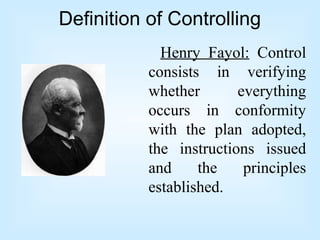
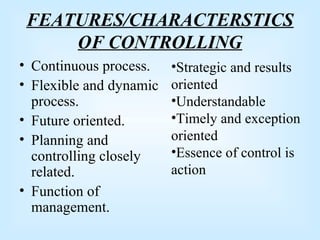
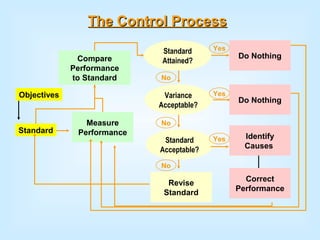
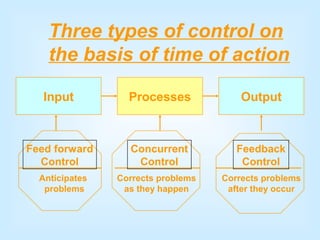
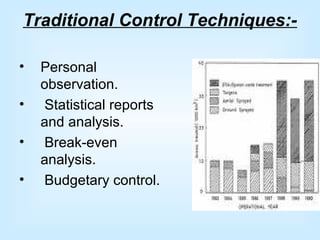
Controlling is a key managerial function that involves establishing standards, measuring performance, comparing results to standards, and taking corrective action. It is a continuous process of monitoring performance, identifying variances, and ensuring objectives are met according to plan. The control process includes establishing objectives and standards, measuring actual performance, comparing results to standards, and taking corrective action when needed. Control can happen at different times - preliminary controls anticipate problems, concurrent controls monitor ongoing work, and feedback controls examine end results. Traditional control techniques include personal observation and statistical reports, while modern techniques include management information systems and program evaluation review techniques.