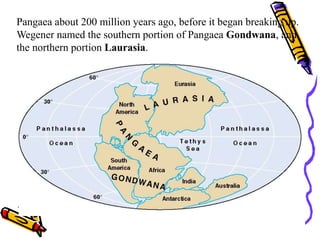
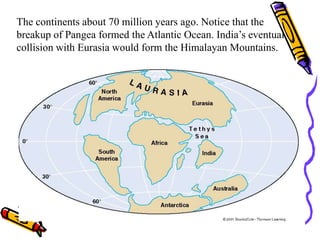
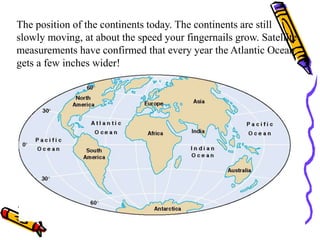
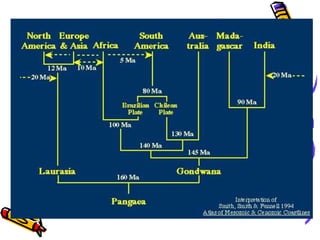
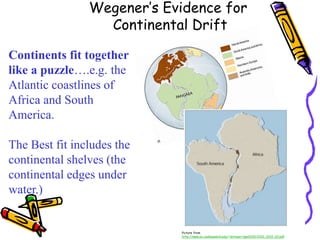
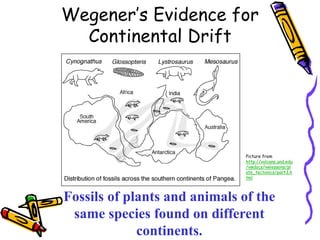
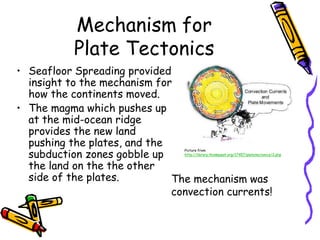
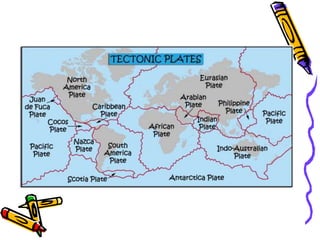
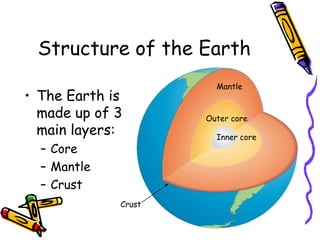
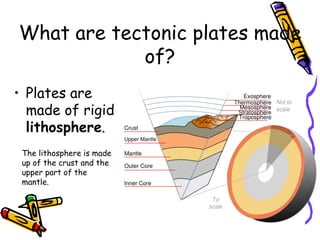
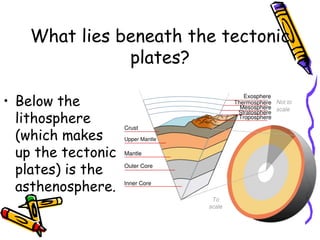
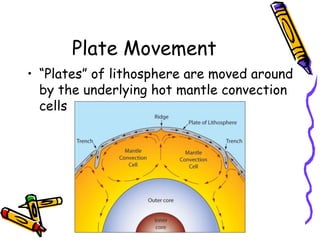
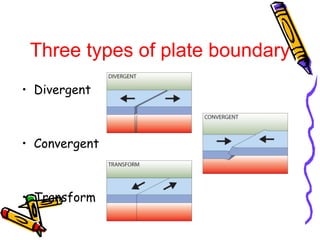
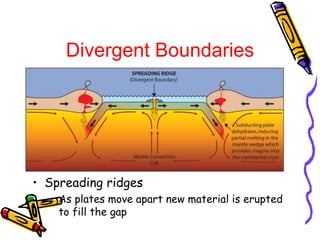
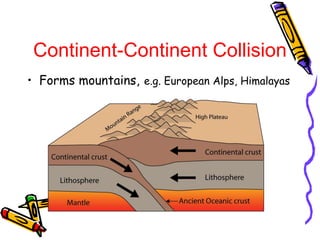
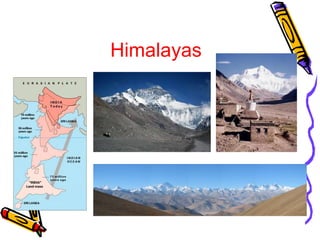
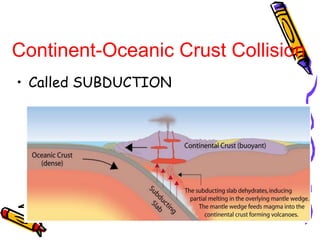
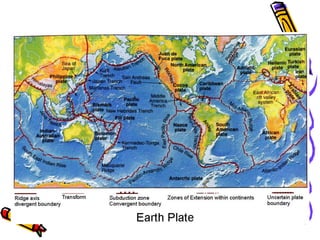
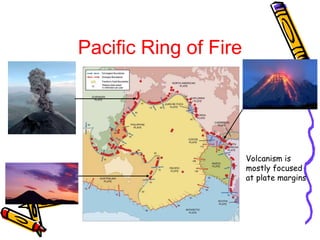
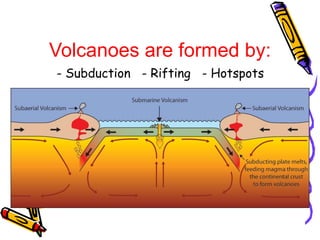
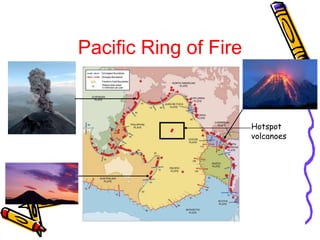
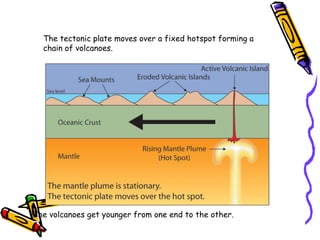
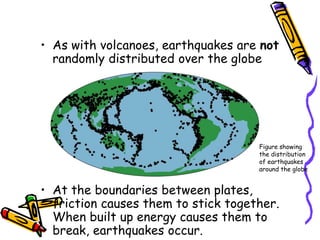
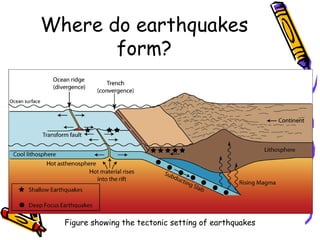
According to the theory of plate tectonics:
- The Earth's crust is broken into plates that slowly move over time;
- Plates interact at boundaries where they can collide, pull apart, or slide past one another;
- These interactions are responsible for geologic events like earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building.