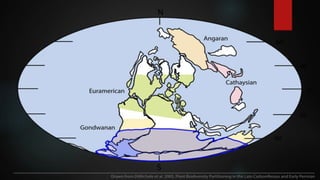
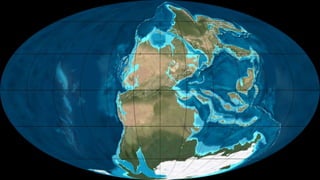
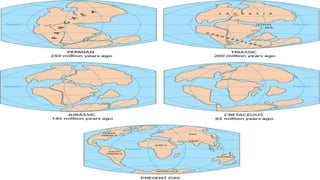
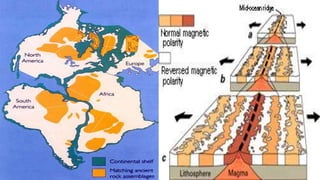
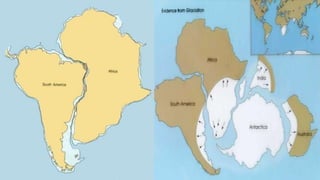
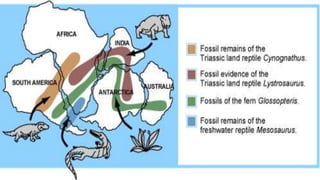
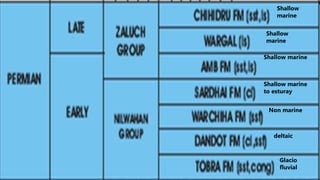
This document summarizes information about Pangaea, the most recent supercontinent that existed approximately 300-180 million years ago. It formed as the result of continental drift, bringing together most landmasses into a single giant continent surrounded by a single ocean. Pangaea then broke apart, splitting into separate landmasses and oceans over millions of years through the process of plate tectonics. Life on Pangaea included a variety of plants, marine life, and early reptiles and mammals.