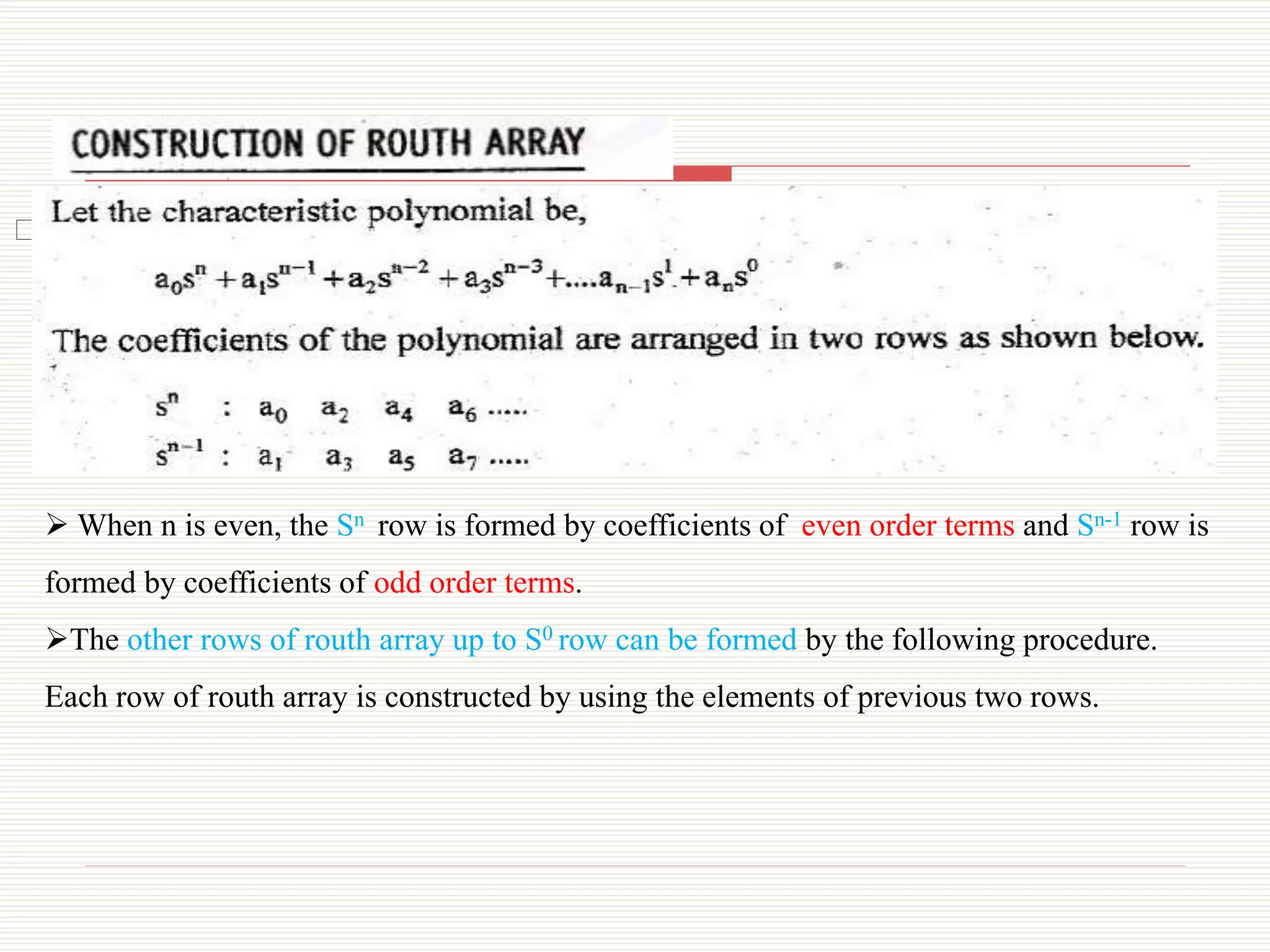
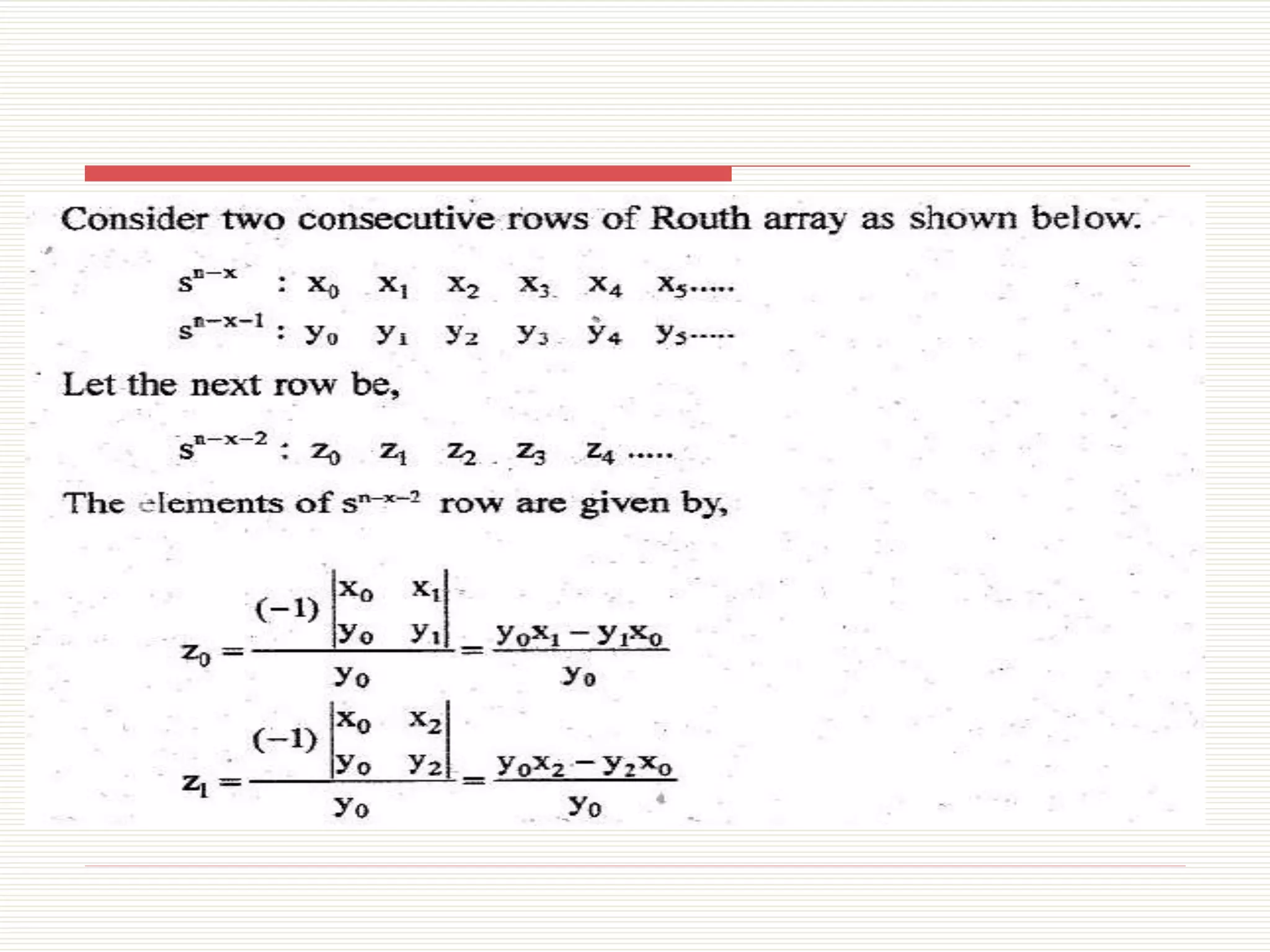
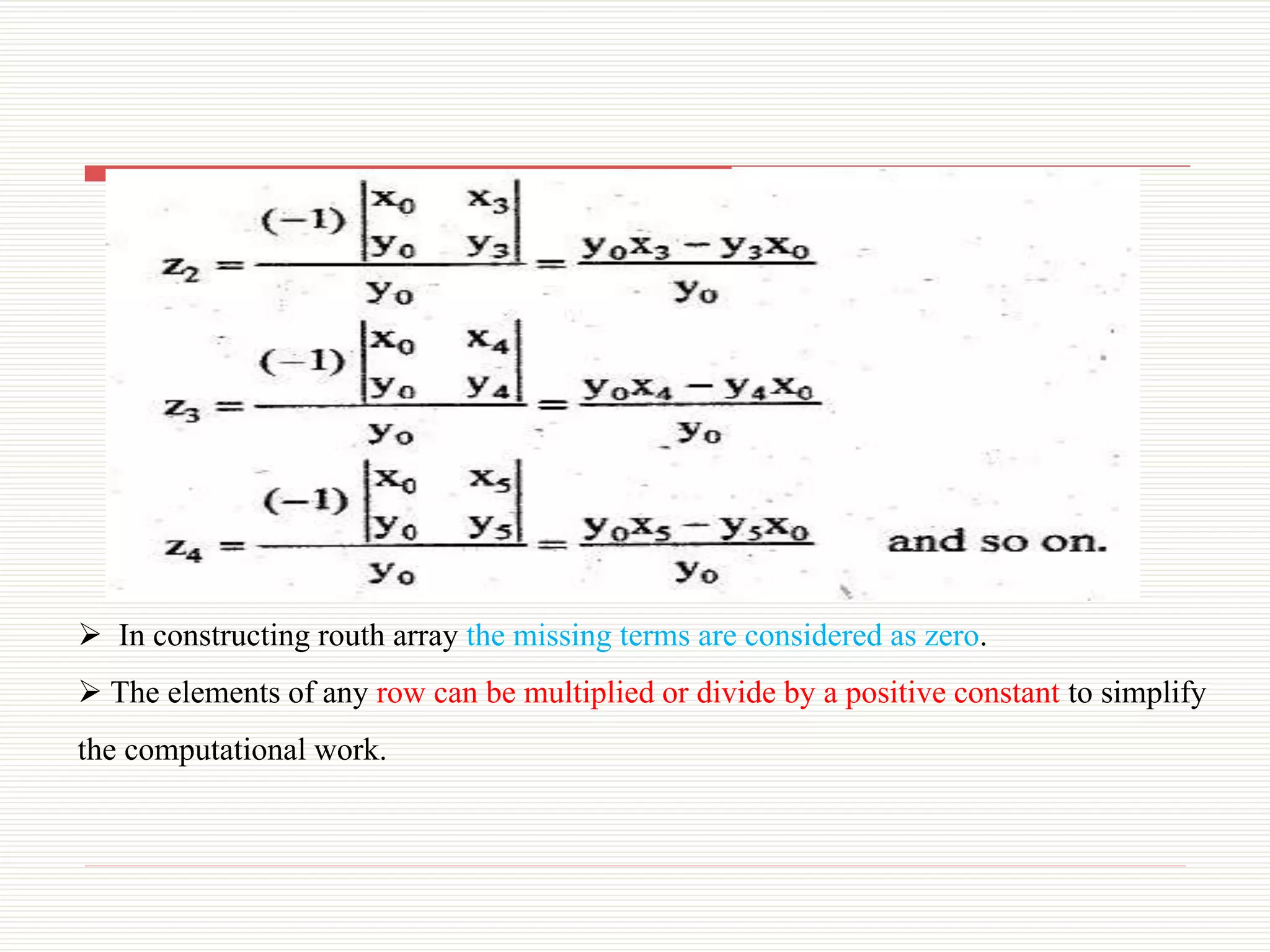
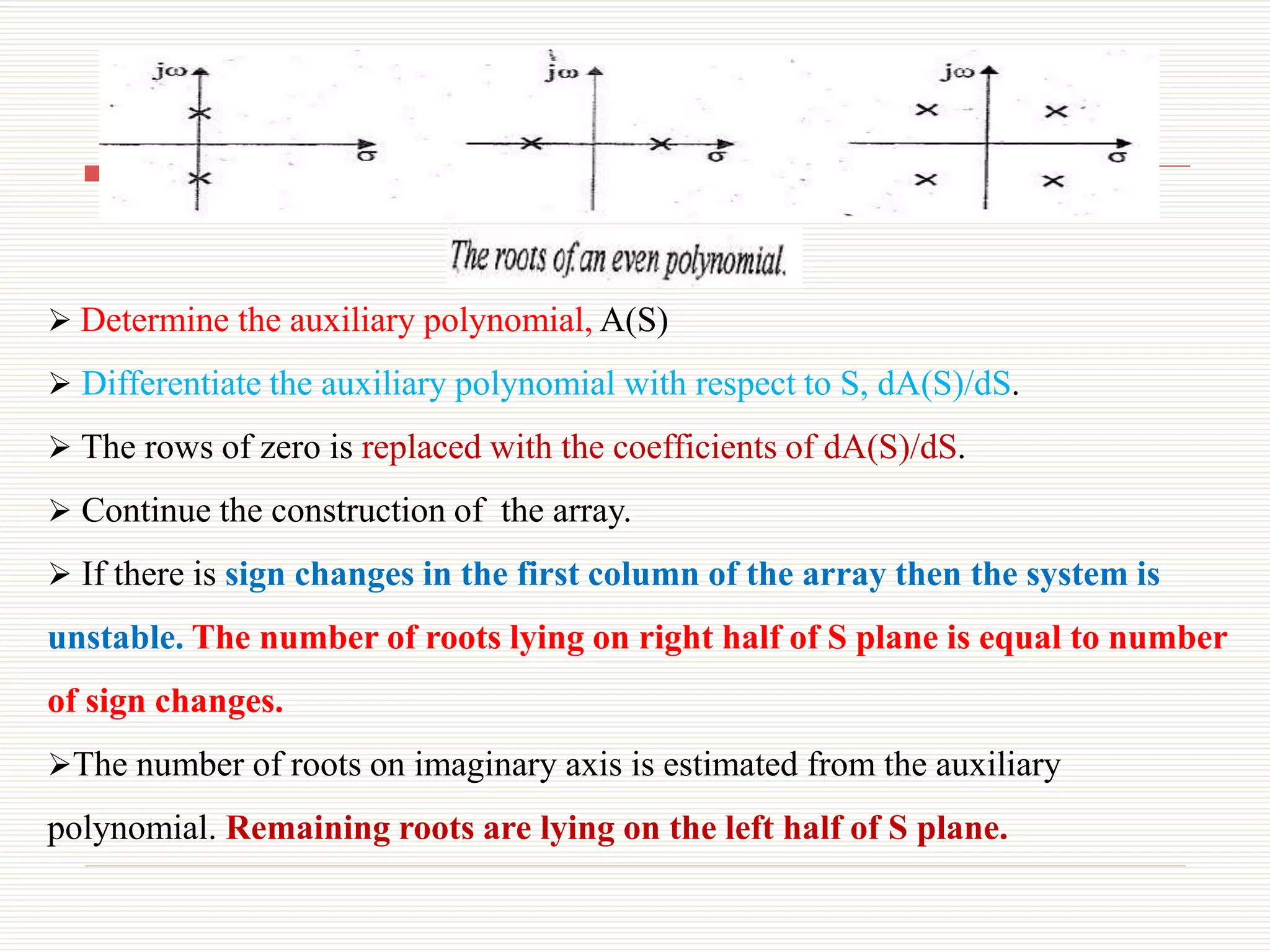
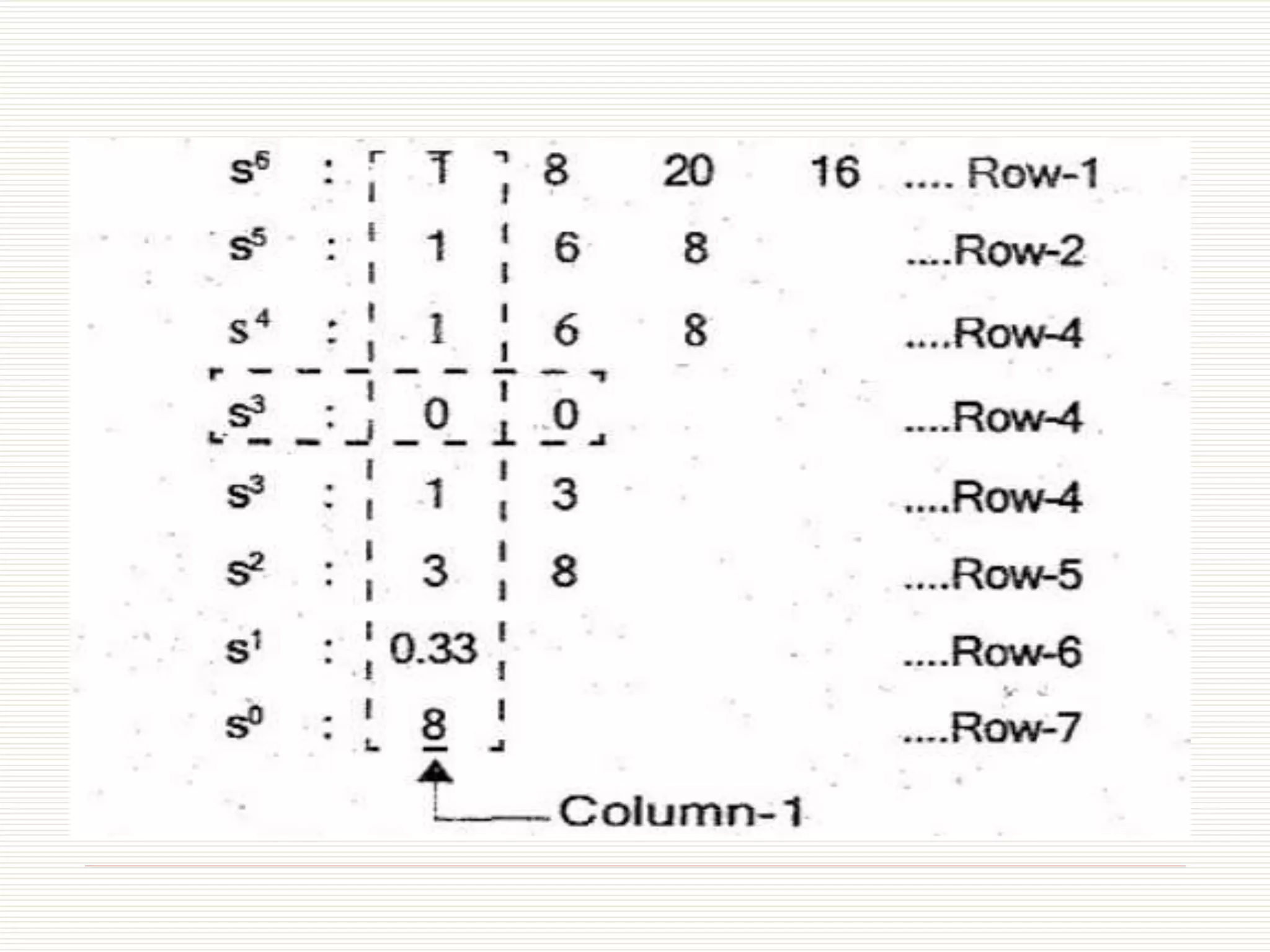
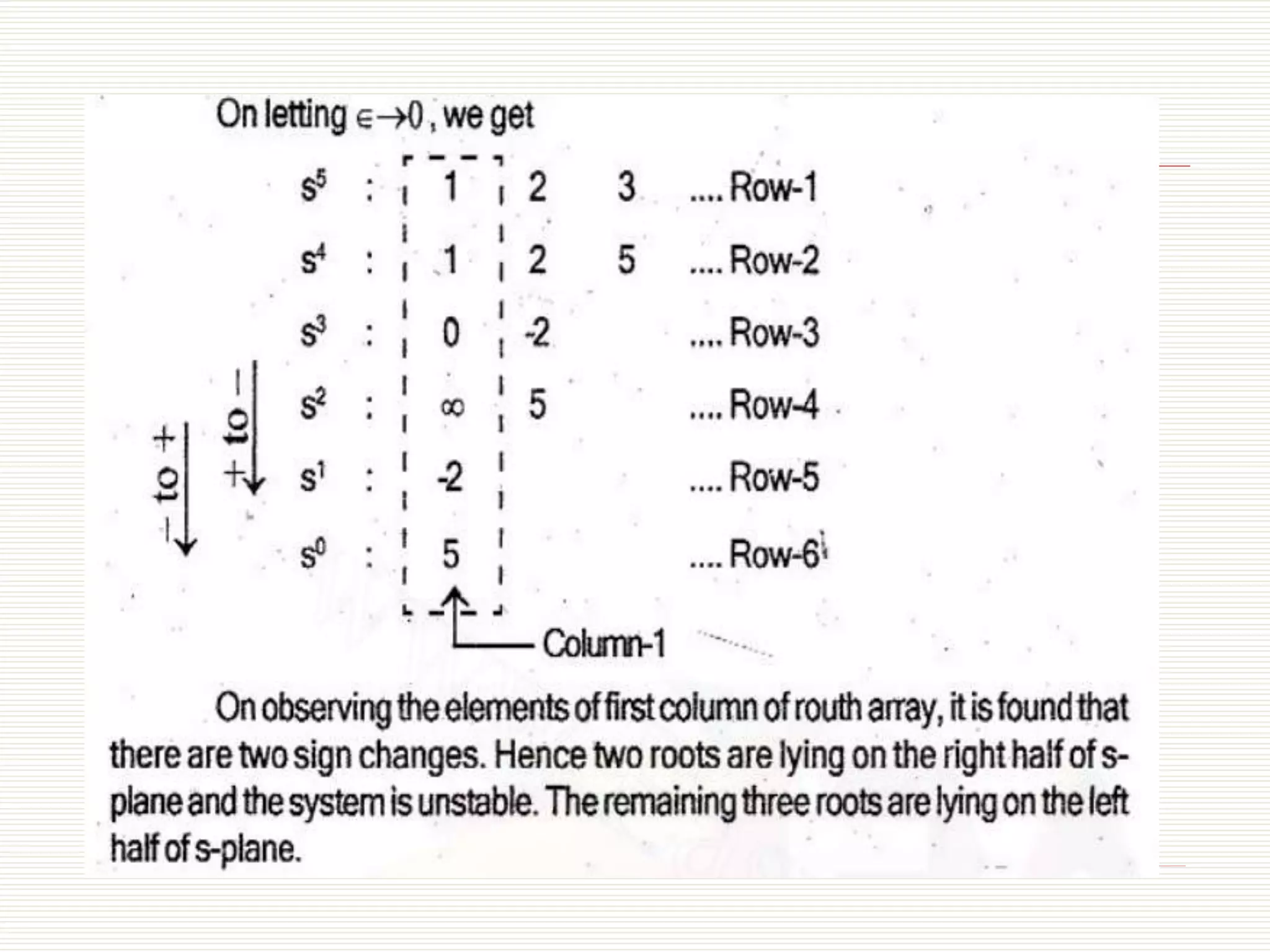
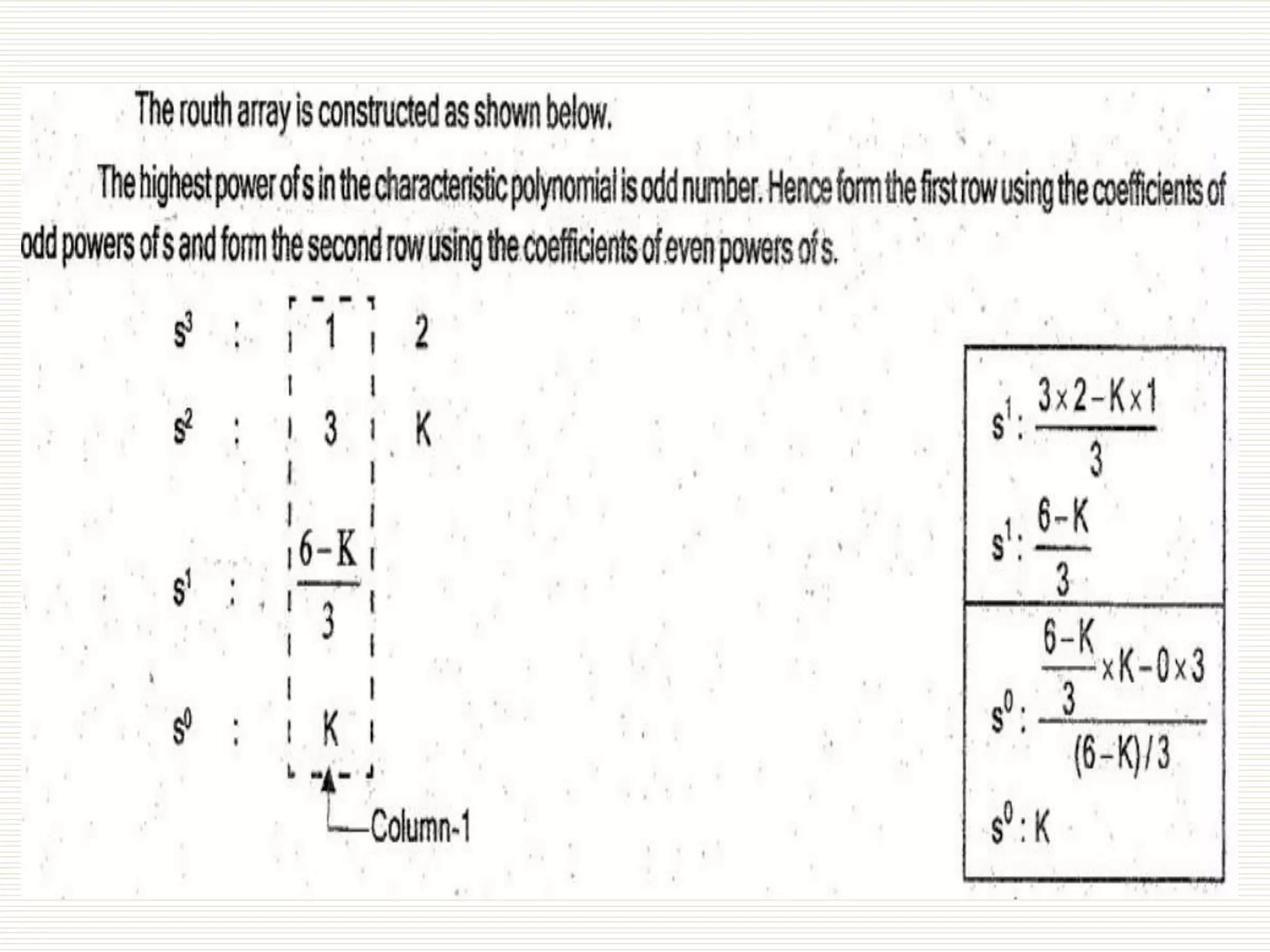
The document presents an overview of the Routh-Hurwitz criterion for analyzing the stability of control systems, as discussed by Mr. C.S. Satheesh from Muthayammal Engineering College. It explains the construction of the Routh array and how to interpret its results to determine system stability based on the sign changes in the first column. Various cases for handling specific scenarios in the array are outlined, including dealing with zero coefficients and rows.