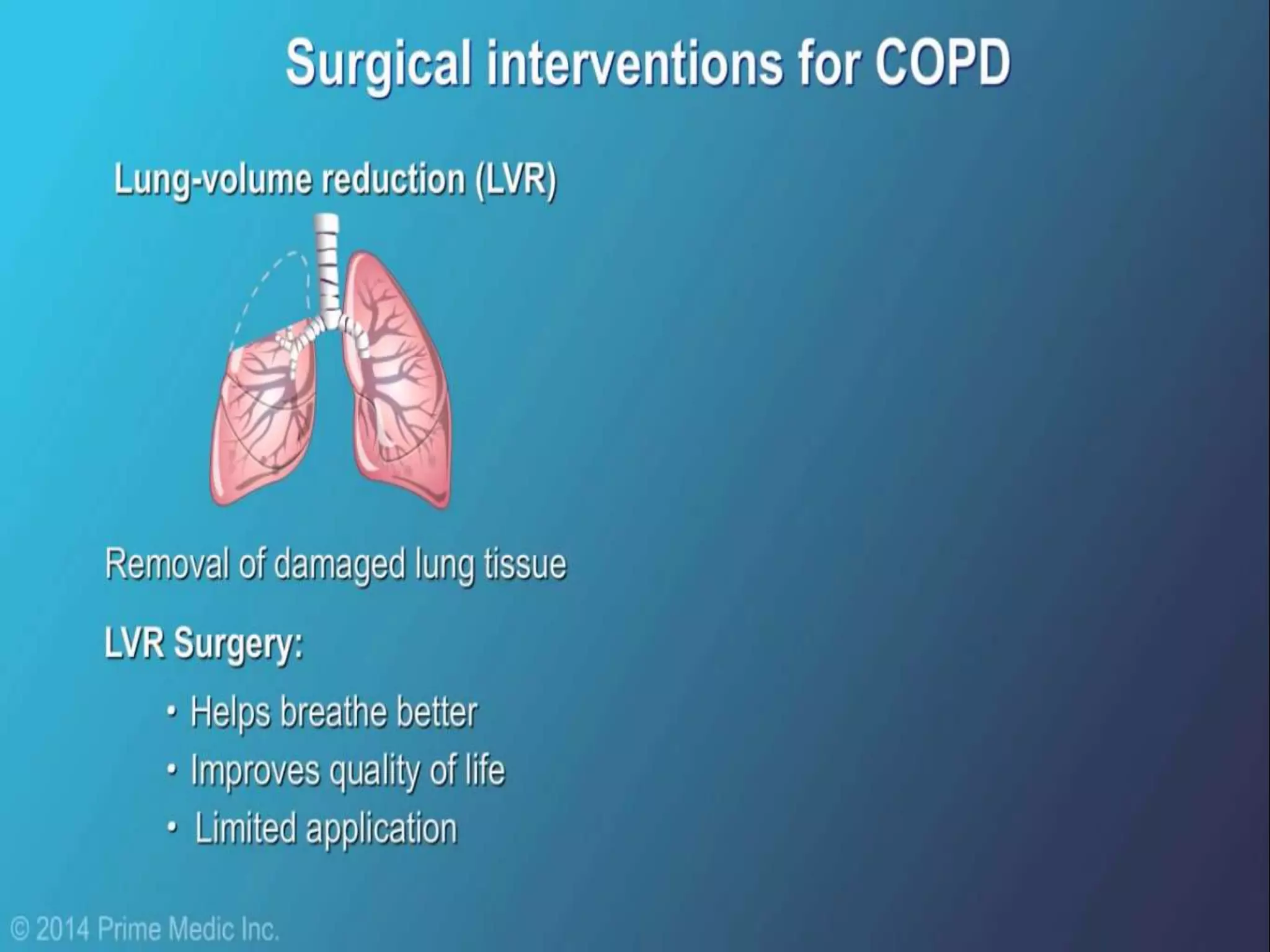
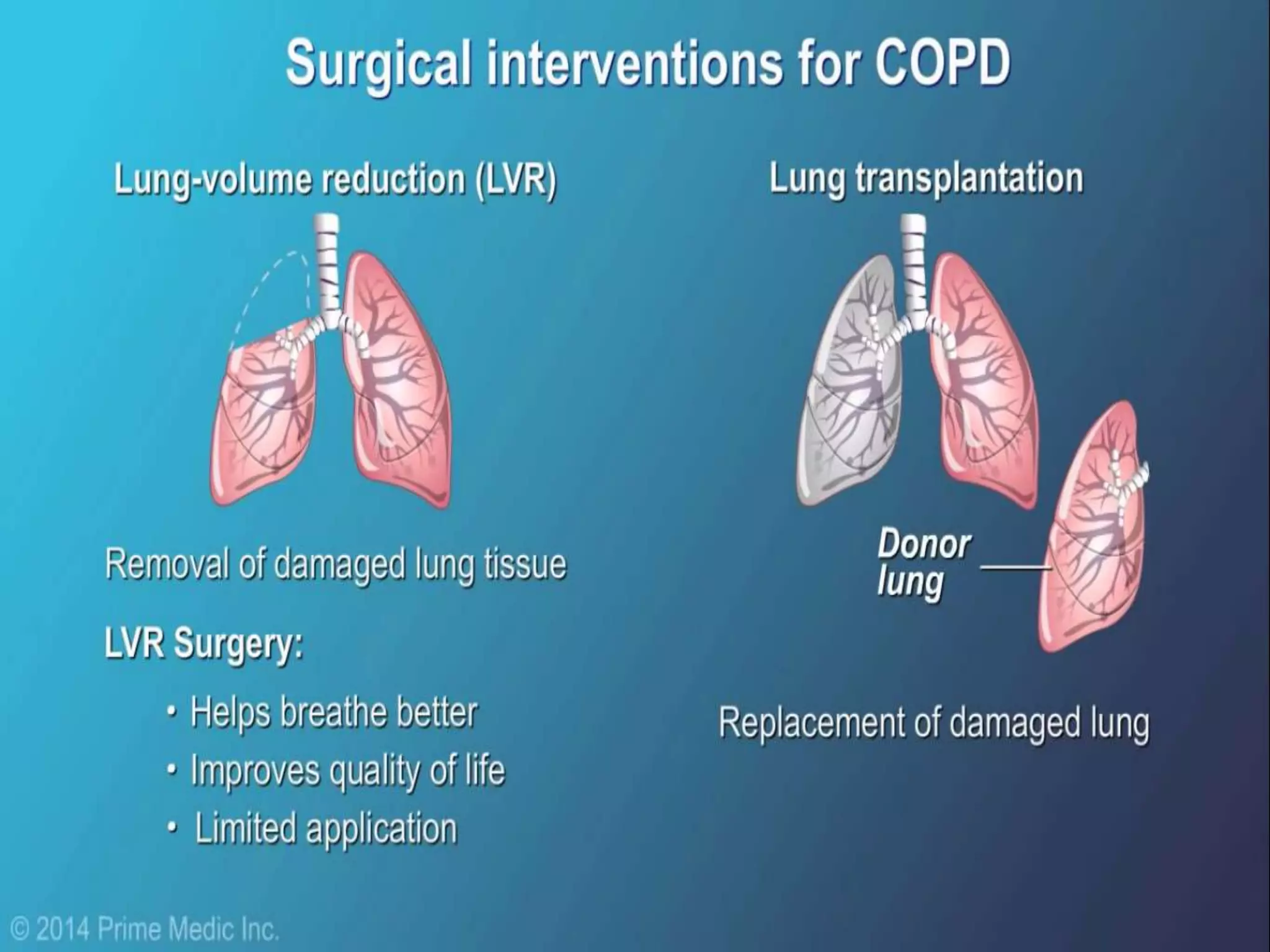
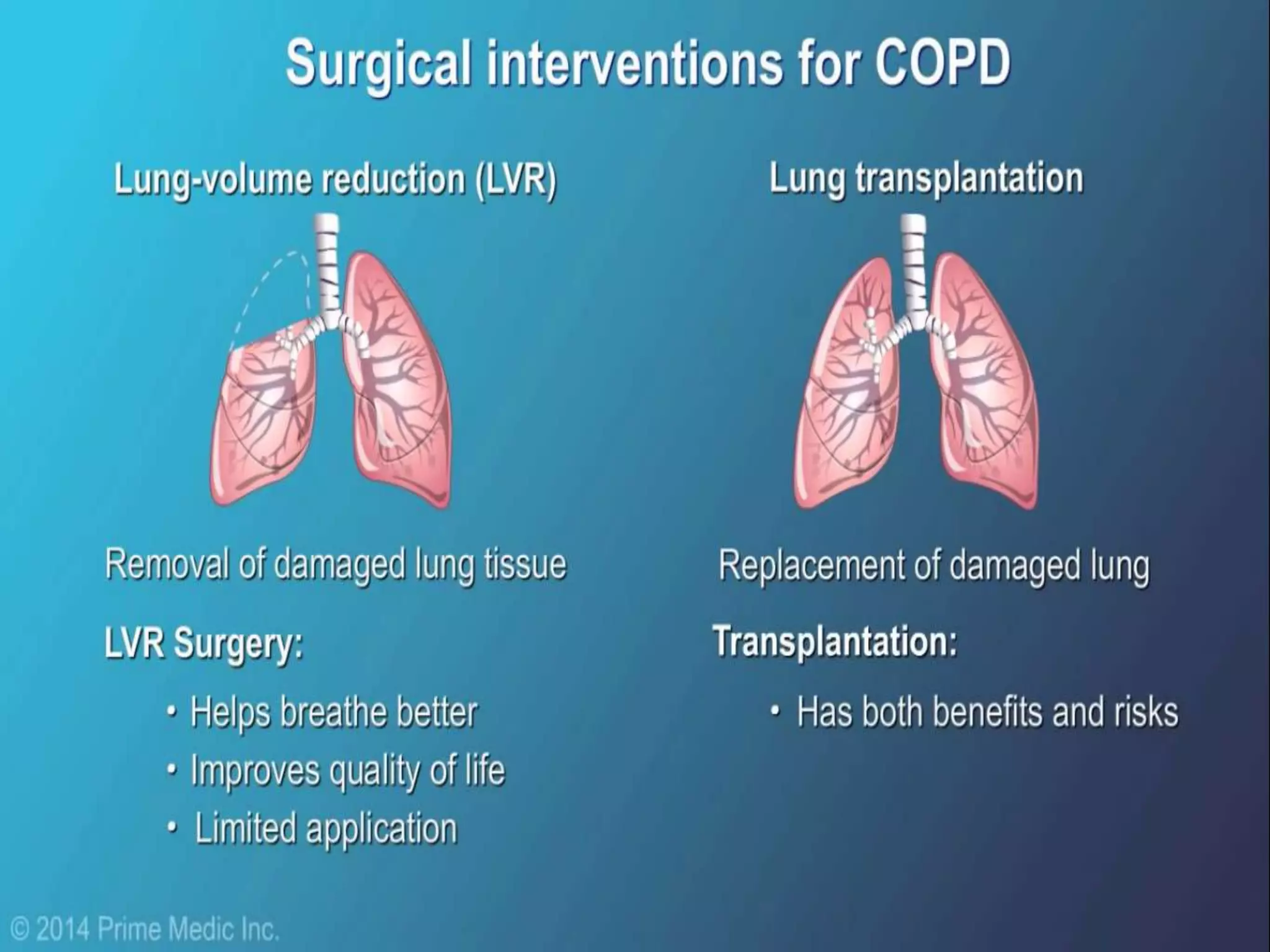
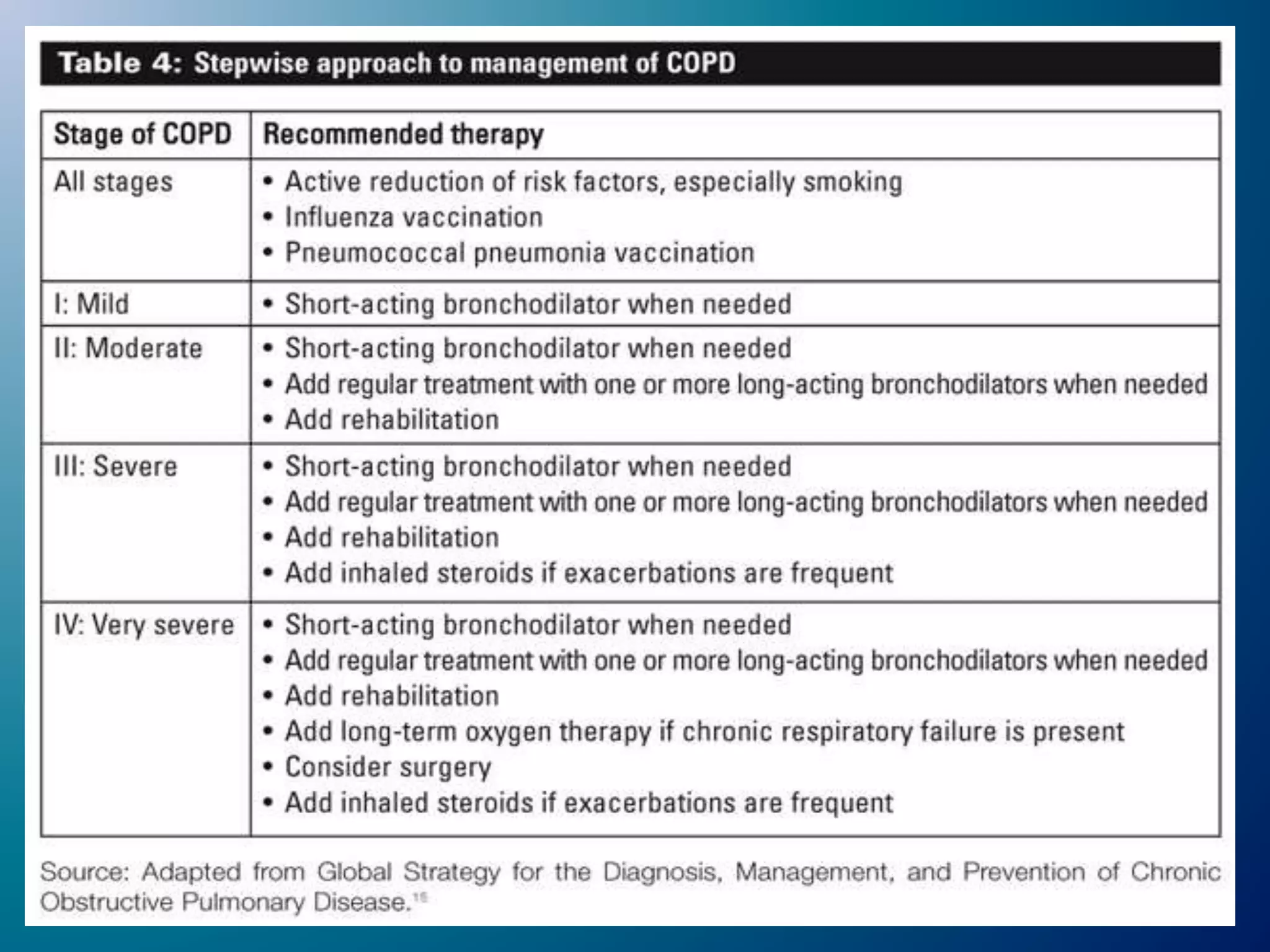
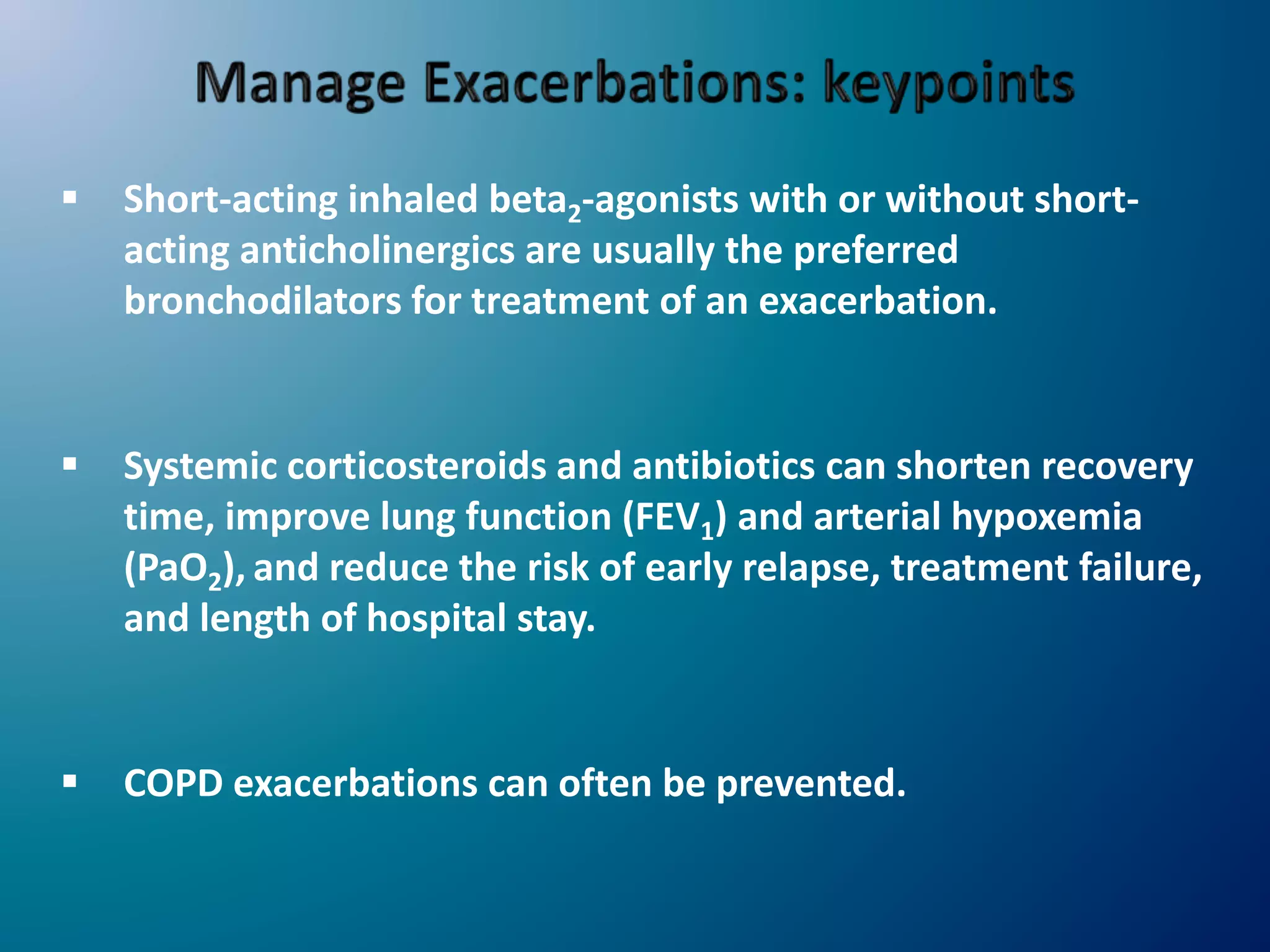
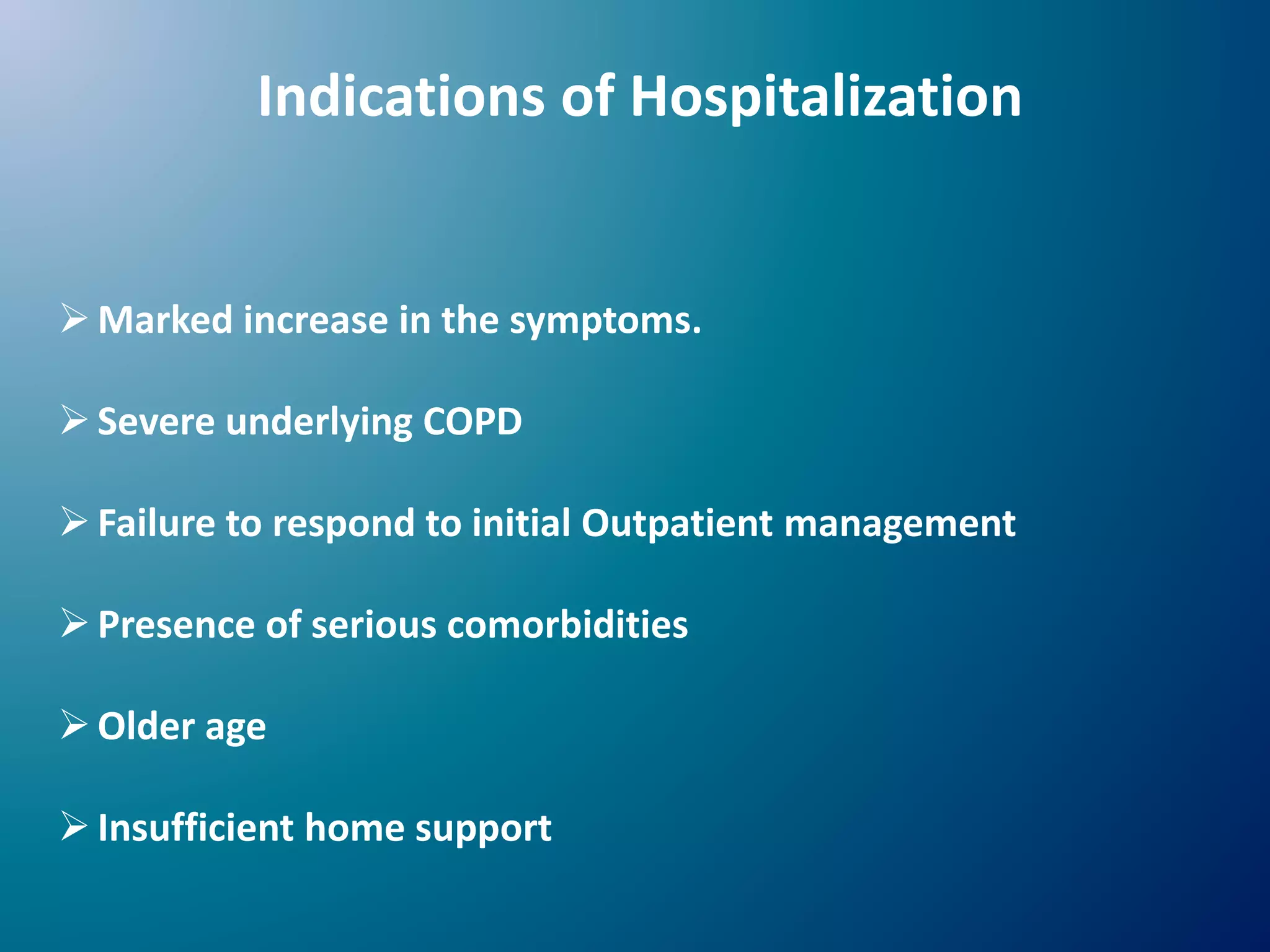
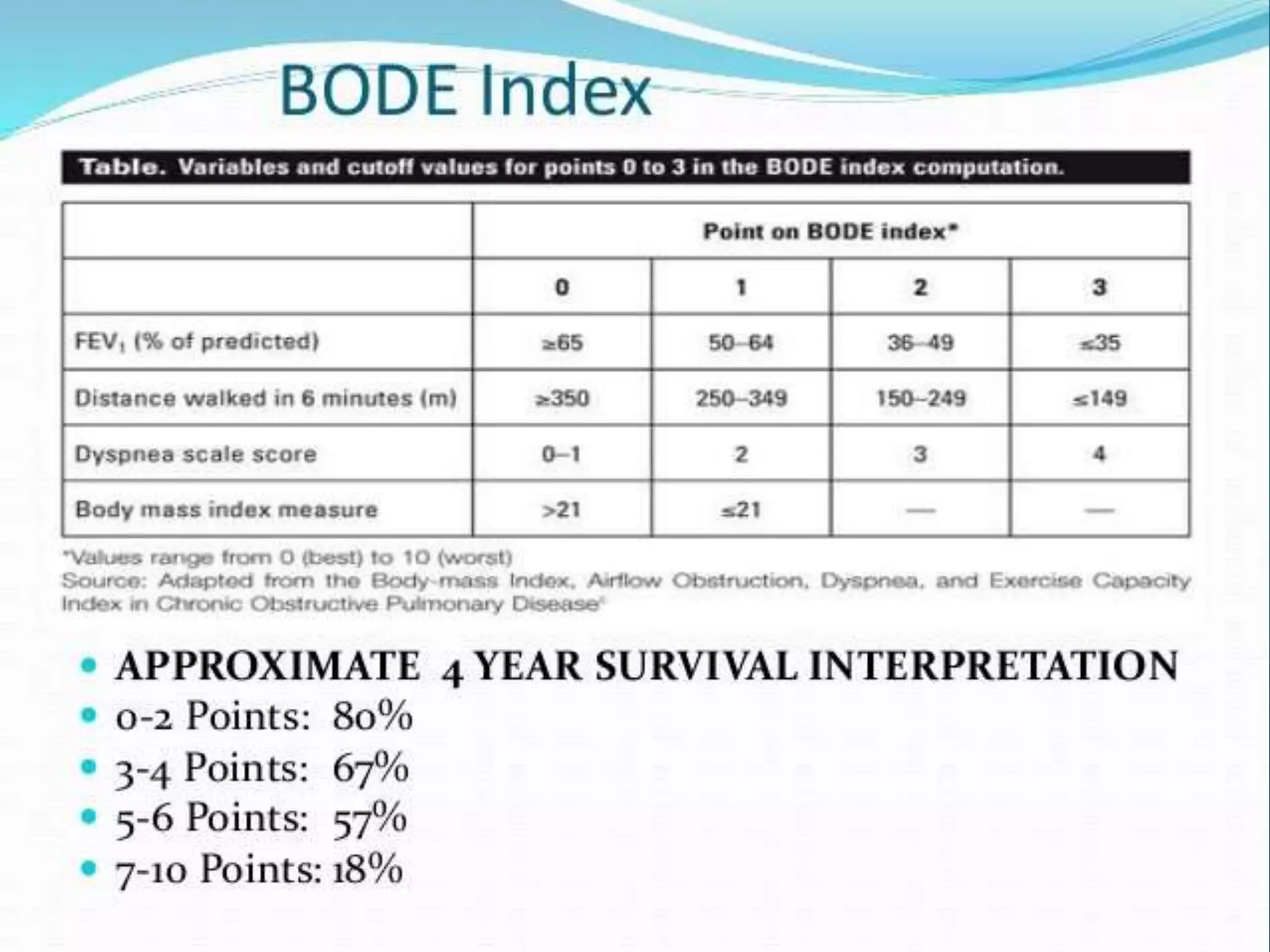
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is characterized by airflow limitation due to chronic bronchitis and emphysema, with symptoms including cough, dyspnea, and wheezing, often leading to significant health decline and comorbidities. Patients can be classified as 'blue bloaters' (chronic bronchitis) or 'pink puffers' (emphysema) based on their symptoms and physiological responses, with a need for careful management including smoking cessation and bronchodilator therapy. Exacerbations are typically triggered by infections and require prompt intervention with short-acting bronchodilators, systemic corticosteroids, and antibiotics, along with possible hospitalization in severe cases.