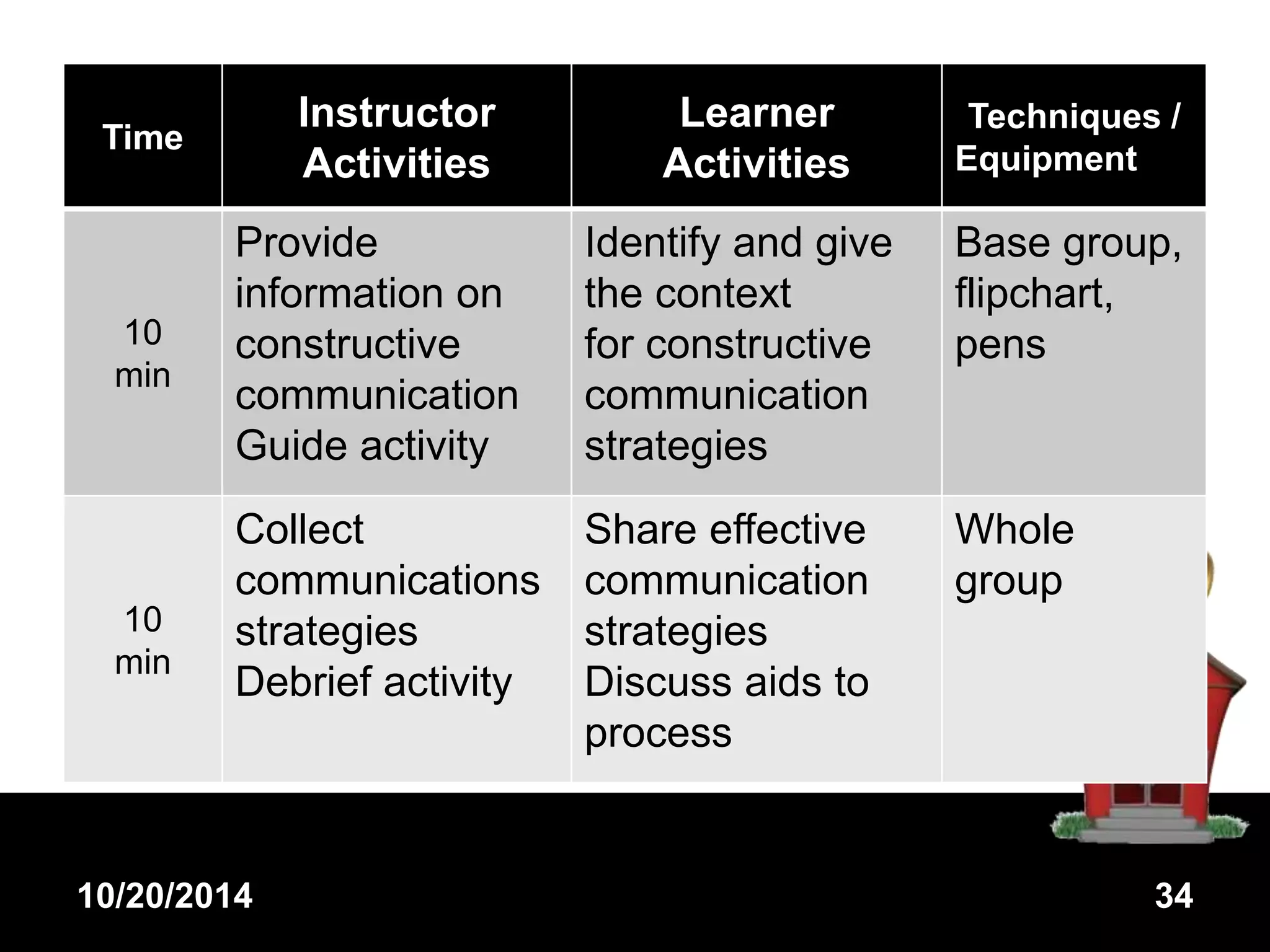
Cooperative learning involves students working in groups to help each other learn. It has two key components: a cooperative incentive structure and cooperative task structure. Groups are made up of students with mixed abilities. Each student is accountable for their own learning while also contributing to the group. Effective cooperative learning involves heterogeneous grouping, ensuring students have necessary social skills, clear goals and evaluation methods for tasks. The document then describes various cooperative learning structures and their purposes, advantages of cooperative learning, potential disadvantages, and provides an example lesson on constructive communication strategies.