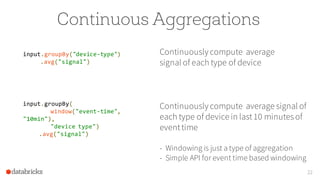
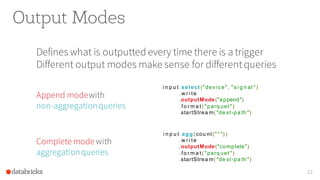
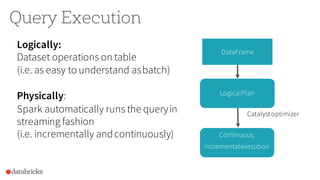
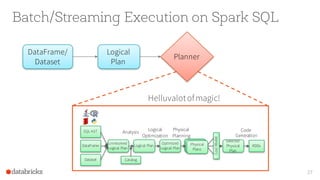
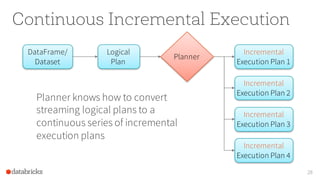
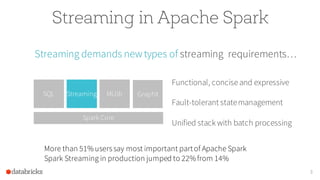
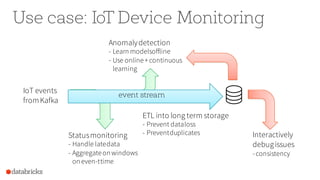
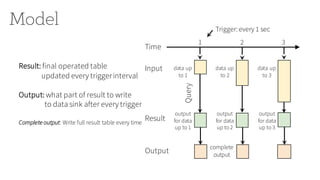
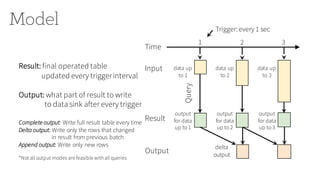
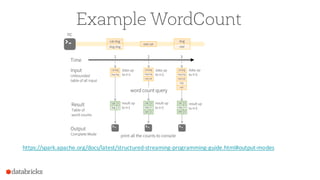
The document discusses the advancements in Apache Spark 2.0, particularly focusing on structured streaming which unifies batch, interactive, and streaming queries. It highlights the importance of handling complex streaming requirements such as event-time processing, state management, and real-time analytics through a high-level API. Additionally, it presents use cases, advantages, and practical examples, emphasizing the continuous and incremental execution capabilities of Spark structured streaming.






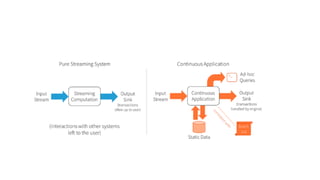

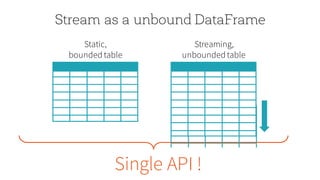
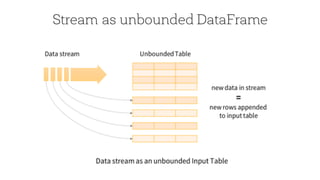


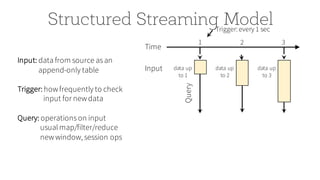


![Streaming ETL with DataFrame
input = spark.read
.format("json")
.stream("source-path")
result = input
.select("device", "signal")
.where("signal > 15")
result.write
.format("parquet")
.outputMode("append")
.startStream("dest-path")
1 2 3
Result
[append-only table]
Input
Output
[append mode]
new rows
in result
of 2
new rows
in result
of 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contininousappsqconfstructuredstreaming-161210012908/85/Continuous-Application-with-Structured-Streaming-2-0-21-320.jpg)