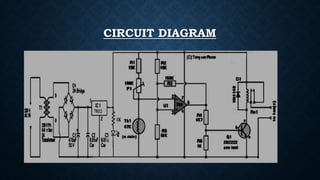
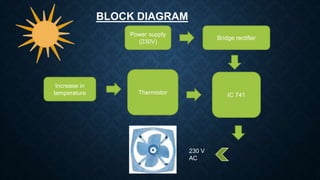
This document describes an automatic fan controller circuit that uses a thermistor and operational amplifier to monitor temperature. If the temperature exceeds a predefined limit, the thermistor sends a signal to the operational amplifier to activate a relay and fan, maintaining the temperature. Key components include a bridge rectifier, voltage regulator, thermistor, variable resistor, capacitor, transistor, diode, and relay. The circuit provides automatic fan control without human intervention to ensure cooling when temperatures rise.