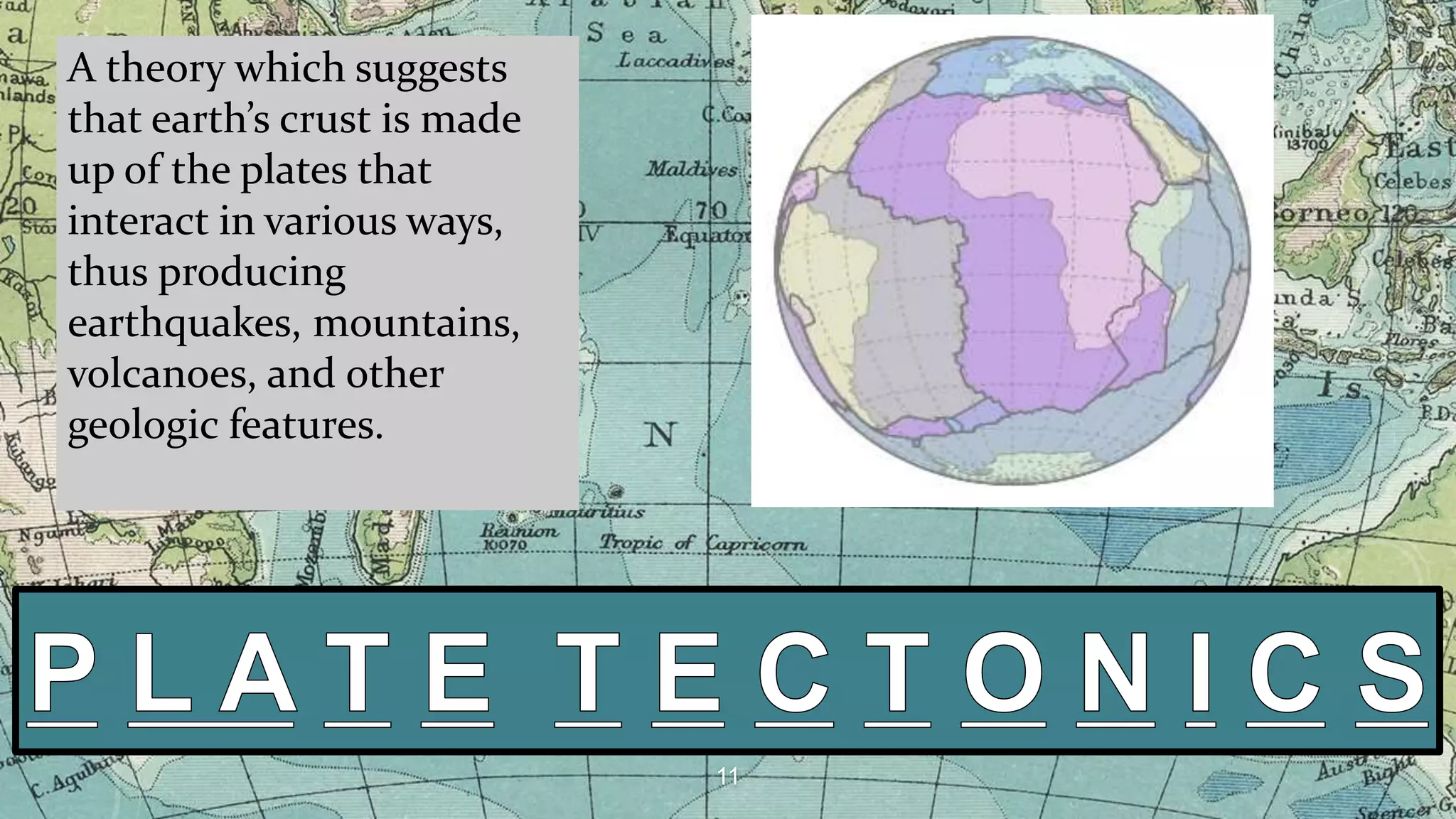
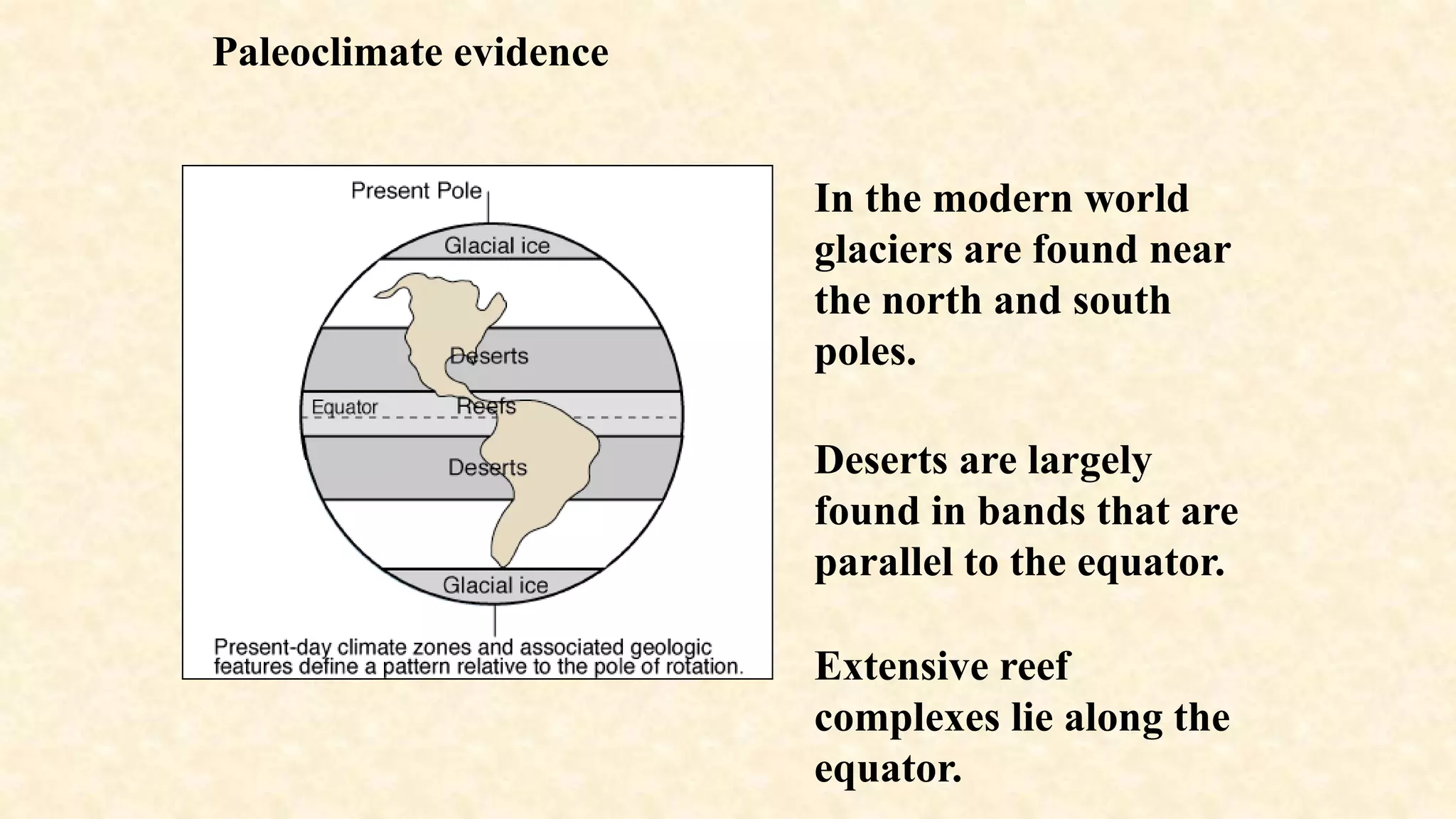
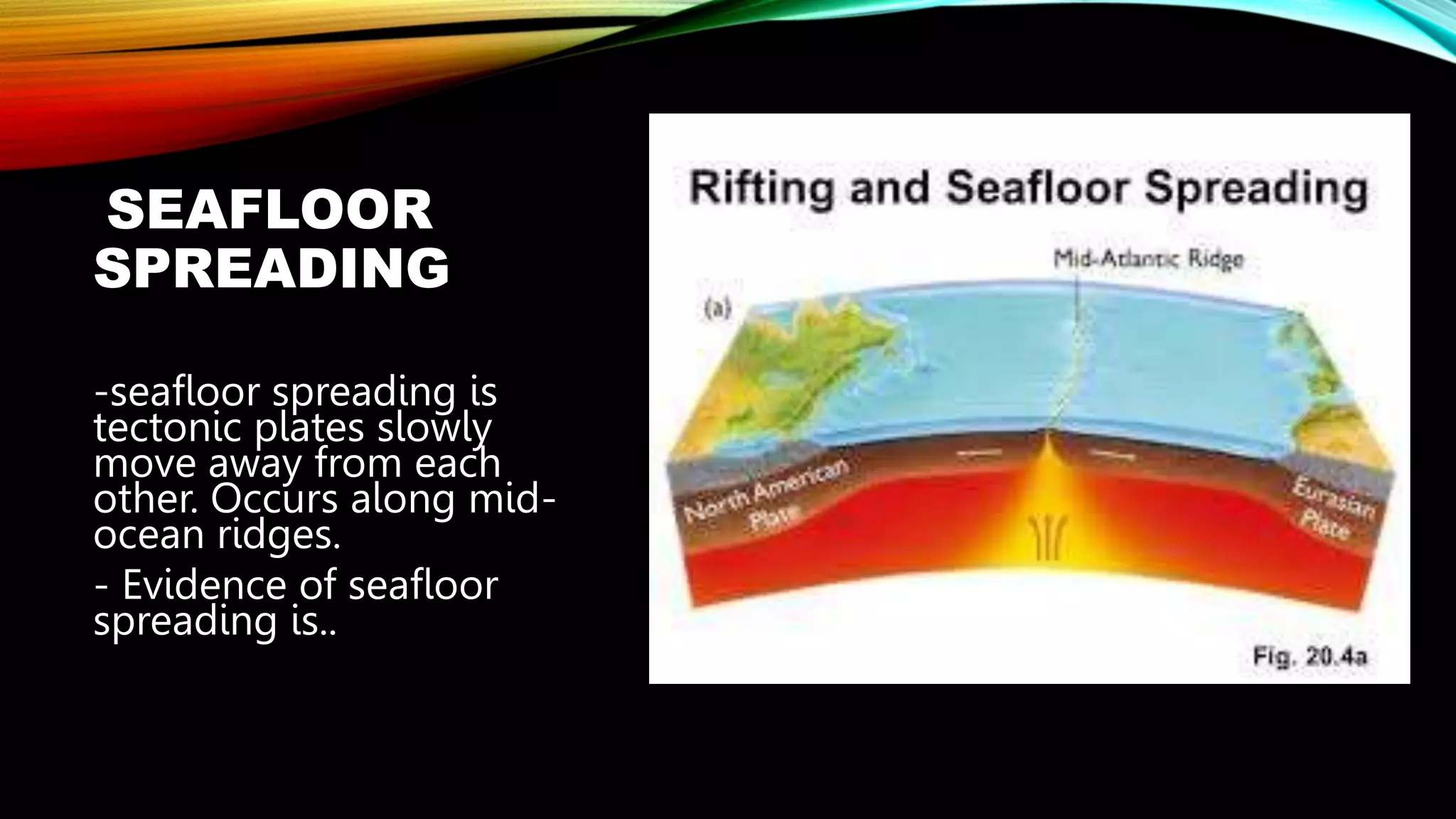
The document discusses evidence that supports the continental drift theory. It describes how the continents were once joined together in a supercontinent called Pangaea before drifting apart. Key lines of evidence include fossil matches between continents, matching coastline shapes, identical rock formations, glacial deposits found in incompatible climates, and magnetic striping in ocean floors that indicates plate movement. The theory was initially rejected but was later proven correct by the discovery of seafloor spreading.