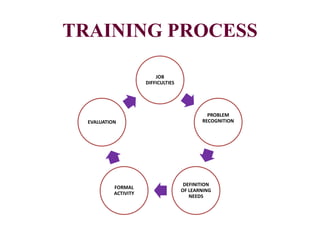
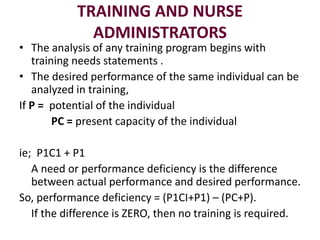
This document discusses training in staff development for nursing. It defines training as an organized method to ensure employees have the necessary knowledge and skills for their jobs. The importance of training is outlined, including for achieving organizational objectives, developing uniform attitudes, job security, and enhancing standards. Different types of training are described such as formal, informal, pre-entry, in-service, post-entry, and orientation. The training process and methods like on-the-job, vestibule, and classroom training are also summarized.