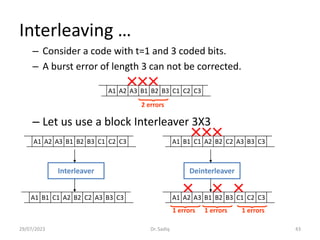
This document discusses channel coding techniques for digital communication systems. It describes two major classes of channel coding: 1) waveform coding, which transforms waveforms to make them more robust to noise and interference, and 2) structured sequence coding, which adds redundancy to sequences to enable error detection and correction. Convolutional coding is discussed in detail, including how convolutional encoders work, representations using generator polynomials and state diagrams, encoding and decoding using trellis diagrams, and the Viterbi algorithm for maximum likelihood decoding. The concept of free distance is also introduced as a way to evaluate the minimum distance between codewords in convolutional codes.