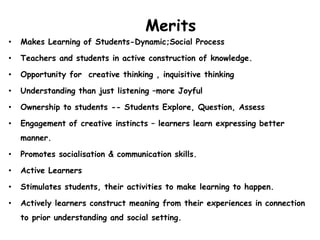
The constructivist approach promotes active learning where students construct knowledge through hands-on problem solving and connecting new information to prior understanding. It emphasizes student-centered learning over standardized curricula and assessments. Students build knowledge through social interaction and group work. The teacher acts as a facilitator, providing opportunities for dialogue, exploration, and knowledge construction while students take ownership over the learning process. While challenging to implement, the constructivist approach makes learning a dynamic social process and promotes skills like creative and critical thinking.