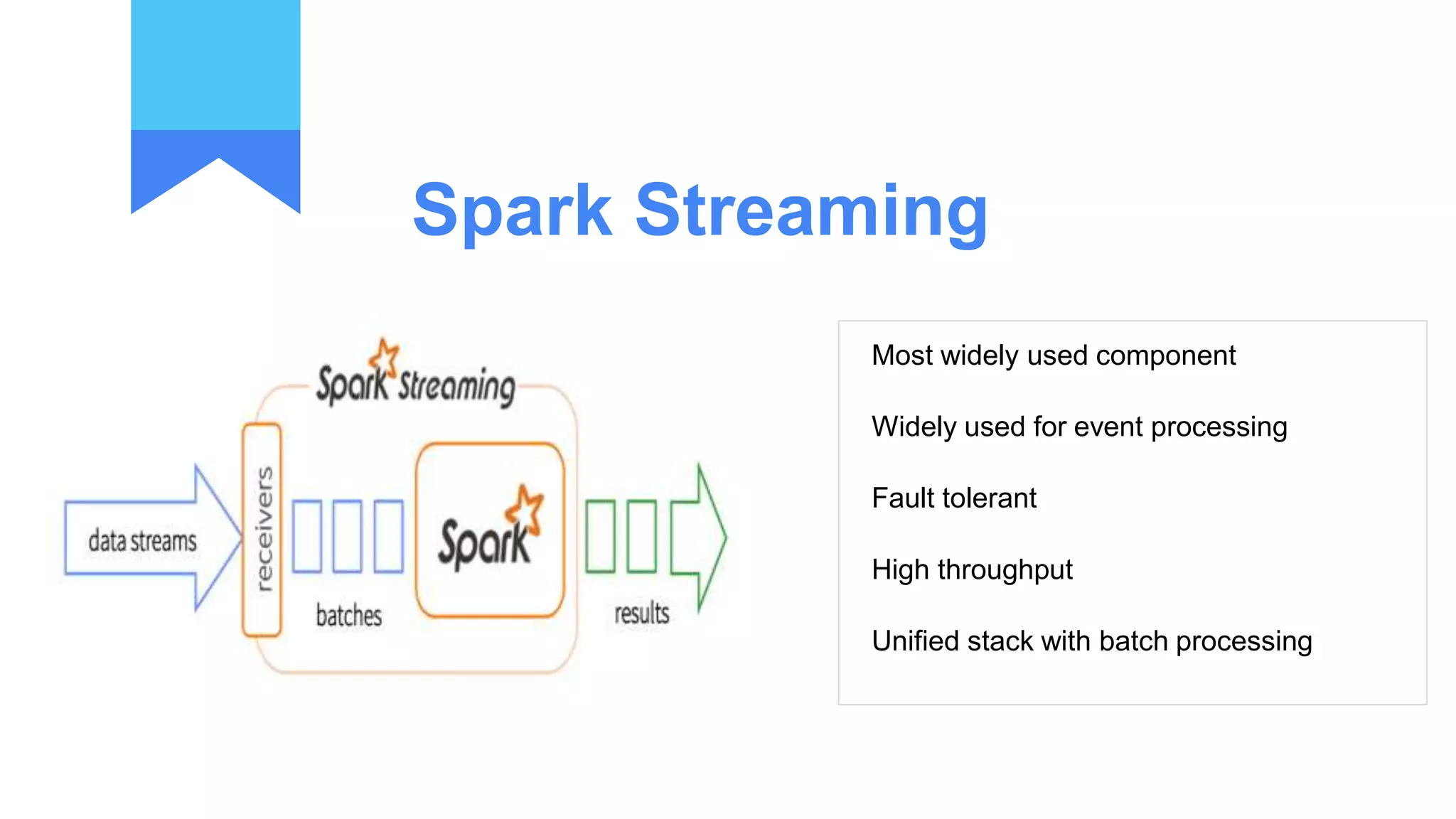
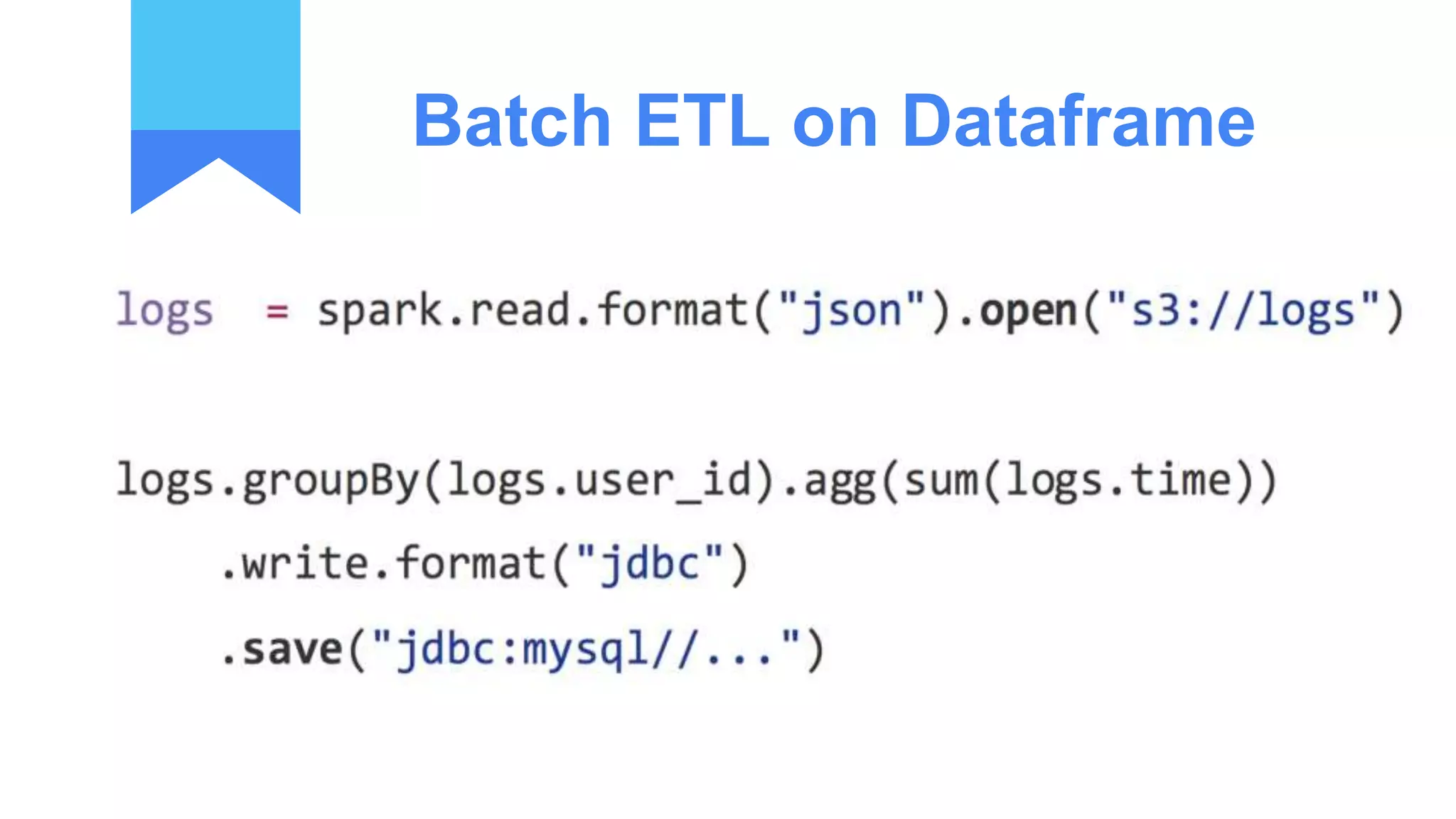
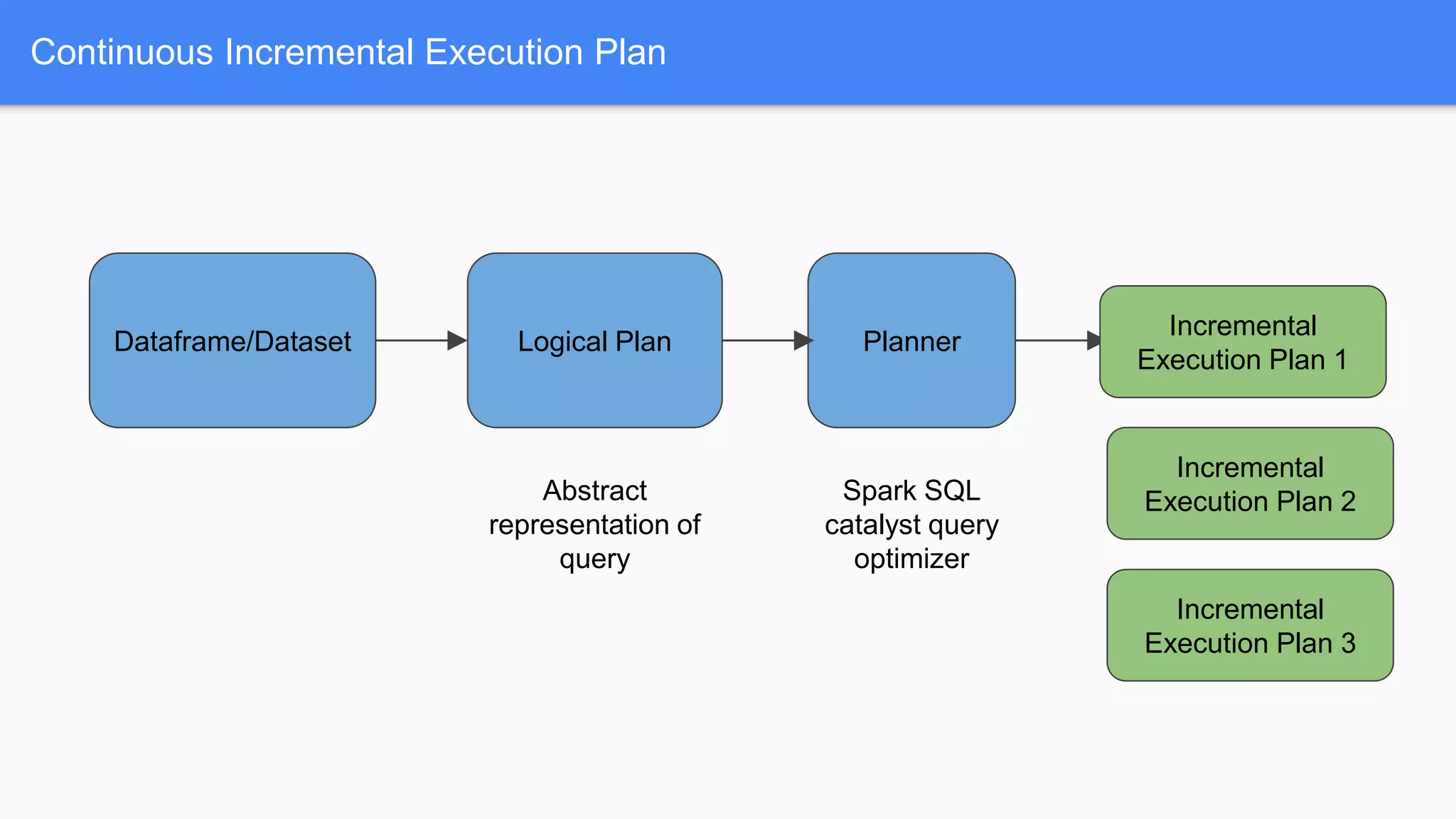
Structured streaming provides a scalable and fault-tolerant stream processing engine built on the Spark SQL engine. It allows processing live data streams using continuous queries that look identical to batch queries. The presentation discusses Spark components including RDDs, DataFrames and Datasets. It then covers limitations of the traditional Spark Streaming model and how structured streaming addresses them by using incremental execution plans and exactly-once semantics. An example of a word count application and demo is presented to illustrate structured streaming concepts.


![Spark Data Models - RDD
- Lineage ( Dependency)
- Partitioning (Distributed data)
- Compute function: Partition => Iterator[T]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unicomsummit2017-210425092854/75/Spark-Kafka-summit-2017-4-2048.jpg)
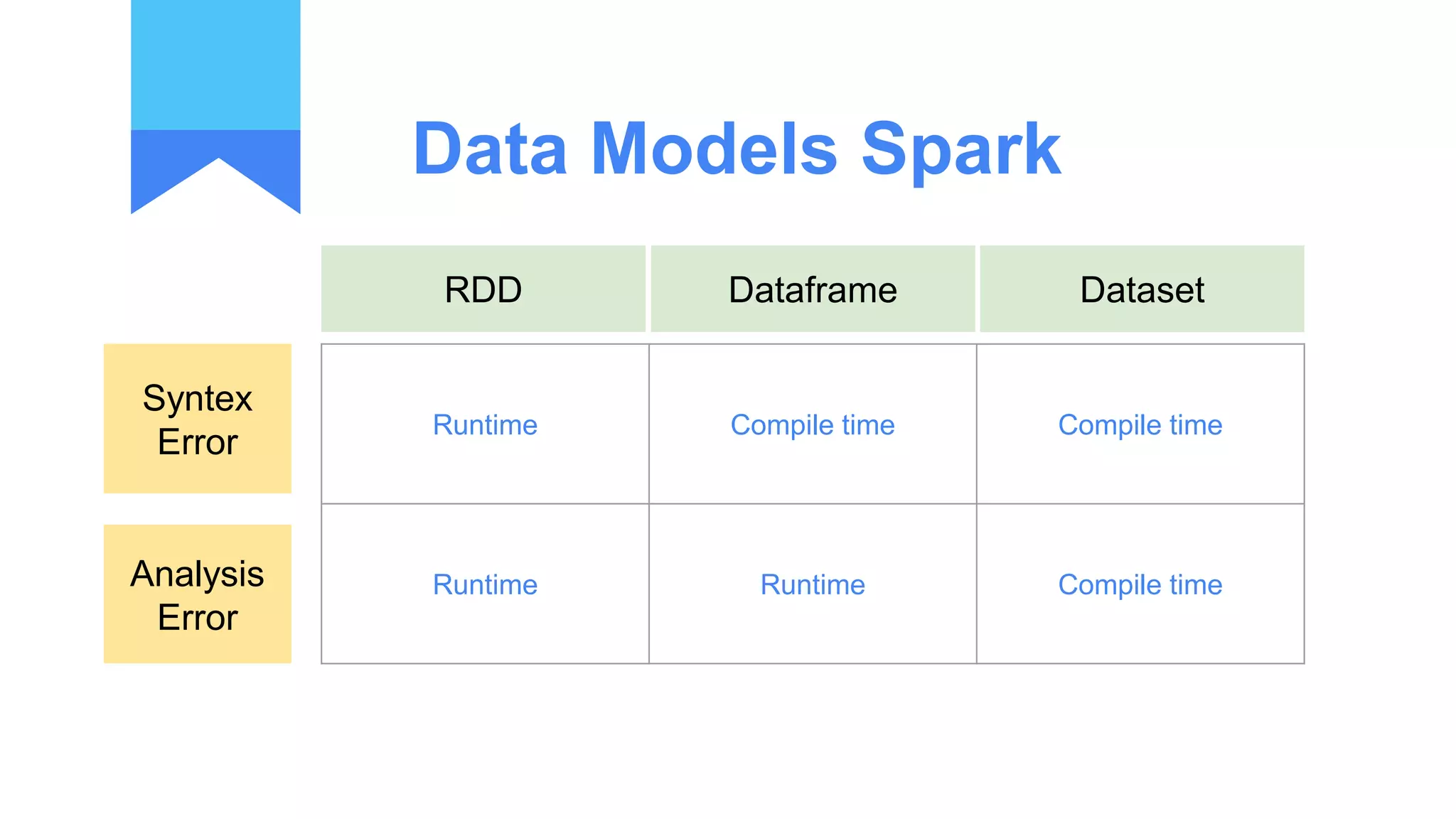
![Spark Data Models
- [T]Structure
- Arrange data according to plan
- More optimization
- Will limit what we can do, but still can do majority of operations
(RDD’s are still available)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unicomsummit2017-210425092854/75/Spark-Kafka-summit-2017-5-2048.jpg)
![DATASET API’s
Type safe
Domain objects
lambda functions
private[spark] val df = spark.read.json("people.json")
// Convert data to domain objects.
case class Person(name: String, age: Int)
val ds = df.as[Person] ds.filter(_.age > 30)
// Compute histogram of age by name.
val hist = ds.groupBy(_.name).mapGroups { case (name, people:
Iter[Person]) =>
val buckets = new Array[Int](10) people.map(_.age).foreach { a =>
buckets(a / 10) += 1
}
(name, buckets)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unicomsummit2017-210425092854/75/Spark-Kafka-summit-2017-7-2048.jpg)
![DATAFRAM
E =
DATASET
[RAW]
- Unified API since 2.0
- Dataframe is Dataset of Generic Row objects
- Types can be enforced on generic rows by
using df.as[MyClass]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unicomsummit2017-210425092854/75/Spark-Kafka-summit-2017-8-2048.jpg)