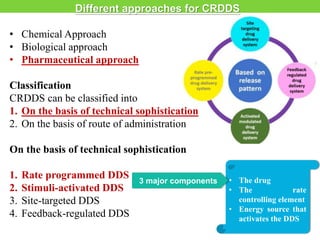
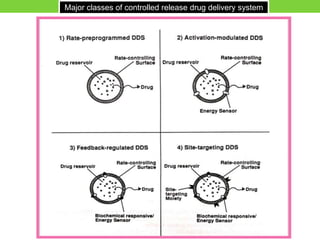
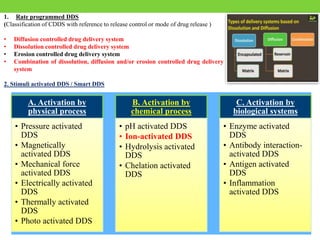
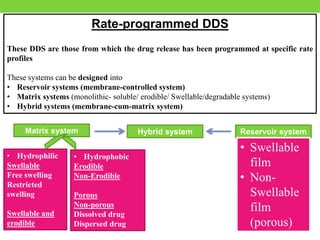
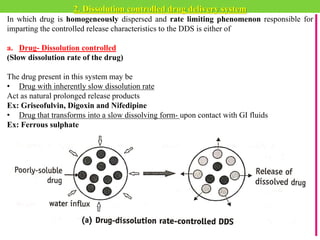
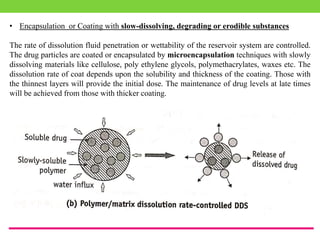
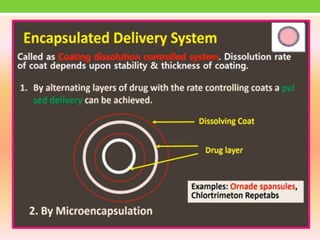
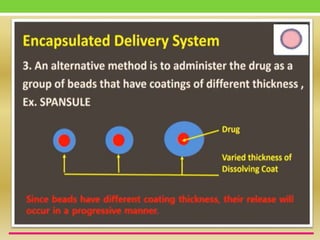
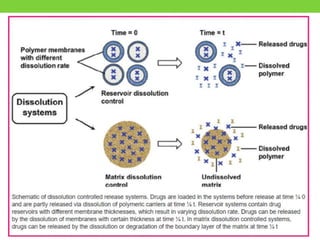
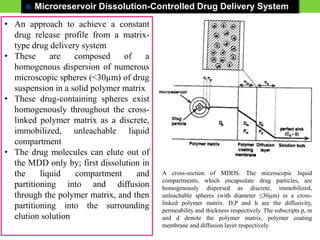
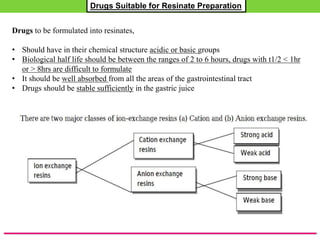
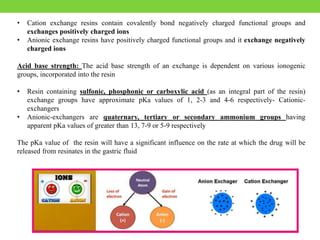
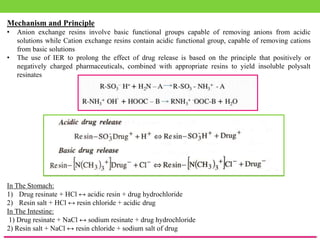
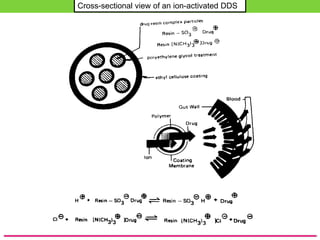
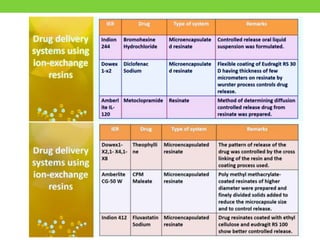
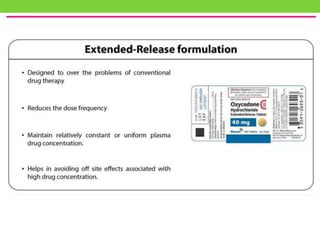
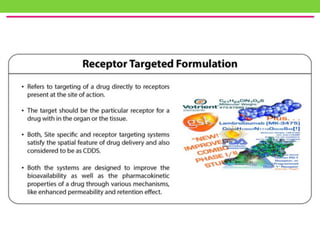
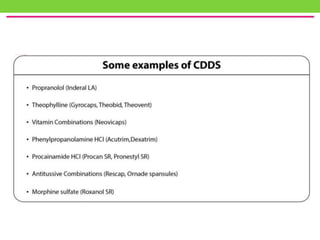
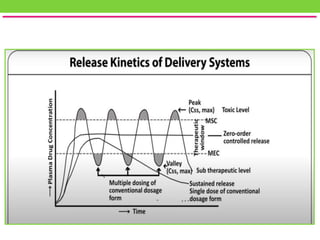
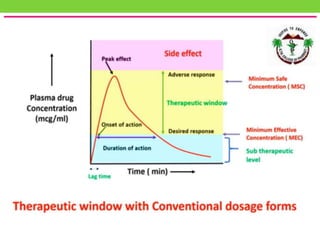
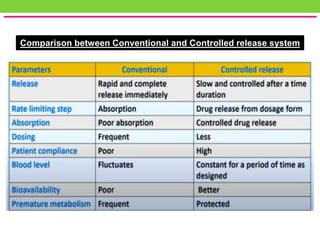
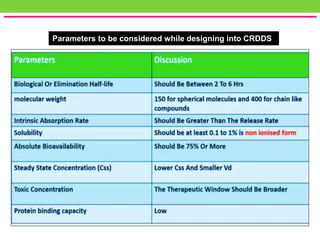
The document discusses various approaches to designing controlled release drug delivery systems (CRDDS) based on principles like diffusion, dissolution, and ion exchange. It classifies CRDDS into categories such as rate programmed systems, stimuli-activated systems, and site-targeted systems, each with distinct mechanisms for drug release. Additionally, it elaborates on the components and classifications of these systems, including the advantages and disadvantages of using ion-exchange resins in drug formulations.